Abstract
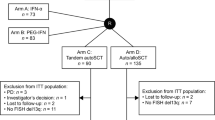
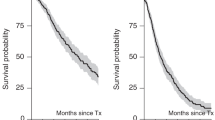
Despite survival improvement with novel agents and use of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), cure of patients with multiple myeloma (MM) remains anecdotal. Initial observations suggested that chronic GvHD was accompanied by an anti-myeloma effect after myeloablative HSCT, but unfortunately this procedure was hampered by high non-relapse mortality (NRM). To maximize the anti-myeloma effect and minimize NRM, we developed a non-myeloablative (NMA) regimen associated with a high incidence of chronic GvHD and tested its efficacy on patient survival and disease eradication. From 2001 to 2010, 92 patients aged⩽65 years with a compatible sibling donor received autologous HSCT followed by an outpatient NMA allogeneic HSCT using a conditioning of fludarabine and cyclophosphamide. Patient median age was 52 years and 97% presented Durie–Salmon stages II–III disease. After a median follow-up of 8.8 years, probability of 10-year progression free and overall survival were 41% and 62%, respectively. Although the cumulative incidence of extensive chronic GvHD was high (at 79%), the majority of long-term survivors were off immunosuppressive drugs by year 5 and NRM was low (at 10%). Together, our results suggest that potential MM cure can be achieved with NMA transplantation regimens that maximize graft-versus-myeloma effect and minimize NRM.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kastritis E, Zervas K, Symeonidis A, Terpos E, Delimbassi S, Anagnostopoulos N et al. Improved survival of patients with multiple myeloma after the introduction of novel agents and the applicability of the International Staging System (ISS): an analysis of the Greek Myeloma Study Group (GMSG). Leukemia 2009; 23: 1152–1157.
Kumar SK, Rajkumar SV, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Hayman SR, Buadi FK et al. Improved survival in multiple myeloma and the impact of novel therapies. Blood 2008; 111: 2516–2520.
Kumar SK, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Gertz MA, Buadi FK, Pandey S et al. Continued improvement in survival in multiple myeloma: changes in early mortality and outcomes in older patients. Leukemia 2014; 28: 1122–1128.
Attal M, Harousseau JL, Facon T, Guilhot F, Doyen C, Fuzibet JG et al. Single versus double autologous stem-cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 2495–2502.
Sonneveld P, Schmidt-Wolf IG, van der Holt B, El Jarari L, Bertsch U, Salwender H et al. Bortezomib induction and maintenance treatment in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: results of the randomized phase III HOVON-65/ GMMG-HD4 trial. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 2946–2955.
McCarthy PL, Owzar K, Hofmeister CC, Hurd DD, Hassoun H, Richardson PG et al. Lenalidomide after stem-cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 1770–1781.
Bensinger WI, Buckner CD, Anasetti C, Clift R, Storb R, Barnett T et al. Allogeneic marrow transplantation for multiple myeloma: an analysis of risk factors on outcome. Blood 1996; 88: 2787–2793.
Gahrton G, Tura S, Ljungman P, Belanger C, Brandt L, Cavo M et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in multiple myeloma. European Group for Bone Marrow Transplantation. N Engl J Med 1991; 325: 1267–1273.
Gahrton G, Tura S, Ljungman P, Blade J, Brandt L, Cavo M et al. Prognostic factors in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 1995; 13: 1312–1322.
Perez-Simon JA, Martino R, Alegre A, Tomas JF, De Leon A, Caballero D et al. Chronic but not acute graft-versus-host disease improves outcome in multiple myeloma patients after non-myeloablative allogeneic transplantation. Br J Haematol 2003; 121: 104–108.
Le Blanc R, Montminy-Metivier S, Belanger R, Busque L, Fish D, Roy DC et al. Allogeneic transplantation for multiple myeloma: further evidence for a GVHD-associated graft-versus-myeloma effect. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 841–848.
Donato ML, Siegel DS, Vesole DH, McKiernan P, Nyirenda T, Pecora AL et al. The graft-versus-myeloma effect: chronic graft-versus-host disease but not acute graft-versus-host disease prolongs survival in patients with multiple myeloma receiving allogeneic transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 1211–1216.
Krishnan A, Pasquini MC, Logan B, Stadtmauer EA, Vesole DH, Alyea E 3rd et al. Autologous haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation followed by allogeneic or autologous haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma (BMT CTN 0102): a phase 3 biological assignment trial. Lancet Oncol 2011; 12: 1195–1203.
Crawley C, Lalancette M, Szydlo R, Gilleece M, Peggs K, Mackinnon S et al. Outcomes for reduced-intensity allogeneic transplantation for multiple myeloma: an analysis of prognostic factors from the Chronic Leukaemia Working Party of the EBMT. Blood 2005; 105: 4532–4539.
van de Donk NW, Kroger N, Hegenbart U, Corradini P, San Miguel JF, Goldschmidt H et al. Prognostic factors for donor lymphocyte infusions following non-myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 37: 1135–1141.
Kroger N, Shimoni A, Zagrivnaja M, Ayuk F, Lioznov M, Schieder H et al. Low-dose thalidomide and donor lymphocyte infusion as adoptive immunotherapy after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood 2004; 104: 3361–3363.
Bellucci R, Wu CJ, Chiaretti S, Weller E, Davies FE, Alyea EP et al. Complete response to donor lymphocyte infusion in multiple myeloma is associated with antibody responses to highly expressed antigens. Blood 2004; 103: 656–663.
Crawley C, Iacobelli S, Bjorkstrand B, Apperley JF, Niederwieser D, Gahrton G . Reduced-intensity conditioning for myeloma: lower nonrelapse mortality but higher relapse rates compared with myeloablative conditioning. Blood 2007; 109: 3588–3594.
Armeson KE, Hill EG, Costa LJ . Tandem autologous vs autologous plus reduced intensity allogeneic transplantation in the upfront management of multiple myeloma: meta-analysis of trials with biological assignment. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 562–567.
Gahrton G, Iacobelli S, Bjorkstrand B, Hegenbart U, Gruber A, Greinix H et al. Autologous/reduced-intensity allogeneic stem cell transplantation vs autologous transplantation in multiple myeloma: long-term results of the EBMT-NMAM2000 study. Blood 2013; 121: 5055–5063.
Sabry W, Le Blanc R, Labbe AC, Sauvageau G, Couban S, Kiss T et al. Graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis with tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil in HLA-matched nonmyeloablative transplant recipients is associated with very low incidence of GVHD and nonrelapse mortality. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 919–929.
Greipp PR, San Miguel J, Durie BG, Crowley JJ, Barlogie B, Blade J et al. International staging system for multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 3412–3420.
Labbe AC, Su SH, Laverdiere M, Pepin J, Patino C, Cohen S et al. High incidence of invasive aspergillosis associated with intestinal graft-versus-host disease following nonmyeloablative transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 1192–1200.
Durie BG, Harousseau JL, Miguel JS, Blade J, Barlogie B, Anderson K et al. International uniform response criteria for multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1467–1473.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 945–956.
Rotta M, Storer BE, Sahebi F, Shizuru JA, Bruno B, Lange T et al. Long-term outcome of patients with multiple myeloma after autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation and nonmyeloablative allografting. Blood 2009; 113: 3383–3391.
Bensinger WI . Is there still a role for allogeneic stem-cell transplantation in multiple myeloma? Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2007; 20: 783–795.
Bruno B, Rotta M, Patriarca F, Mordini N, Allione B, Carnevale-Schianca F et al. A comparison of allografting with autografting for newly diagnosed myeloma. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 1110–1120.
Giaccone L, Storer B, Patriarca F, Rotta M, Sorasio R, Allione B et al. Long-term follow-up of a comparison of nonmyeloablative allografting with autografting for newly diagnosed myeloma. Blood 2011; 117: 6721–6727.
Rosinol L, Perez-Simon JA, Sureda A, de la Rubia J, de Arriba F, Lahuerta JJ et al. A prospective PETHEMA study of tandem autologous transplantation versus autograft followed by reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic transplantation in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood 2008; 112: 3591–3593.
Garban F, Attal M, Michallet M, Hulin C, Bourhis JH, Yakoub-Agha I et al. Prospective comparison of autologous stem cell transplantation followed by dose-reduced allograft (IFM99-03 trial) with tandem autologous stem cell transplantation (IFM99-04 trial) in high-risk de novo multiple myeloma. Blood 2006; 107: 3474–3480.
Moreau P, Garban F, Attal M, Michallet M, Marit G, Hulin C et al. Long-term follow-up results of IFM99-03 and IFM99-04 trials comparing nonmyeloablative allotransplantation with autologous transplantation in high-risk de novo multiple myeloma. Blood 2008; 112: 3914–3915.
Lokhorst HM, van der Holt B, Cornelissen JJ, Kersten MJ, van Oers M, Raymakers R et al. Donor versus no-donor comparison of newly diagnosed myeloma patients included in the HOVON-50 multiple myeloma study. Blood 2012; 119: 6219–6225; quiz 6399.
Bjorkstrand B, Iacobelli S, Hegenbart U, Gruber A, Greinix H, Volin L et al. Tandem autologous/reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic stem-cell transplantation versus autologous transplantation in myeloma: long-term follow-up. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 3016–3022.
Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storb R, Baron F, Sandmaier BM, Maloney DG et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: a new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood 2005; 106: 2912–2919.
Saad A, Mahindra A, Zhang MJ, Zhong X, Costa LJ, Dispenzieri A et al. Hematopoietic cell transplant comorbidity index is predictive of survival after autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation in multiple myeloma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 402–408.
Mikhael JR, Dingli D, Roy V, Reeder CB, Buadi FK, Hayman SR et al. Management of newly diagnosed symptomatic multiple myeloma: updated Mayo Stratification of Myeloma and Risk-Adapted Therapy (mSMART) consensus guidelines. Mayo Clin Proc 2013; 88: 360–376.
El-Cheikh J, Crocchiolo R, Furst S, Stoppa AM, Ladaique P, Faucher C et al. Long-term outcome after allogeneic stem-cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning in patients with multiple myeloma. Am J Hematol 2013; 88: 370–374.
Bruno B, Rotta M, Patriarca F, Mattei D, Allione B, Carnevale-Schianca F et al. Nonmyeloablative allografting for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: the experience of the Gruppo Italiano Trapianti di Midollo. Blood 2009; 113: 3375–3382.
Beaussant Y, Daguindau E, Pugin A, Mohty M, Avet-Loiseau H, Roos-Weil D et al. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Multiple Myeloma: A Retrospective Study of the Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle et de Therapie Cellulaire (SFGM-TC). Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2015; 21: 1452–1459.
Rajkumar SV . Multiple myeloma: 2013 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 2013; 88: 226–235.
Roos-Weil D, Moreau P, Avet-Loiseau H, Golmard JL, Kuentz M, Vigouroux S et al. Impact of genetic abnormalities after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma: a report of the Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle et de Therapie Cellulaire. Haematologica 2011; 96: 1504–1511.
Kroger N, Badbaran A, Zabelina T, Ayuk F, Wolschke C, Alchalby H et al. Impact of high-risk cytogenetics and achievement of molecular remission on long-term freedom from disease after autologous-allogeneic tandem transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 398–404.
Lokhorst HM, Schattenberg A, Cornelissen JJ, van Oers MH, Fibbe W, Russell I et al. Donor lymphocyte infusions for relapsed multiple myeloma after allogeneic stem-cell transplantation: predictive factors for response and long-term outcome. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 3031–3037.
Tricot G, Vesole DH, Jagannath S, Hilton J, Munshi N, Barlogie B . Graft-versus-myeloma effect: proof of principle. Blood 1996; 87: 1196–1198.
Aschan J, Lonnqvist B, Ringden O, Kumlien G, Gahrton G . Graft-versus-myeloma effect. Lancet 1996; 348: 346.
Stewart AK . Reduced-intensity allogeneic transplantation for myeloma: reality bites. Blood 2009; 113: 3135–3136.
Moreau P . Death of frontline allo-SCT in myeloma. Blood 2012; 119: 6178–6179.
Fernandez de Larrea C, Kyle RA, Durie BG, Ludwig H, Usmani S, Vesole DH et al. Plasma cell leukemia: consensus statement on diagnostic requirements, response criteria and treatment recommendations by the International Myeloma Working Group. Leukemia 2013; 27: 780–791.
Ludwig H, Bolejack V, Crowley J, Blade J, Miguel JS, Kyle RA et al. Survival and years of life lost in different age cohorts of patients with multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 1599–1605.
Alsina M, Becker PS, Zhong X, Adams A, Hari P, Rowley S et al. Lenalidomide maintenance for high-risk multiple myeloma after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 1183–1189.
Koreth J, Stevenson KE, Kim HT, McDonough SM, Bindra B, Armand P et al. Bortezomib-based graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in HLA-mismatched unrelated donor transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 3202–3208.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the William Brock fund of the Université de Montréal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, I., LeBlanc, R., Cohen, S. et al. Favorable long-term outcome of patients with multiple myeloma using a frontline tandem approach with autologous and non-myeloablative allogeneic transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 51, 529–535 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.319
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.319
This article is cited by
-
Outcomes in newly diagnosed young or high-risk myeloma patients receiving tandem autologous/allogeneic transplant followed by bortezomib maintenance: a phase II study
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2022)
-
Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation for multiple myeloma: a systematic review and meta-analysis from 2007 to 2017
Cancer Cell International (2018)
-
Donor T-cell responses and disease progression patterns of multiple myeloma
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)
-
A View from the Plateau: Is There a Role for Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in the Era of Highly Effective Therapies for Multiple Myeloma?
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2017)
-
Allogeneic transplantation for multiple myeloma: yes, no or maybe?
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2016)