Abstract
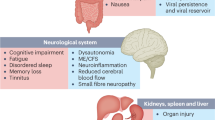
Human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) encephalitis following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation is a serious and often fatal complication accompanying reactivation of HHV-6B. Incidence varies among studies, but is reportedly 0–11.6% after bone marrow or PBSC transplantation and 4.9–21.4% after umbilical cord blood transplantation, typically around 2–6 weeks post transplant. Symptoms are characterized by memory loss, loss of consciousness and seizures. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) typically shows bilateral signal abnormalities in the limbic system. This complication is considered to represent acute encephalitis caused by direct virally induced damage to the central nervous system, but our understanding of the etiologies and pathogenesis is still limited. The mortality rate attributable to this pathology remains high, and survivors are often left with serious sequelae such as impaired memory and epilepsy. Despite the poor prognosis, no validated treatments or preventative measures have been established. Establishment of preventative strategies represents an important challenge. This article reviews the current knowledge of the clinical features, incidence, pathogenesis and treatment of HHV-6 encephalitis, and discusses issues needing clarification in the future to overcome this serious complication.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zerr DM, Corey L, Kim HW, Huang ML, Nguy L, Boeckh M . Clinical outcomes of human herpesvirus 6 reactivation after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40: 932–940.
Hentrich M, Oruzio D, Jager G, Schlemmer M, Schleuning M, Schiel X et al. Impact of human herpesvirus-6 after haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol 2005; 128: 66–72.
Ogata M, Kikuchi H, Satou T, Kawano R, Ikewaki J, Kohno K et al. Human herpesvirus 6 DNA in plasma after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: incidence and clinical significance. J Infect Dis 2006; 193: 68–79.
Yamane A, Mori T, Suzuki S, Mihara A, Yamazaki R, Aisa Y et al. Risk factors for developing human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) reactivation after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and its association with central nervous system disorders. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 100–106.
Ogata M, Satou T, Kadota J, Saito N, Yoshida T, Okumura H et al. Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) reactivation and HHV-6 encephalitis after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a multicenter, prospective study. Clin Infect Dis 2013; 57: 671–681.
Ljungman P, Wang FZ, Clark DA, Emery VC, Remberger M, Ringden O et al. High levels of human herpesvirus 6 DNA in peripheral blood leucocytes are correlated to platelet engraftment and disease in allogeneic stem cell transplant patients. Br J Haematol 2000; 111: 774–781.
Ogata M, Satou T, Kawano R, Goto K, Ikewaki J, Kohno K et al. Plasma HHV-6 viral load-guided preemptive therapy against HHV-6 encephalopathy after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a prospective evaluation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 41: 279–285.
Ogata M, Satou T, Kawano R, Takakura S, Goto K, Ikewaki J et al. Correlations of HHV-6 viral load and plasma IL-6 concentration with HHV-6 encephalitis in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant 2010; 45: 129–136.
Drobyski WR, Knox KK, Majewski D, Carrigan DR . Brief report: fatal encephalitis due to variant B human herpesvirus-6 infection in a bone marrow-transplant recipient. N Engl J Med 1994; 330: 1356–1360.
Adams MJ, Carstens EB . Ratification vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Arch Virol 2012; 157: 1411–1422.
Zerr DM, Meier AS, Selke SS, Frenkel LM, Huang ML, Wald A et al. A population-based study of primary human herpesvirus 6 infection. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 768–776.
Reddy S, Manna P . Quantitative detection and differentiation of human herpesvirus 6 subtypes in bone marrow transplant patients by using a single real-time polymerase chain reaction assay. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 530–541.
Kadakia MP, Rybka WB, Stewart JA, Patton JL, Stamey FR, Elsawy M et al. Human herpesvirus 6: infection and disease following autologous and allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1996; 87: 5341–5354.
Wang FZ, Linde A, Hagglund H, Testa M, Locasciulli A, Ljungman P . Human herpesvirus 6 DNA in cerebrospinal fluid specimens from allogeneic bone marrow transplant patients: does it have clinical significance? Clin Infect Dis 1999; 28: 562–568.
Zerr DM, Ogata M . HHV-6A and HHV-6B in recipients of hematopoietic cell transplantation. In: Flamand L, Lautenschlager I, Krueger G, Ablashi D (eds). Human Herpesviruses HHV-6A, HHV-6B & HHV-7. Diagnosis and Clinical Management 3rd edn. Elsevier: Kidlington, Oxford, UK, 2014 pp 217–234.
Hill AB . The environment and disease: association or causation? Proc R Soc Med 1965; 58: 295–300.
Weed DL . On the use of causal criteria. Int J Epidemiol 1997; 26: 1137–1141.
Zerr DM, Fann JR, Breiger D, Boeckh M, Adler AL, Xie H et al. HHV-6 reactivation and its effect on delirium and cognitive functioning in hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients. Blood 2011; 117: 5243–5249.
Johnston RE, Geretti AM, Prentice HG, Clark AD, Wheeler AC, Potter M et al. HHV-6-related secondary graft failure following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol 1999; 105: 1041–1043.
Lagadinou ED, Marangos M, Liga M, Panos G, Tzouvara E, Dimitroulia E et al. Human herpesvirus 6-related pure red cell aplasia, secondary graft failure, and clinical severe immune suppression after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation successfully treated with foscarnet. Transpl Infect Dis 2010; 12: 437–440.
Le Bourgeois A, Labopin M, Guillaume T, Delaunay J, Foucher Y, Tessoulin B et al. Human herpesvirus 6 reactivation before engraftment is strongly predictive of graft failure after double umbilical cord blood allogeneic stem cell transplantation in adults. Exp Hematol 2014; 42: 945–954.
Cone RW, Hackman RC, Huang ML, Bowden RA, Meyers JD, Metcalf M et al. Human herpesvirus 6 in lung tissue from patients with pneumonitis after bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med 1993; 329: 156–161.
Nakayama T, Okada F, Ando Y, Honda K, Ogata M, Goto K et al. A case of pneumonitis and encephalitis associated with human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) infection after bone marrow transplantation. Br J Radiol 2010; 83: e255–e258.
Amo K, Tanaka-Taya K, Inagi R, Miyagawa H, Miyoshi H, Okusu I et al. Human herpesvirus 6B infection of the large intestine of patients with diarrhea. Clin Infect Dis 2003; 36: 120–123.
Zerr DM, Boeckh M, Delaney C, Martin PJ, Xie H, Adler AL et al. HHV-6 reactivation and associated sequelae after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18: 1700–1708.
Dulery R, Salleron J, Dewilde A, Rossignol J, Boyle EM, Gay J et al. Early human herpesvirus type 6 reactivation after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a large-scale clinical study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18: 1080–1089.
Pellett PE, Ablashi DV, Ambros PF, Agut H, Caserta MT, Descamps V et al. Chromosomally integrated human herpesvirus 6: questions and answers. Rev Med Virol 2012; 22: 144–155.
Leong HN, Tuke PW, Tedder RS, Khanom AB, Eglin RP, Atkinson CE et al. The prevalence of chromosomally integrated human herpesvirus 6 genomes in the blood of UK blood donors. J Med Virol 2007; 79: 45–51.
Hall CB, Caserta MT, Schnabel K, Shelley LM, Marino AS, Carnahan JA et al. Chromosomal integration of human herpesvirus 6 is the major mode of congenital human herpesvirus 6 infection. Pediatrics 2008; 122: 513–520.
Gravel A, Hall CB, Flamand L . Sequence analysis of transplacentally acquired human herpesvirus 6 DNA is consistent with transmission of a chromosomally integrated reactivated virus. J Infect Dis 2013; 207: 1585–1589.
Endo A, Watanabe K, Ohye T, Suzuki K, Matsubara T, Shimizu N et al. Molecular and virological evidence of viral activation from chromosomally integrated human herpesvirus 6A in a patient with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Clin Infect Dis 2014; 59: 545–548.
Hill JA, Sedlak RH, Zerr DM, Huang ML, Yeung C, Myerson D et al. Prevalence of chromosomally integrated human herpesvirus 6 in patients with human herpesvirus 6-central nervous system dysfunction. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2015; 21: 371–373.
Lee SO, Brown RA, Razonable RR . Chromosomally integrated human herpesvirus-6 in transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis 2012; 14: 346–354.
Clark DA, Nacheva EP, Leong HN, Brazma D, Li YT, Tsao EH et al. Transmission of integrated human herpesvirus 6 through stem cell transplantation: implications for laboratory diagnosis. J Infect Dis 2006; 193: 912–916.
Ward KN, Leong HN, Nacheva EP, Howard J, Atkinson CE, Davies NW et al. Human herpesvirus 6 chromosomal integration in immunocompetent patients results in high levels of viral DNA in blood, sera, and hair follicles. J Clin Microbiol 2006; 44: 1571–1574.
Zerr DM . Human herpesvirus 6 and central nervous system disease in hematopoietic cell transplantation. J Clin Virol 2006; 37: S52–S56.
Muta T, Fukuda T, Harada M . Human herpesvirus-6 encephalitis in hematopoietic SCT recipients in Japan: a retrospective multicenter study. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 43: 583–585.
Seeley WW, Marty FM, Holmes TM, Upchurch K, Soiffer RJ, Antin JH et al. Post-transplant acute limbic encephalitis: clinical features and relationship to HHV6. Neurology 2007; 69: 156–165.
Toriumi N, Kobayashi R, Yoshida M, Iguchi A, Sarashina T, Okubo H et al. Risk factors for human herpesvirus 6 reactivation and its relationship with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion after stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2014; 36: 379–383.
Kawaguchi T, Takeuchi M, Kawajiri C, Abe D, Nagao Y, Yamazaki A et al. Severe hyponatremia caused by syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone developed as initial manifestation of human herpesvirus-6-associated acute limbic encephalitis after unrelated bone marrow transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis 2013; 15: E54–E57.
Ogata M, Satou T, Inoue Y, Takano K, Ikebe T, Ando T et al. Foscarnet against human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 reactivation after allo-SCT: breakthrough HHV-6 encephalitis following antiviral prophylaxis. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 257–264.
Hill JA, Koo S, Guzman Suarez BB, Ho VT, Cutler C, Koreth J et al. Cord-blood hematopoietic stem cell transplant confers an increased risk for human herpesvirus-6-associated acute limbic encephalitis: a cohort analysis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18: 1638–1648.
Howell KB, Tiedemann K, Haeusler G, Mackay MT, Kornberg AJ, Freeman JL et al. Symptomatic generalized epilepsy after HHV6 posttransplant acute limbic encephalitis in children. Epilepsia 2012; 53: e122–e126.
Cheng FW, Lee V, Leung WK, Chan PK, Leung TF, Shing MK et al. HHV-6 encephalitis in pediatric unrelated umbilical cord transplantation: a role for ganciclovir prophylaxis? Pediatr Transplant 2010; 14: 483–487.
Bhanushali MJ, Kranick SM, Freeman AF, Cuellar-Rodriguez JM, Battiwalla M, Gea-Banacloche JC et al. Human herpes 6 virus encephalitis complicating allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Neurology 2013; 80: 1494–1500.
Mori T, Mihara A, Yamazaki R, Shimizu T, Aisa Y, Suzuki S et al. Myelitis associated with human herpes virus 6 (HHV-6) after allogeneic cord blood transplantation. Scand J Infect Dis 2007; 39: 276–278.
Mori Y, Miyamoto T, Nagafuji K, Kamezaki K, Yamamoto A, Saito N et al. High incidence of human herpes virus 6-associated encephalitis/myelitis following a second unrelated cord blood transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010; 16: 1596–1602.
Aoki K, Arima H, Kato A, Hashimoto H, Tabata S, Matsushita A et al. Human herpes virus 6-associated myelitis following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Ann Hematol 2012; 91: 1663–1665.
Granerod J, Cunningham R, Zuckerman M, Mutton K, Davies NW, Walsh AL et al. Causality in acute encephalitis: defining aetiologies. Epidemiol Infect 2010; 138: 783–800.
Dewhurst S . Human herpesvirus type 6 and human herpesvirus type 7 infections of the central nervous system. Herpes 2004; 11: 105a–111a.
Ljungman P, de la Camara R, Cordonnier C, Einsele H, Engelhard D, Reusser P et al. Management of CMV, HHV-6, HHV-7 and Kaposi-sarcoma herpesvirus (HHV-8) infections in patients with hematological malignancies and after SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 42: 227–240.
Tunkel AR, Glaser CA, Bloch KC, Sejvar JJ, Marra CM, Roos KL et al. The management of encephalitis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47: 303–327.
Tomblyn M, Chiller T, Einsele H, Gress R, Sepkowitz K, Storek J et al. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients: a global perspective. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 1143–1238.
Fujimaki K, Mori T, Kida A, Tanaka M, Kawai N, Matsushima T et al. Human herpesvirus 6 meningoencephalitis in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Int J Hematol 2006; 84: 432–437.
Hill JA, Boeckh MJ, Sedlak RH, Jerome KR, Zerr DM . Human herpesvirus 6 can be detected in cerebrospinal fluid without associated symptoms after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. J Clin Virol 2014; 61: 289–292.
Olson AL, Dahi PB, Zheng J, Devlin SM, Lubin M, Gonzales AM et al. Frequent human herpesvirus-6 viremia but low incidence of encephalitis in double-unit cord blood recipients transplanted without antithymocyte globulin. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 787–793.
Betts BC, Young JA, Ustun C, Cao Q, Weisdorf DJ . Human herpesvirus 6 infection after hematopoietic cell transplantation: is routine surveillance necessary? Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 1562–1568.
Jeulin H, Agrinier N, Guery M, Salmon A, Clement L, Bordigoni P et al. Human herpesvirus 6 infection after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: incidence, outcome, and factors associated with HHV-6 reactivation. Transplantation 2013; 95: 1292–1298.
Vu T, Carrum G, Hutton G, Heslop HE, Brenner MK, Kamble R . Human herpesvirus-6 encephalitis following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 39: 705–709.
Sakai R, Kanamori H, Motohashi K, Yamamoto W, Matsuura S, Fujita A et al. Long-term outcome of human herpesvirus-6 encephalitis after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 1389–1394.
Shimazu Y, Kondo T, Ishikawa T, Yamashita K, Takaori-Kondo A . Human herpesvirus-6 encephalitis during hematopoietic stem cell transplantation leads to poor prognosis. Transpl Infect Dis 2013; 15: 195–201.
Scheurer ME, Pritchett JC, Amirian ES, Zemke NR, Lusso P, Ljungman P . HHV-6 encephalitis in umbilical cord blood transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 574–580.
Quereda C, Corral I, Laguna F, Valencia ME, Tenorio A, Echeverria JE et al. Diagnostic utility of a multiplex herpesvirus PCR assay performed with cerebrospinal fluid from human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients with neurological disorders. J Clin Microbiol 2000; 38: 3061–3067.
Prasad A, Remick J, Zeichner SL . Activation of human herpesvirus replication by apoptosis. J Virol 2013; 87: 10641–10650.
Tang H, Serada S, Kawabata A, Ota M, Hayashi E, Naka T et al. CD134 is a cellular receptor specific for human herpesvirus-6B entry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 9096–9099.
Gewurz BE, Marty FM, Baden LR, Katz JT . Human herpesvirus 6 encephalitis. Curr Infect Dis Rep 2008; 10: 292–299.
Donati D, Martinelli E, Cassiani-Ingoni R, Ahlqvist J, Hou J, Major EO et al. Variant-specific tropism of human herpesvirus 6 in human astrocytes. J Virol 2005; 79: 9439–9448.
Ahlqvist J, Fotheringham J, Akhyani N, Yao K, Fogdell-Hahn A, Jacobson S . Differential tropism of human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) variants and induction of latency by HHV-6A in oligodendrocytes. J Neurovirol 2005; 11: 384–394.
De Filippis L, Foglieni C, Silva S, Vescovi A, Lusso P, Malnati MS . Differentiated human neural stem cells: a new ex vivo model to study HHV-6 infection of the central nervous system. J Clin Virol 2006; 37: S27–S32.
Fotheringham J, Akhyani N, Vortmeyer A, Donati D, Williams E, Oh U et al. Detection of active human herpesvirus-6 infection in the brain: correlation with polymerase chain reaction detection in cerebrospinal fluid. J Infect Dis 2007; 195: 450–454.
Fotheringham J, Williams EL, Akhyani N, Jacobson S . Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) induces dysregulation of glutamate uptake and transporter expression in astrocytes. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2008; 3: 105–116.
The Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (JSHCT) Monograph. 2012; 34 (Japanese). http://www.jshct.com/guideline/pdf/kansenkanri.pdf.
Manichanh C, Grenot P, Gautheret-Dejean A, Debre P, Huraux JM, Agut H . Susceptibility of human herpesvirus 6 to antiviral compounds by flow cytometry analysis. Cytometry 2000; 40: 135–140.
Akesson-Johansson A, Harmenberg J, Wahren B, Linde A . Inhibition of human herpesvirus 6 replication by 9-[4-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)butyl]guanine (2HM-HBG) and other antiviral compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1990; 34: 2417–2419.
De Clercq E, Naesens L, De Bolle L, Schols D, Zhang Y, Neyts J . Antiviral agents active against human herpesviruses HHV-6, HHV-7 and HHV-8. Rev Med Virol 2001; 11: 381–395.
Yoshida M, Yamada M, Tsukazaki T, Chatterjee S, Lakeman FD, Nii S et al. Comparison of antiviral compounds against human herpesvirus 6 and 7. Antiviral Res 1998; 40: 73–84.
Raffi F, Taburet AM, Ghaleh B, Huart A, Singlas E . Penetration of foscarnet into cerebrospinal fluid of AIDS patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1993; 37: 1777–1780.
Williams-Aziz SL, Hartline CB, Harden EA, Daily SL, Prichard MN, Kushner NL et al. Comparative activities of lipid esters of cidofovir and cyclic cidofovir against replication of herpesviruses in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2005; 49: 3724–3733.
Bonnafous P, Bogaert S, Godet AN, Agut H . HDP-CDV as an alternative for treatment of human herpesvirus-6 infections. J Clin Virol 2013; 56: 175–176.
De Bolle L, Andrei G, Snoeck R, Zhang Y, Van Lommel A, Otto M et al. Potent, selective and cell-mediated inhibition of human herpesvirus 6 at an early stage of viral replication by the non-nucleoside compound CMV423. Biochem Pharmacol 2004; 67: 325–336.
Prichard MN, Williams JD, Komazin-Meredith G, Khan AR, Price NB, Jefferson GM et al. Synthesis and antiviral activities of methylenecyclopropane analogs with 6-alkoxy and 6-alkylthio substitutions that exhibit broad-spectrum antiviral activity against human herpesviruses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2013; 57: 3518–3527.
Milbradt J, Auerochs S, Korn K, Marschall M . Sensitivity of human herpesvirus 6 and other human herpesviruses to the broad-spectrum antiinfective drug artesunate. J Clin Virol 2009; 46: 24–28.
Painter W, Robertson A, Trost LC, Godkin S, Lampert B, Painter G . First pharmacokinetic and safety study in humans of the novel lipid antiviral conjugate CMX001, a broad-spectrum oral drug active against double-stranded DNA viruses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2012; 56: 2726–2734.
Hakacova N, Klingel K, Kandolf R, Engdahl E, Fogdell-Hahn A, Higgins T . First therapeutic use of Artesunate in treatment of human herpesvirus 6B myocarditis in a child. J Clin Virol 2013; 57: 157–160.
Papadopoulou A, Gerdemann U, Katari UL, Tzannou I, Liu H, Martinez C et al. Activity of broad-spectrum T cells as treatment for AdV, EBV, CMV, BKV, and HHV6 infections after HSCT. Sci Transl Med 2014; 6: 242ra283.
Tischer S, Priesner C, Heuft HG, Goudeva L, Mende W, Barthold M et al. Rapid generation of clinical-grade antiviral T cells: selection of suitable T-cell donors and GMP-compliant manufacturing of antiviral T cells. J Transl Med 2014; 12: 336.
Becerra A, Gibson L, Stern LJ, Calvo-Calle JM . Immune response to HHV-6 and implications for immunotherapy. Curr Opin Virol 2014; 9: 154–161.
Caserta MT, Dewhurst S . Dazed and confused by HHV-6. Blood 2011; 117: 5016–5018.
Ward KN . Child and adult forms of human herpesvirus 6 encephalitis: looking back, looking forward. Curr Opin Neurol 2014; 27: 349–355.
Ishiyama K, Katagiri T, Hoshino T, Yoshida T, Yamaguchi M, Nakao S . Preemptive therapy of human herpesvirus-6 encephalitis with foscarnet sodium for high-risk patients after hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2011; 46: 863–869.
Marty FM, Winston DJ, Rowley SD, Vance E, Papanicolaou GA, Mullane KM et al. CMX001 to prevent cytomegalovirus disease in hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 1227–1236.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Health Labour Science Research grant (Grant Number H26-kakushintekigan-ippan-140).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogata, M., Fukuda, T. & Teshima, T. Human herpesvirus-6 encephalitis after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: What we do and do not know. Bone Marrow Transplant 50, 1030–1036 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.76
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.76
This article is cited by
-
The preceding hyponatremia is a useful hallmark for the diagnosis of HHV-6 encephalitis after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)
-
Human seminal virome: a panel based on recent literature
Basic and Clinical Andrology (2022)
-
Differentiating central nervous system infection from disease infiltration in hematological malignancy
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Clinical and microbiological characteristics of bacterial meningitis in umbilical cord blood transplantation recipients
International Journal of Hematology (2022)
-
Effect of methotrexate dose in graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis after single-unit cord blood transplantation in adult acute myeloid leukemia
International Journal of Hematology (2021)