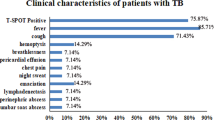
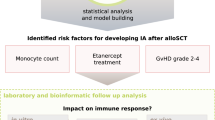
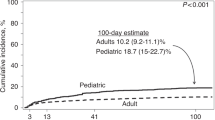
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is well-known as a disorder that increases the risk of infectious diseases. Various reports have shown that innate immunity is impaired in patients with DM, which is considered to be a major cause of increased risk of infectious diseases. However, there is a paucity of data about the actual risk of mold infections in patients with DM. Several treatment procedures, such as solid organ transplantation and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), are intrinsically associated with a high risk of mold infections and also correlated with an increased risk of post-transplant DM. Therefore, we could assume that organ transplant recipients or HSCT recipients with DM are at quite high risk of mold infections. Here, we aim to summarize the information about the increased risk of mold infections in patients with DM, and propose possible interventions such as intensive glucose control to reduce this risk in patients with DM.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geerlings SE, Hoepelman AI . Immune dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM). FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 1999; 26: 259–265.
Seshasai SR, Kaptoge S, Thompson A, Di Angelantonio E, Gao P, Sarwar N et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of cause-specific death. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 829–841.
Delamaire M, Maugendre D, Moreno M, Le Goff MC, Allannic H, Genetet B . Impaired leucocyte functions in diabetic patients. Diabet Med 1997; 14: 29–34.
Marhoffer W, Stein M, Maeser E, Federlin K . Impairment of polymorphonuclear leukocyte function and metabolic control of diabetes. Diabetes Care 1992; 15: 256–260.
Fuji S, Rovo A, Ohashi K, Griffith M, Einsele H, Kapp M et al. How do I manage hyperglycemia/post-transplant diabetes mellitus after allogeneic HSCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2016; 51: 1041–1049.
Lewis RE, Lortholary O, Spellberg B, Roilides E, Kontoyiannis DP, Walsh TJ . How does antifungal pharmacology differ for mucormycosis versus aspergillosis? Clin Infect Dis 2012; 54: S67–S72.
Heinekamp T, Schmidt H, Lapp K, Pahtz V, Shopova I, Koster-Eiserfunke N et al. Interference of Aspergillus fumigatus with the immune response. Semin Immunopathol 2015; 37: 141–152.
Brakhage AA, Bruns S, Thywissen A, Zipfel PF, Behnsen J . Interaction of phagocytes with filamentous fungi. Curr Opin Microbiol 2010; 13: 409–415.
Waldorf AR . Pulmonary defense mechanisms against opportunistic fungal pathogens. Immunol Ser 1989; 47: 243–271.
Fuji S, Loffler J, Einsele H, Kapp M . Immunotherapy for opportunistic infections: current status and future perspectives. Virulence, (e-pub ahead of print 16 July 2016; doi:10.1080/21505594.2016.1207038).
Dotis J, Pana ZD, Roilides E . Non-Aspergillus fungal infections in chronic granulomatous disease. Mycoses 2013; 56: 449–462.
Hasenberg M, Behnsen J, Krappmann S, Brakhage A, Gunzer M . Phagocyte responses towards Aspergillus fumigatus. Int J Med Microbiol 2011; 301: 436–444.
Marciano BE, Spalding C, Fitzgerald A, Mann D, Brown T, Osgood S et al. Common severe infections in chronic granulomatous disease. Clin Infect Dis 2015; 60: 1176–1183.
Rammaert B, Lanternier F, Poiree S, Kania R, Lortholary O . Diabetes and mucormycosis: a complex interplay. Diabetes Metab 2012; 38: 193–204.
McManus LM, Bloodworth RC, Prihoda TJ, Blodgett JL, Pinckard RN . Agonist-dependent failure of neutrophil function in diabetes correlates with extent of hyperglycemia. J Leukoc Biol 2001; 70: 395–404.
Stegenga ME, van der Crabben SN, Blumer RM, Levi M, Meijers JC, Serlie MJ et al. Hyperglycemia enhances coagulation and reduces neutrophil degranulation, whereas hyperinsulinemia inhibits fibrinolysis during human endotoxemia. Blood 2008; 112: 82–89.
Oldenborg PA, Sehlin J . Hyperglycemia in vitro attenuates insulin-stimulated chemokinesis in normal human neutrophils. Role of protein kinase C activation. J Leukoc Biol 1999; 65: 635–640.
de Souza Ferreira C, Araujo TH, Angelo ML, Pennacchi PC, Okada SS, de Araujo Paula FB et al. Neutrophil dysfunction induced by hyperglycemia: modulation of myeloperoxidase activity. Cell Biochem Funct 2012; 30: 604–610.
Gyurko R, Siqueira CC, Caldon N, Gao L, Kantarci A, Van Dyke TE . Chronic hyperglycemia predisposes to exaggerated inflammatory response and leukocyte dysfunction in Akita mice. J Immunol 2006; 177: 7250–7256.
Yano H, Kinoshita M, Fujino K, Nakashima M, Yamamoto Y, Miyazaki H et al. Insulin treatment directly restores neutrophil phagocytosis and bactericidal activity in diabetic mice and thereby improves surgical site Staphylococcus aureus infection. Infect Immun 2012; 80: 4409–4416.
Schaffner A, Douglas H, Braude A . Selective protection against conidia by mononuclear and against mycelia by polymorphonuclear phagocytes in resistance to Aspergillus. Observations on these two lines of defense in vivo and in vitro with human and mouse phagocytes. J Clin Invest 1982; 69: 617–631.
Waldorf AR, Ruderman N, Diamond RD . Specific susceptibility to mucormycosis in murine diabetes and bronchoalveolar macrophage defense against Rhizopus. J Clin Invest 1984; 74: 150–160.
Waldorf AR, Levitz SM, Diamond RD . In vivo bronchoalveolar macrophage defense against Rhizopus oryzae and Aspergillus fumigatus. J Infect Dis 1984; 150: 752–760.
Thursky K, Byrnes G, Grigg A, Szer J, Slavin M . Risk factors for post-engraftment invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 34: 115–121.
Marr KA, Carter RA, Boeckh M, Martin P, Corey L . Invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: changes in epidemiology and risk factors. Blood 2002; 100: 4358–4366.
Mikulska M, Raiola AM, Bruno B, Furfaro E, Van Lint MT, Bregante S et al. Risk factors for invasive aspergillosis and related mortality in recipients of allogeneic SCT from alternative donors: an analysis of 306 patients. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 44: 361–370.
O'Donnell MR, Schmidt GM, Tegtmeier BR, Faucett C, Fahey JL, Ito J et al. Prediction of systemic fungal infection in allogeneic marrow recipients: impact of amphotericin prophylaxis in high-risk patients. J Clin Oncol 1994; 12: 827–834.
Dandona P, Suri M, Hamouda W, Aljada A, Kumbkarni Y, Thusu K . Hydrocortisone-induced inhibition of reactive oxygen species by polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Crit Care Med 1999; 27: 2442–2444.
Aljada A, Ghanim H, Assian E, Mohanty P, Hamouda W, Garg R et al. Increased IkappaB expression and diminished nuclear NF-kappaB in human mononuclear cells following hydrocortisone injection. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84: 3386–3389.
Corzo-Leon DE, Satlin MJ, Soave R, Shore TB, Schuetz AN, Jacobs SE et al. Epidemiology and outcomes of invasive fungal infections in allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients in the era of antifungal prophylaxis: a single-centre study with focus on emerging pathogens. Mycoses 2015; 58: 325–336.
Neofytos D, Fishman JA, Horn D, Anaissie E, Chang CH, Olyaei A et al. Epidemiology and outcome of invasive fungal infections in solid organ transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis 2010; 12: 220–229.
Slavin M, van Hal S, Sorrell TC, Lee A, Marriott DJ, Daveson K et al. Invasive infections due to filamentous fungi other than Aspergillus: epidemiology and determinants of mortality. Clin Microbiol Infect 2015; 21: 490.e1–10.
Riches ML, Trifilio S, Chen M, Ahn KW, Langston A, Lazarus HM et al. Risk factors and impact of non-Aspergillus mold infections following allogeneic HCT: a CIBMTR infection and immune reconstitution analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant 2016; 51: 277–282.
De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 46: 1813–1821.
Nivoix Y, Velten M, Letscher-Bru V, Moghaddam A, Natarajan-Ame S, Fohrer C et al. Factors associated with overall and attributable mortality in invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47: 1176–1184.
Skiada A, Pagano L, Groll A, Zimmerli S, Dupont B, Lagrou K et al. Zygomycosis in Europe: analysis of 230 cases accrued by the registry of the European Confederation of Medical Mycology (ECMM) Working Group on Zygomycosis between 2005 and 2007. Clin Microbiol Infect 2011; 17: 1859–1867.
Ruping MJ, Heinz WJ, Kindo AJ, Rickerts V, Lass-Florl C, Beisel C et al. Forty-one recent cases of invasive zygomycosis from a global clinical registry. J Antimicrob Chemother 2010; 65: 296–302.
Roden MM, Zaoutis TE, Buchanan WL, Knudsen TA, Sarkisova TA, Schaufele RL et al. Epidemiology and outcome of zygomycosis: a review of 929 reported cases. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 41: 634–653.
Rammaert B, Lanternier F, Zahar JR, Dannaoui E, Bougnoux ME, Lecuit M et al. Healthcare-associated mucormycosis. Clin Infect Dis 2012; 54: S44–S54.
Girmenia C, Raiola AM, Piciocchi A, Algarotti A, Stanzani M, Cudillo L et al. Incidence and outcome of invasive fungal diseases after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a prospective study of the Gruppo Italiano Trapianto Midollo Osseo (GITMO). Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 872–880.
Martino R, Subira M, Rovira M, Solano C, Vazquez L, Sanz GF et al. Invasive fungal infections after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation: incidence and risk factors in 395 patients. Br J Haematol 2002; 116: 475–482.
Lanternier F, Sun HY, Ribaud P, Singh N, Kontoyiannis DP, Lortholary O . Mucormycosis in organ and stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 2012; 54: 1629–1636.
Sahin SZ, Akalin H, Ersoy A, Yildiz A, Ocakoglu G, Cetinoglu ED et al. Invasive fungal infections in renal transplant recipients: epidemiology and risk factors. Mycopathologia 2015; 180: 43–50.
Tharayil John G, Shankar V, Talaulikar G, Mathews MS, Abraham Abraham M, Punnakuzhathil Thomas P et al. Epidemiology of systemic mycoses among renal-transplant recipients in India. Transplantation 2003; 75: 1544–1551.
Altiparmak MR, Apaydin S, Trablus S, Serdengecti K, Ataman R, Ozturk R et al. Systemic fungal infections after renal transplantation. Scand J Infect Dis 2002; 34: 284–288.
Abbott KC, Hypolite I, Poropatich RK, Hshieh P, Cruess D, Hawkes CA et al. Hospitalizations for fungal infections after renal transplantation in the United States. Transpl Infect Dis 2001; 3: 203–211.
Garcia-Vidal C, Upton A, Kirby KA, Marr KA . Epidemiology of invasive mold infections in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients: biological risk factors for infection according to time after transplantation. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47: 1041–1050.
Liu YC, Chien SH, Fan NW, Hu MH, Gau JP, Liu CJ et al. Incidence and risk factors of probable and proven invasive fungal infection in adult patients receiving allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2016; 49: 567–574.
Caira M, Candoni A, Verga L, Busca A, Delia M, Nosari A et al. Pre-chemotherapy risk factors for invasive fungal diseases: prospective analysis of 1,192 patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (SEIFEM 2010-a multicenter study). Haematologica 2015; 100: 284–292.
Kontoyiannis DP, Lionakis MS, Lewis RE, Chamilos G, Healy M, Perego C et al. Zygomycosis in a tertiary-care cancer center in the era of Aspergillus-active antifungal therapy: a case-control observational study of 27 recent cases. J Infect Dis 2005; 191: 1350–1360.
Singh N, Aguado JM, Bonatti H, Forrest G, Gupta KL, Safdar N et al. Zygomycosis in solid organ transplant recipients: a prospective, matched case-control study to assess risks for disease and outcome. J Infect Dis 2009; 200: 1002–1011.
Lanternier F, Dannaoui E, Morizot G, Elie C, Garcia-Hermoso D, Huerre M et al. A global analysis of mucormycosis in France: the RetroZygo Study (2005-2007). Clin Infect Dis 2012; 54: S35–S43.
Xhaard A, Lanternier F, Porcher R, Dannaoui E, Bergeron A, Clement L et al. Mucormycosis after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a French multicentre cohort study (2003-2008). Clin Microbiol Infect 2012; 18: E396–E400.
Park BJ, Pappas PG, Wannemuehler KA, Alexander BD, Anaissie EJ, Andes DR et al. Invasive non-Aspergillus mold infections in transplant recipients, United States, 2001-2006. Emerg Infect Dis 2011; 17: 1855–1864.
Takano K, Fuji S, Uchida N, Ogawa H, Ohashi K, Eto T et al. Pre-transplant diabetes mellitus is a risk factor for non-relapse mortality, especially infection-related mortality, after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2015; 50: 553–558.
Davoudi S, Kumar VA, Jiang Y, Kupferman M, Kontoyiannis DP . Invasive mould sinusitis in patients with haematological malignancies: a 10 year single-centre study. J Antimicrob Chemother 2015; 70: 2899–2905.
Dutta P, Premkumar A, Chakrabarti A, Shah VN, Behera A, De D et al. Fusarium falciforme infection of foot in a patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a case report and review of the literature. Mycopathologia 2013; 176: 225–232.
Garnica M, da Cunha MO, Portugal R, Maiolino A, Colombo AL, Nucci M . Risk factors for invasive fusariosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 2015; 60: 875–880.
Fuji S, Einsele H, Savani BN, Kapp M . Systematic nutritional support in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2015; 21: 1707–1713.
Fuji S, Yakushijin K, Kim SW, Yoshimura K, Kurosawa S, Fukuda T . Dynamic change of glycemic status during the early phase after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2015; 50: 1473–1475.
Fuji S, Kim SW, Mori S, Fukuda T, Kamiya S, Yamasaki S et al. Hyperglycemia during the neutropenic period is associated with a poor outcome in patients undergoing myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transplantation 2007; 84: 814–820.
Fuji S, Kapp M, Einsele H . Possible implication of bacterial infection in acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Front Oncol 2014; 4: 89.
Fuji S, Kim SW, Fukuda T, Mori S, Yamasaki S, Morita-Hoshi Y et al. Preengraftment serum C-reactive protein (CRP) value may predict acute graft-versus-host disease and nonrelapse mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 510–517.
Fuji S, Kim SW, Mori S, Kamiya S, Yoshimura K, Yokoyama H et al. Intensive glucose control after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a retrospective matched-cohort study. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 44: 105–111.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Furukawa Medical and Welfare Foundation in Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuji, S., Löffler, J., Savani, B. et al. Hyperglycemia as a possible risk factor for mold infections—the potential preventative role of intensified glucose control in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 52, 657–662 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.306
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.306
This article is cited by
-
Focusing COVID-19-associated mucormycosis: a major threat to immunocompromised COVID-19
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2022)
-
How we can mitigate the side effects associated with systemic glucocorticoid after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Severe acute graft-versus-host disease increases the incidence of blood stream infection and mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: Japanese transplant registry study
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of COVID-19-Associated Mucormycosis: India Versus the Rest of the World
Mycopathologia (2021)
-
Temporal trajectory of quality of life and its predictors in recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Annals of Hematology (2018)