Abstract
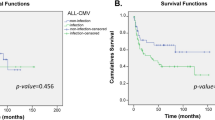
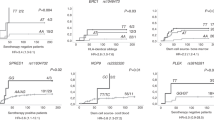
Steroid refractory acute GVHD (SR aGVHD) is associated with high morbidity and mortality. This study attempted to generate a risk model for SR aGVHD using 259 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 53 genes of recipients and donors. A total of 268 patients with aGVHD who were treated with systemic steroids were included. Patients were randomly divided into training (n=180) and validation sets (n=88). Clinical risk factors were also evaluated. In the training set, 85 (47.2%) developed SR aGVHD. Gastrointestinal involvement (P<0.0001) and donor genotypes of IL6 (rs1800797; P=6.2 × 10−4) and IFNG (rs2069727; P=4.4 × 10−4) were significant risk factors. Scores were assigned to the above risk factors. Patients were divided into low (score 0, n=74) vs high risk (scores 1–3; n=106) in risk model. Higher incidence of SR aGVHD was noted in the high risk (61.3%) vs the low-risk group (27%; P<0.0001, odds ratio (OR) 4.28). Predictive effect of risk model was replicated in the validation set (P=0.0045, OR 3.74). This risk model was associated with response to therapy, overall and GVHD-specific survival and non-relapse mortality. Our study suggested that this risk model could identify patients at high risk of SR aGVHD with donor genotype of IL6 (rs1800797) and IFNG (rs2069727) along with gastrointestinal involvement of aGVHD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weisdorf D, Haake R, Blazar B, Miller W, McGlave P, Ramsay N et al. Treatment of moderate/severe acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: an analysis of clinical risk features and outcome. Blood 1990; 75: 1024–1030.
Martinez C, Solano C, Ferra C, Sampol A, Valcarcel D, Perez-Simon JA . Alemtuzumab as treatment of steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: results of a phase II study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 639–642.
MacMillan ML, Weisdorf DJ, Wagner JE, DeFor TE, Burns LJ, Ramsay NK et al. Response of 443 patients to steroids as primary therapy for acute graft-versus-host disease: comparison of grading systems. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2002; 8: 387–394.
Hings IM, Severson R, Filipovich AH, Blazar BR, Kersey JH, Ramsay NK et al. Treatment of moderate and severe acute GVHD after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 1994; 58: 437–442.
Westin JR, Saliba RM, De Lima M, Alousi A, Hosing C, Qazilbash MH et al. Steroid-refractory acute GVHD: predictors and outcomes. Adv Hematol 2011; 2011: 601953.
Vander Lugt MT, Braun TM, Hanash S, Ritz J, Ho VT, Antin JH et al. ST2 as a marker for risk of therapy-resistant graft-versus-host disease and death. N Engl J Med 2013; 369: 529–539.
Arora M, Lindgren B, Basu S, Nagaraj S, Gross M, Weisdorf D et al. Polymorphisms in the base excision repair pathway and graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia 2010; 24: 1470–1475.
Lee JC, Espeli M, Anderson CA, Linterman MA, Pocock JM, Williams NJ et al. Human SNP links differential outcomes in inflammatory and infectious disease to a FOXO3-regulated pathway. Cell 2013; 155: 57–69.
Koumakis E, Bouaziz M, Dieude P, Ruiz B, Riemekasten G, Airo P et al. A regulatory variant in CCR6 is associated with anti-topoisomerase positive systemic sclerosis susceptibility. Arthritis Rheum 2013; 65: 3202–3208.
Xiang Q, Chen L, Fang J, Hou S, Wei L, Bai L et al. TNF receptor-associated factor 5 gene confers genetic predisposition to acute anterior uveitis and pediatric uveitis. Arthritis Res Ther 2013; 15: R113.
Kim DD, Yun J, Won HH, Cheng L, Su J, Xu W et al. Multiple single-nucleotide polymorphism-based risk model for clinical outcomes after allogeneic stem-cell transplantation, especially for acute graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation 2012; 94: 1250–1257.
Wermke M, Maiwald S, Schmelz R, Thiede C, Schetelig J, Ehninger G et al. Genetic variations of interleukin-23 R (1143 A>G) and BPI (A645G), but not of NOD2, are associated with acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010; 16: 1718–1727.
Murphy N, Diviney M, Szer J, Bardy P, Grigg A, Hoyt R et al. Donor methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase genotype is associated with graft-versus-host disease in hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients treated with methotrexate. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 37: 773–779.
Viel DO, Tsuneto LT, Sossai CR, Lieber SR, Marques SB, Vigorito AC et al. IL2 and TNFA gene polymorphisms and the risk of graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Scand J Immunol 2007; 66: 703–710.
Ambruzova Z, Mrazek F, Raida L, Jindra P, Vidan-Jeras B, Faber E et al. Association of IL6 and CCL2 gene polymorphisms with the outcome of allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 44: 227–235.
Kim DH, Jamal N, Saragosa R, Loach D, Wright J, Gupta V et al. Similar outcomes of cryopreserved allogeneic peripheral stem cell transplants (PBSCT) compared to fresh allografts. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 1233–1243.
Kim DH, Kumar D, Messner HA, Minden M, Gupta V, Kuruvilla J et al. Clinical efficacy of prophylactic strategy of long-term low-dose acyclovir for Varicella-Zoster virus infection after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Clin Transplant 2008; 22: 770–779.
Siegal D, Keller A, Xu W, Bhuta S, Kim DH, Kuruvilla J et al. Central nervous system complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: incidence, manifestations, and clinical significance. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 1369–1379.
Kim DH, Popradi G, Xu W, Gupta V, Kuruvilla J, Wright J et al. Peripheral blood eosinophilia has a favorable prognostic impact on transplant outcomes after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 471–482.
Alam N, Marras TK, Atenafu EG, Gupta V, Kuruvilla J, Lipton JH et al. Allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation significantly increases risk of chronic graft-versus-host disease of lung compared with bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18: 1905–1910.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al1994 Consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
EBMT-ESH HANDBOOK 2012.
Parimon T, Au DH, Martin PJ, Chien JW . A risk score for mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Ann Intern Med 2006; 144: 407–414.
Lee KH, Choi SJ, Lee JH, Lee JS, Kim WK, Lee KB et al. Prognostic factors identifiable at the time of onset of acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Haematologica 2005; 90: 939–948.
Li Q, Zhai Z, Xu X, Shen Y, Zhang A, Sun Z et al. Decrease of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells and TGF-beta at early immune reconstitution is associated to the onset and severity of graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic haematogenesis stem cell transplantation. Leuk Res 2010; 34: 1158–1168.
Shirasugi N, Aramaki O, Hatano M, Suda H, Tanaka K, Inoue F et al. Synergistic effect of 15-deoxyspergualin with costimulation blockade on alloimmune response. Transplant Proc 2004; 36: 2446–2447.
Magro L, Catteau B, Coiteux V, Bruno B, Jouet JP, Yakoub-Agha I . Efficacy of imatinib mesylate in the treatment of refractory sclerodermatous chronic GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 42: 757–760.
Ochs LA, Blazar BR, Roy J, Rest EB, Weisdorf DJ . Cytokine expression in human cutaneous chronic graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: 1085–1092.
Kanda Y . Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software 'EZR' for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 452–458.
Bowcock AM, Kidd JR, Lathrop GM, Daneshvar L, May LT, Ray A et al. The human ‘interferon-beta 2/hepatocyte stimulating factor/interleukin-6’ gene: DNA polymorphism studies and localization to chromosome 7p21. Genomics 1988; 3: 8–16.
Wine E, Mack DR, Hyams J, Otley AR, Markowitz J, Crandall WV et al. Interleukin-6 is associated with steroid resistance and reflects disease activity in severe pediatric ulcerative colitis. J Crohns Colitis 2013; 7: 916–922.
Bonifati C, Solmone M, Trento E, Pietravalle M, Fazio M, Ameglio F . Serum interleukin-6 levels as an early marker of therapeutic response to UVB radiation and topical steroids in psoriatic patients. Int J Clin Lab Res 1994; 24: 122–123.
Dittrich A, Khouri C, Sackett SD, Ehlting C, Bohmer O, Albrecht U et al. Glucocorticoids increase interleukin-6-dependent gene induction by interfering with the expression of the suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 feedback inhibitor. Hepatology 2012; 55: 256–266.
Le Huu D, Matsushita T, Jin G, Hamaguchi Y, Hasegawa M, Takehara K et al. IL-6 blockade attenuates the development of murine sclerodermatous chronic graft-versus-host disease. J Invest Dermatol 2012; 132: 2752–2761.
Dicarlo J, Agarwal-Hashmi R, Shah A, Kim P, Craveiro L, Killen R et al. Cytokine and chemokine patterns across one hundred days following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 361–369.
Fishman D, Faulds G, Jeffery R, Mohamed-Ali V, Yudkin JS, Humphries S et al. The effect of novel polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene on IL-6 transcription and plasma IL-6 levels, and an association with systemic-onset juvenile chronic arthritis. J Clin Invest 1998; 102: 1369–1376.
Choi B, Lee DE, Park HY, Jeong S, Lee SM, Ji E et al. A meta-analysis of the effects of interleukin-6 -174 G>C genetic polymorphism on acute graft-versus-host disease susceptibility. Clin Ther 2012; 34: 295–304.
Guichelaar T, Emmelot ME, Rozemuller H, Martini B, Groen RW, Storm G et al. Human regulatory T cells do not suppress the antitumor immunity in the bone marrow: a role for bone marrow stromal cells in neutralizing regulatory T cells. Clin Cancer Res 2013; 19: 1467–1475.
Chen X, Das R, Komorowski R, Beres A, Hessner MJ, Mihara M et al. Blockade of interleukin-6 signaling augments regulatory T-cell reconstitution and attenuates the severity of graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2009; 114: 891–900.
Drobyski WR, Pasquini M, Kovatovic K, Palmer J, Douglas Rizzo J, Saad A et al. Tocilizumab for the treatment of steroid refractory graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 1862–1868.
Pawlik A, Czerny B, Dabrowska-Zamojcin E, Gornik W, Poziomkowska I, Gawronska-Szklarz B et al. [The influence of IL-6 polymorphism on efficacy of treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients with methotrexate and prednisone]. Pol Arch Med Wewn 2005; 114: 843–847.
Ruiz-Linares A . Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism in the interferon-gamma (IFNG) gene. Hum Mol Genet 1993; 2: 1508.
Sun K, Hsiao HH, Li M, Ames E, Bouchlaka M, Welniak LA et al. IFN-gamma receptor-deficient donor T cells mediate protection from graft-versus-host disease and preserve graft-versus-tumor responses after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Immunol 2012; 189: 2033–2042.
Lu Y, Giver CR, Sharma A, Li JM, Darlak KA, Owens LM et al. IFN-gamma and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase signaling between donor dendritic cells and T cells regulates graft versus host and graft versus leukemia activity. Blood 2012; 119: 1075–1085.
Goleva E, Li LB, Leung DY . IFN-gamma reverses IL-2- and IL-4-mediated T-cell steroid resistance. Am J Respir cell Mol Biol 2009; 40: 223–230.
Lai HY, Chou TY, Tzeng CH, Lee OK . Cytokine profiles in various graft-versus-host disease target organs following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cell Transplant 2012; 21: 2033–2045.
Das R, Komorowski R, Hessner MJ, Subramanian H, Huettner CS, Cua D et al. Blockade of interleukin-23 signaling results in targeted protection of the colon and allows for separation of graft-versus-host and graft-versus-leukemia responses. Blood 2010; 115: 5249–5258.
Das R, Chen X, Komorowski R, Hessner MJ, Drobyski WR . Interleukin-23 secretion by donor antigen-presenting cells is critical for organ-specific pathology in graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2009; 113: 2352–2362.
Burman AC, Banovic T, Kuns RD, Clouston AD, Stanley AC, Morris ES et al. IFNgamma differentially controls the development of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome and GVHD of the gastrointestinal tract. Blood 2007; 110: 1064–1072.
McCandless EE, Rai SK, Mwangi D, Sly L, Franz LC . Hydrocortisone inhibits IFN-gamma production in equine, ovine, and bovine PBMCs. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 2013; 153: 128–133.
Li JJ, Wang W, Baines KJ, Bowden NA, Hansbro PM, Gibson PG et al. IL-27/IFN-gamma induce MyD88-dependent steroid-resistant airway hyperresponsiveness by inhibiting glucocorticoid signaling in macrophages. J Immunol 2010; 185: 4401–4409.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Author Contributions
NA and DDHK contributed to the design of the study, supervision of data collection and data interpretation, data analysis and writing the manuscript. EGA and WX prepared statistical plan, performed statistical analysis and interpreted results. MS, VG, JU, JK, JHL and HAM were involved in the supervision of data collection and interpretation of the data. All authors critically reviewed and approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Bone Marrow Transplantation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alam, N., Xu, W., Atenafu, E. et al. Risk model incorporating donor IL6 and IFNG genotype and gastrointestinal GVHD can discriminate patients at high risk of steroid refractory acute GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant 50, 734–742 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.19
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.19
This article is cited by
-
Investigation of TGFB1 −1347C>T variant as a biomarker after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
Seeking biomarkers for acute graft-versus-host disease: where we are and where we are heading?
Biomarker Research (2019)
-
Baricitinib-induced blockade of interferon gamma receptor and interleukin-6 receptor for the prevention and treatment of graft-versus-host disease
Leukemia (2018)