Abstract
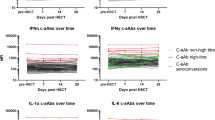
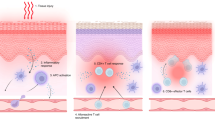
Graft versus host disease (GVHD) is a major complication of haematopoietic SCT (HSCT). A number of inflammatory cytokines/chemokines are implicated in GVHD and have been identified in numerous single centre studies as potential biomarkers for acute and/or chronic GVHD. In this study, we analysed candidate inflammatory biomarkers (B-cell activating factor (BAFF), interleukin 33 (IL-33), CXCL10 and CXCL11) in a two-centre study. Biomarkers were evaluated pre-transplant and at serial time points post transplant in acute and chronic GVHD patient sera with time-matched control samples from patients without GVHD. Further validation was performed using the human skin explant assay, clinical GVHD biopsies and mRNA expression analysis. BAFF was significantly increased pre-transplant. BAFF, IL-33, CXCL10 and CXCL11 showed increased levels in acute GVHD patient sera and high protein expression in grades II–III of the in vitro skin explant graft versus host reaction (GVHR) group. BAFF, CXCL10 and CXCL11 also showed increased mRNA expression levels in clinical biopsies compared with the no/low-grade GVHD group. BAFF, CXCL10 and CXCL11 levels were increased in chronic GVHD patient sera. The results identify BAFF and CXCL10 as predictive biomarkers for acute GVHD and BAFF, CXCL10 and CXCL11 as useful diagnostic biomarkers for acute GVHD and chronic GVHD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flowers ME, Inamoto Y, Carpenter PA, Lee SJ, Kiem HP, Petersdorf EW et al. Comparative analysis of risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease and for chronic graft-versus-host disease according to National Institutes of Health consensus criteria. Blood 2011; 117: 3214–3219.
Reddy P, Teshima T, Kukuruga M, Ordemann R, Liu C, Lowler K et al. Interleukin-18 regulates acute graft-versus-host disease by enhancing Fas-mediated donor T cell apoptosis. J Exp Med 2001; 194: 1433–1440.
Zhang C, Todorov I, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Kandeel F, Forman S et al. Donor CD4+ T and B cells in transplants induce chronic graft-versus-host disease with autoimmune manifestations. Blood 2006; 107: 2993–3001.
Ferrara JL, Deeg HJ . Graft-versus-host disease. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 667–674.
Miura Y, Thoburn CJ, Bright EC, Chen W, Nakao S, Hess AD . Cytokine and chemokine profiles in autologous graft-versus-host disease (GVHD): interleukin 10 and interferon gamma may be critical mediators for the development of autologous GVHD. Blood 2002; 100: 2650–2658.
Jaksch M, Remberger M, Mattsson J . Increased gene expression of chemokine receptors is correlated with acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 280–287.
Paczesny S, Krijanovski OI, Braun TM, Choi SW, Clouthier SG, Kuick R et al. A biomarker panel for acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2009; 113: 273–278.
Miyamoto T, Akashi K, Hayashi S, Gondo H, Murakawa M, Tanimoto K et al. Serum concentration of the soluble interleukin-2 receptor for monitoring acute graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: 185–190.
Or R, Kalinkovich A, Nagler A, Weisman Z, Naparstek E, Weiss L et al. Soluble tumor necrosis factor (sTNF) receptors: a possible prognostic marker for bone marrow transplantation-related complications. Cytokines Mol Ther 1996; 2: 243–250.
Imamura M, Hashino S, Kobayashi H, Kubayashi S, Hirano S, Minagawa T et al. Serum cytokine levels in bone marrow transplantation: synergistic interaction of interleukin-6, interferon-gamma, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 1994; 13: 745–751.
Levine JE, Logan BR, Wu J, Alousi AM, Bolanos-Meade J, Ferrara JL et al. Acute graft-versus-host disease biomarkers measured during therapy can predict treatment outcomes: a Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network study. Blood 2012; 119: 3854–3860.
Levine JE, Braun TM, Harris AC, Holler E, Taylor A, Miller H et al. A prognostic score for acute graft-versus-host disease based on biomarkers: a multicenter study. Lancet Haematol 2015; 2: e21–e29.
MacMillan ML, Robin M, Harris AC, DeFor TE, Martin PJ, Alousi A et al. A refined risk score for acute graft-versus-host disease that predicts response to initial therapy, survival, and transplant-related mortality. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2015; 21: 761–767.
Harris AC, Ferrara JL, Braun TM, Holler E, Teshima T, Levine JE et al. Plasma biomarkers of lower gastrointestinal and liver acute GVHD. Blood 2012; 119: 2960–2963.
Shin OS, Harris JB . Innate immunity and transplantation tolerance: the potential role of TLRs/NLRs in GVHD. Korean J Hematol 2011; 46: 69–79.
Sarantopoulos S, Stevenson KE, Kim HT, Bhuiya NS, Cutler CS, Soiffer RJ et al. High levels of B-cell activating factor in patients with active chronic graft-versus-host disease. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 6107–6114.
Piper KP, Horlock C, Curnow SJ, Arrazi J, Nicholls S, Mahendra P et al. CXCL10-CXCR3 interactions play an important role in the pathogenesis of acute graft-versus-host disease in the skin following allogeneic stem-cell transplantation. Blood 2007; 110: 3827–3832.
Croudace JE, Inman CF, Abbotts BE, Nagra S, Nunnick J, Mahendra P et al. Chemokine-mediated tissue recruitment of CXCR3+ CD4+ T cells plays a major role in the pathogenesis of chronic GVHD. Blood 2012; 120: 4246–4255.
Pavletic SZ, Carter SL, Kernan NA, Henslee-Downey J, Mendizabal AM, Papadopoulos E et al. Influence of T-cell depletion on chronic graft-versus-host disease: results of a multicenter randomized trial in unrelated marrow donor transplantation. Blood 2005; 106: 3308–3313.
Khan WN . B cell receptor and BAFF receptor signaling regulation of B cell homeostasis. J Immunol 2009; 183: 3561–3567.
Melchers F . Actions of BAFF in B cell maturation and its effects on the development of autoimmune disease. Ann Rheum Dis 2003; 62 (Suppl 2): ii25–ii27.
Sarantopoulos S, Stevenson KE, Kim HT, Cutler CS, Bhuiya NS, Schowalter M et al. Altered B-cell homeostasis and excess BAFF in human chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2009; 113: 3865–3874.
Nasti TH, Timares L . Inflammasome activation of IL-1 family mediators in response to cutaneous photodamage. Photochem Photobiol 2012; 88: 1111–1125.
Landfried K, Bataille F, Rogler G, Brenmoehl J, Kosovac K, Wolff D et al. Recipient NOD2/CARD15 status affects cellular infiltrates in human intestinal graft-versus-host disease. Clin Exp Immunol 2009; 159: 87–92.
Watson MJ, Ke B, Shen XD, Gao F, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW et al. Intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury triggers activation of innate toll-like receptor 4 and adaptive chemokine programs. Transplant Proc 2008; 40: 3339–3341.
Zeiser R, Penack O, Holler E, Idzko M . Danger signals activating innate immunity in graft-versus-host disease. J Mol Med (Berl) 2011; 89: 833–845.
Schroder K, Tschopp J . The inflammasomes. Cell 2010; 140: 821–832.
Zlotnik A, Yoshie O . Chemokines: a new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity 2000; 12: 121–127.
Dickinson AM, Sviland L, Carey P, Reid MM, Hamilton PJ, Pearson AJ et al. Skin explant culture as a model for cutaneous graft-versus-host disease in humans. Bone Marrow Transplant 1988; 3: 323–329.
Vogelsang GB, Hess AD, Berkman AW, Tutschka PJ, Farmer ER, Converse PJ et al. An in vitro predictive test for graft versus host disease in patients with genotypic HLA-identical bone marrow transplants. N Engl J Med 1985; 313: 645–650.
Wang XN, Collin M, Sviland L, Marshall S, Jackson G, Schulz U et al. Skin explant model of human graft-versus-host disease: prediction of clinical outcome and correlation with biological risk factors. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 152–159.
Dignan FL, Clark A, Amrolia P, Cornish J, Jackson G, Mahendra P et al. Diagnosis and management of acute graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol 2012; 158: 30–45.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 945–956.
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ . Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 2008; 3: 1101–1108.
Atkinson K, Horowitz MM, Gale RP, van Bekkum DW, Gluckman E, Good RA et al. Risk factors for chronic graft-versus-host disease after HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1990; 75: 2459–2464.
Arora M, Klein JP, Weisdorf DJ, Hassebroek A, Flowers ME, Cutler CS et al. Chronic GVHD risk score: a Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research analysis. Blood 2011; 117: 6714–6720.
Stohl W, Metyas S, Tan SM, Cheema GS, Oamar B, Xu D et al. B lymphocyte stimulator overexpression in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: longitudinal observations. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 3475–3486.
Quartuccio L, Fabris M, Moretti M, Barone F, Bombardieri M, Rupolo M et al. Resistance to rituximab therapy and local BAFF overexpression in Sjogren's syndrome-related myoepithelial sialadenitis and low-grade parotid B-cell lymphoma. Open Rheumatol J 2008; 2: 38–43.
Mapara MY, Leng C, Kim YM, Bronson R, Lokshin A, Luster A et al. Expression of chemokines in GVHD target organs is influenced by conditioning and genetic factors and amplified by GVHR. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 623–634.
Storek J, Ferrara S, Ku N, Giorgi JV, Champlin RE, Saxon A . B cell reconstitution after human bone marrow transplantation: recapitulation of ontogeny? Bone Marrow Transplant 1993; 12: 387–398.
Brink R . Regulation of B cell self-tolerance by BAFF. Semin Immunol 2006; 18: 276–283.
Reichenbach DK, Schwarze V, Matta BM, Tkachev V, Lieberknecht E, Liu Q et al. The IL-33/ST2 axis augments effector T cell responses during acute GVHD. Blood 2015; 125: 3183–3192.
Hancock WW, Lu B, Gao W, Csizmadia V, Faia K, King JA et al. Requirement of the chemokine receptor CXCR3 for acute allograft rejection. J Exp Med 2000; 192: 1515–1520.
Hancock WW, Gao W, Faia KL, Csizmadia V . Chemokines and their receptors in allograft rejection. Curr Opin Immunol 2000; 12: 511–516.
Uppaluri R, Sheehan KC, Wang L, Bui JD, Brotman JJ, Lu B et al. Prolongation of cardiac and islet allograft survival by a blocking hamster anti-mouse CXCR3 monoclonal antibody. Transplantation 2008; 86: 137–147.
Hancock WW, Gao W, Csizmadia V, Faia KL, Shemmeri N, Luster AD . Donor-derived IP-10 initiates development of acute allograft rejection. J Exp Med 2001; 193: 975–980.
Mavin E, Ahmed SS, O'Boyle G, Turner B, Douglass S, Norden J et al. Regulatory T cells inhibit CD8(+) T-cell tissue invasion in human skin graft-versus-host reactions. Transplantation 2012; 94: 456–464.
Grenier JM, Wang L, Manji GA, Huang WJ, Al-Garawi A, Kelly R et al. Functional screening of five PYPAF family members identifies PYPAF5 as a novel regulator of NF-kappaB and caspase-1. FEBS Lett 2002; 530: 73–78.
Cayrol C, Girard JP . The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is inactivated after maturation by caspase-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 9021–9026.
Ponce DM, Hilden P, Mumaw C, Devlin SM, Lubin M, Giralt S et al. High day 28 ST2 levels predict for acute graft-versus-host disease and transplant-related mortality after cord blood transplantation. Blood 2014; 125: 199–205.
Acknowledgements
We thank Elizabeth Douglas, Cindy Carr for technical support, Shelagh Lowerson for providing Clinical Data from Euro Bank and help with ROC analysis and Shazmeen Surtee for helping as part of her undergraduate project. This study was funded by FP6 EC Stemdiagnostics (Contract No. 037703), FP7 Marie Curie Initial Training Network Celleurope (Contract No. 315963), Leukemia and Lymphoma Research and Tyneside Leukaemia Research Association.
Author contributions
SSA, XNW, JN and EE-G performed experiments. SSA, KP and SA carried out the statistical analysis. SSA and AMD wrote the paper. EH, MC and IH contributed to collaborating on the research and contributed patient samples and clinical data. AMD and EH designed the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Bone Marrow Transplantation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, S., Wang, X., Norden, J. et al. Identification and validation of biomarkers associated with acute and chronic graft versus host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 50, 1563–1571 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.191
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.191
This article is cited by
-
Variable selection methods for predicting clinical outcomes following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Ergebnisse der Sicca-Forschungsförderung 2016
Der Ophthalmologe (2021)
-
Chemokine analysis as a novel diagnostic modality in the early prediction of the outcome of non-union therapy: a matched pair analysis
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018)
-
Biomarkers in chronic graft-versus-host disease: quo vadis?
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2018)
-
Extracellular vesicles as potential biomarkers of acute graft-vs-host disease
Leukemia (2018)