Abstract
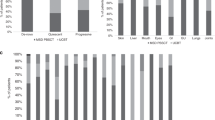
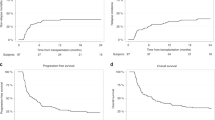
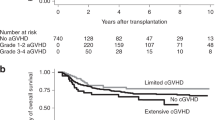
Adult umbilical cord blood transplantation (CBT) has emerged as an important option for patients lacking matched related (MRD) and matched unrelated donors (MUD). We compared chronic GVHD (cGVHD) incidence, immunosuppression burden and late infections and hospitalizations in consecutive patients undergoing CBT (n=51) versus peripheral blood MUD transplant (n=57) at our center between June 2009 and April 2014. At 3 years post transplantation, the cumulative incidence (CI) of moderate to severe cGVHD was 44% following MUD versus 8% following CBT (P=0.0006) and CI of any cGVHD was 68% following MUD versus 32% following CBT (P=0.0017). Median time to being off immunosuppression among CB patients was 268 days versus not reached among MUD patients (P<0.0001). Late infections and late hospitalized days were reduced in CB patients (P=0.1 and <0.001, respectively). Three-year CI of transplant-related mortality (TRM) and relapse as well as 3-year overall survival (OS) were similar following CB and MUD transplantation. We demonstrate a significantly lower incidence of cGVHD, immunosuppression burden and late complication rate following UCB versus peripheral blood MUD transplant without decreased OS, increased relapse or early TRM. Combined with the rapid availability of UCB, these findings have led our center to move primarily to UCB over peripheral blood MUD when a MRD is not available.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gutman JA, Leisenring W, Appelbaum FR, Woolfrey AE, Delaney C . Low relapse without excessive transplant-related mortality following myeloablative cord blood transplantation for acute leukemia in complete remission: a matched cohort analysis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 1122–1129.
Brunstein CG, Gutman JA, Weisdorf DJ, Woolfrey AE, Defor TE, Gooley TA et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for hematologic malignancy: relative risks and benefits of double umbilical cord blood. Blood 2010; 116: 4693–4699.
Eapen M, Rubinstein P, Zhang MJ, Stevens C, Kurtzberg J, Scaradavou A et al. Outcomes of transplantation of unrelated donor umbilical cord blood and bone marrow in children with acute leukaemia: a comparison study. Lancet 2007; 369: 1947–1954.
Eapen M, Rocha V, Sanz G, Scaradavou A, Zhang MJ, Arcese W et al. Effect of graft source on unrelated donor haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation in adults with acute leukaemia: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol 2010; 11: 653–660.
Peffault de Latour R, Brunstein CG, Porcher R, Chevallier P, Robin M, Warlick E et al. Similar overall survival using sibling, unrelated donor, and cord blood grafts after reduced-intensity conditioning for older patients with acute myelogenous leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 1355–1360.
Rodrigues CA, Rocha V, Dreger P, Brunstein C, Sengeloev H, Finke J et al. Alternative donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for mature lymphoid malignancies after reduced-intensity conditioning regimen: similar outcomes with umbilical cord blood and unrelated donor peripheral blood. Haematologica 2014; 99: 370–377.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 945–956.
Kim HT . Cumulative incidence in competing risks data and competing risks regression analysis. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13 (2 Pt 1): 559–565.
Newell LF, Flowers ME, Gooley TA, Milano F, Carpenter PA, Martin PJ et al. Characteristics of chronic GVHD after cord blood transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 1285–1290.
Sauter C, Abboud M, Jia X, Heller G, Gonzales AM, Lubin M et al. Serious infection risk and immune recovery after double-unit cord blood transplantation without antithymocyte globulin. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 1460–1471.
Ponce DM, Zheng J, Gonzales AM, Lubin M, Heller G, Castro-Malaspina H et al. Reduced late mortality risk contributes to similar survival after double-unit cord blood transplantation compared with related and unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 1316–1326.
Ponce DM, Sauter C, Devlin S, Lubin M, Gonzales AM, Kernan NA et al. A novel reduced-intensity conditioning regimen induces a high incidence of sustained donor-derived neutrophil and platelet engraftment after double-unit cord blood transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 799–803.
Scaradavou A, Brunstein CG, Eapen M, Le-Rademacher J, Barker JN, Chao N et al. Double unit grafts successfully extend the application of umbilical cord blood transplantation in adults with acute leukemia. Blood 2013; 121: 752–758.
Barker JN, Weisdorf DJ, DeFor TE, Blazar BR, McGlave PB, Miller JS et al. Transplantation of 2 partially HLA-matched umbilical cord blood units to enhance engraftment in adults with hematologic malignancy. Blood 2005; 105: 1343–1347.
Delaney C, Heimfeld S, Brashem-Stein C, Voorhies H, Manger RL, Bernstein ID . Notch-mediated expansion of human cord blood progenitor cells capable of rapid myeloid reconstitution. Nat Med 2010; 16: 232–236.
de Lima M, McNiece I, Robinson SN, Munsell M, Eapen M, Horowitz M et al. Cord-blood engraftment with ex vivo mesenchymal-cell coculture. N Engl J Med 2012; 367: 2305–2315.
Ponce DM, Gonzales A, Lubin M, Castro-Malaspina H, Giralt S, Goldberg JD et al. Graft-versus-host disease after double-unit cord blood transplantation has unique features and an association with engrafting unit-to-recipient HLA match. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 904–911.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutman, J., Ross, K., Smith, C. et al. Chronic graft versus host disease burden and late transplant complications are lower following adult double cord blood versus matched unrelated donor peripheral blood transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 51, 1588–1593 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.186
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.186
This article is cited by
-
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on cord blood banking and transplantation
Cell and Tissue Banking (2024)
-
Mechanisms of resistance to chimeric antigen receptor-T cells in haematological malignancies
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2023)
-
Venetoclax is safe and tolerable as post-transplant maintenance therapy for AML patients at high risk for relapse
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)
-
Venetoclax and azacitidine followed by allogeneic transplant results in excellent outcomes and may improve outcomes versus maintenance therapy among newly diagnosed AML patients older than 60
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2022)
-
Outcomes of chronic graft-versus-host disease following matched sibling donor versus umbilical cord blood transplant
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)