Abstract
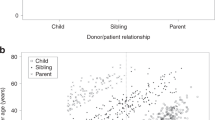
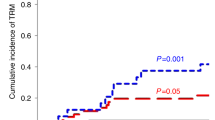
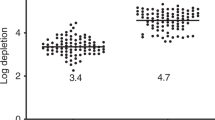
Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using T-cell-depleted grafts is a valid option for pediatric patients with hematological malignancies in need of an allogeneic transplantation and lacking an HLA-identical donor. Seventy-five transplantations were performed in 70 patients. Thirty-eight patients had ALL, 32 had AML, 3 had advanced myelodysplastic syndromes and 2 juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia; 19 were in first CR, 30 in second CR, 12 in greater than second CR and 14 were considered to be in refractory disease at time of transplantation. Four patients developed graft failure. Among engrafted patients, the median time to neutrophil and platelet recovery was 13 (range 8–20) and 10 days (range 8–70), respectively. In 64 (85%) cases, ⩾1 infections were diagnosed after transplant. The probability of nonrelapse mortality by day +100 after transplantation was 10±4%. With a median follow-up of 22 months, the probability of relapse was 32±6% and disease-free survival was 52±6%. Haploidentical transplantation using CD3/CD19 depletion is associated with encouraging results especially in patients in early phase of disease. Killer-cell Ig-like receptor B haplotype donors confer a rapid natural killer cells expansion early after transplantation, resulting in lower probability of relapse and suggesting a GvL effect apart from graft-versus-host reactions. Donor infusion of high numbers of CD34+ cells is recommended in order to improve T-cell reconstitution.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Booth C, Lawson S, Veys P . The current role of T cell depletion in paediatric stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol 2013; 162: 177–190.
Handgretinger R . New approaches to graft engineering for haploidentical bone marrow transplantation. Semin Oncol 2012; 39: 664–673.
Schumm M, Lang P, Taylor G, Kuçi S, Klingebiel T, Bühring HJ et al. Isolation of highly purified autologous and allogeneic peripheral CD34+ cells using the CliniMACS device. J Hematother 1999; 8: 209–218.
Handgretinger R . Negative depletion of CD3(+) and TcRαβ(+) T cells. Curr Opin Hematol 2012; 19: 434–439.
Gonzalez-Vicent M, Perez A, Abad L, Sevilla J, Ramirez M, Diaz MA . Graft manipulation and reduced-intensity conditioning for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from mismatched unrelated and mismatched/haploidentical related donors in pediatric leukemia patients. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2010; 32: 85–90.
Martin AM, Kulski JK, Gaudieri S, Witt CS, Freitas EM, Trowsdale J et al. Comparative genomic analysis, diversity and evolution of two KIR haplotypes A and B. Gene 2004; 335: 121–131.
Pérez-Martínez A, González-Vicent M, Valentín J, Aleo E, Lassaletta A, Sevilla J et al. Early evaluation of immune reconstitution following allogeneic CD3/CD19-depleted grafts from alternative donors in childhood acute leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 1419–1427.
Bethge WA, Haegele M, Faul C, Lang P, Schumm M, Bornhauser M et al. Haploidentical allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in adults with reduced-intensity conditioning and CD3/CD19 depletion: fast engraftment and low toxicity. Exp Hematol 2006; 34: 1746–1752.
Lang P, Teltschik H-M, Feuchtinger T, Müller I, Pfeiffer M, Schumm M et al. Transplantation of CD3/CD19 depleted allografts from haploidentical family donors in paediatric leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2014; 165: 688–698.
Call SK, Kasow KA, Barfield R, Madden R, Leung W, Horwitz E et al. Total and active rabbit antithymocyte globulin (rATG;Thymoglobulin) pharmacokinetics in pediatric patients undergoing unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 274–278.
Aristei C, Santucci A, Corvò R, Gardani G, Ricardi U, Scarzello G et al. Italian TBI Working Group. In haematopoietic SCT for acute leukemia TBI impacts on relapse but not survival: results of a multicentre observational study. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 908–914.
Hamidieh A, Kargar M, Jahani M, Alimoghaddam K, Bahar B, Mousavi SA et al. The outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants without total body irradiation in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: single centre experience. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2012; 34: 101–107.
Hong KT, Kang HJ, Kim NH, Kim MS, Lee JW, Kim H et al. Peri-engraftment syndrome in allogeneic hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 523–528.
Nishio N, Yagasaki H, Takahashi Y, Hama A, Muramatsu H, Tanaka M et al. Engraftment syndrome following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children. Pediatr Transplant 2009; 13: 831–837.
Schmid I, Stachel D, Pagel P, Albert MH . Incidence, predisposing factors, and outcome of engraftment syndrome in pediatric allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 438–444.
Spitzer TR . Engraftment syndrome: double-edged sword of hematopoietic cell transplants. Bone Marrow Transplant 2015; 50: 469–475.
Triplett BM, Horwitz EM, Iyengar R, Turner V, Holladay MS, Gan K et al. Effects of activating NK cell receptor expression and NK cell reconstitution on the outcomes of unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation for hematologic malignancies. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1278–1287.
Oevermann L, Michaelis SU, Mezger M, Lang P, Toporski J, Bertaina A et al. KIR B haplotype donors confer a reduced risk for relapse after haploidentical transplantation in children with ALL. Blood 2014; 124: 2744–2747.
Michaelis SU, Mezger M, Bornhäuser M, Trenschel R, Stuhler G, Federmann B et al. KIR haplotype B donors but not KIR-ligand mismatch result in a reduced incidence of relapse after haploidentical transplantation using reduced intensity conditioning and CD3/CD19-depleted grafts. Ann Hematol 2014; 93: 1579–1586.
Eyrich M, Lang P, Lal S, Handgretinger R, Klingebiel T, Niethammer D et al. A prospective analysis of the pattern of immune reconstitution in a paediatric cohort following transplantation of positively selected human leucocyte antigen-disparate haematopoietic stem cells from parental donors. Br J haematol 2001; 114: 422–432.
Ortin M, Raj R, Kinning E, Williams M, Darbyshire PJ . Partially matched related donor peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation in paediatric patients adding fludarabine and anti-lymphocyte gamma-globulin. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 30: 359–366.
Handgretinger R, Schumm M, Lang P, Greil J, Reiter A, Bader P et al. Transplantation of megadoses of purified haploidentical stem cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1999; 872: 351–361.
Leung W, Campana D, Yang J, Pei D, Coustan Smith E, Gan K et al. High success rate of hematopoietic cell transplantation regardless of donor source in children with very high-risk leukemia. Blood 2011; 118: 223–230.
Gonzalez-Vicent M, Molina B, Andion M, Sevilla J, Ramirez M, Pérez A et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation using haploidentical donor vs unrelated cord blood donor in pediatric patients: a single-center retrospective study. Eur J Haematol 2011; 87: 46–53.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank ServingMed.com for providing English language editing of the manuscript. This work was supported by a National Health Service of Spain grant (FIS EC11/024). AP-M was supported by the CRIS Cancer Foundation (http://criscancer.org).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diaz, M., Pérez-Martínez, A., Herrero, B. et al. Prognostic factors and outcomes for pediatric patients receiving an haploidentical relative allogeneic transplant using CD3/CD19-depleted grafts. Bone Marrow Transplant 51, 1211–1216 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.101
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2016.101
This article is cited by
-
Antithymocyte globulin/fludarabine/melphalan
Reactions Weekly (2018)