Abstract
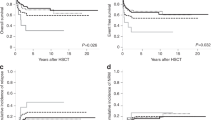
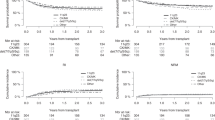
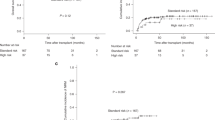
Newer cytogenetic scoring systems for myelodysplastic syndromes (MDSs), like cytogenetic stratification of the revised international prognostic scoring system (IPSS-R) or monosomal karyotype, may also improve outcome prediction after hematopoietic SCT (HCT). We compared the prognostic value of specific cytogenetic abnormalities, IPSS-R karyotype and monosomal karyotype for HCT outcome in 98 patients with MDS and AML post MDS. Higher-risk IPSS-R karyotype, 3q21q26 and transformation to AML before HCT were associated with increased cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR), whereas OS was adversely influenced by del 5q/−5, abnormalities of chromosomes 11 and 17 and cytogenetic IPSS-R very poor category. Karyotype with ⩽2 abnormalities and no abnormalities of chromosomes 3, 5, 7, 11 and 17 was an independent prognostic factor of lower CIR (hazard ratio (HR)=0.2, P=0.01) and longer OS (HR=0.5, P=0.03). In conclusion, some specific cytogenetic abnormalities and high cytogenetic complexity, as reflected by IPSS-R very poor karyotype, rather than monosomal karyotype, were associated with higher CIR and shorter OS after HCT. Conversely, results were encouraging in patients lacking those abnormalities, who may be very good candidates for HCT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 1992; 51: 189–199.
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. ARC press: Lyon, France, 2008.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Greenberg PL, Tuechler H, Schanz J, Sanz G, Garcia-Manero G, Solé F et al. Revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R) for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2012; 120: 2454–2465.
Schanz J, Tüchler H, Solé F, Mallo M, Luño E, Cervera J et al. New comprehensive cytogenetic scoring system for primary myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia after MDS derived from an international database merge. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 820–829.
Breems DA, Van Putten WL, De Greef GE, Van Zelderen-Bhola SL, Gerssen-Schoorl KB, Mellink CH et al. Monosomal karyotype in acute myeloid leukemia: a better indicator of poor prognosis than a complex karyotype. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 4791–4797.
Nevill TJ, Shepherd JD, Sutherland HJ, Abou Mourad YR, Lavoie JC, Barnett MJ et al. IPSS poor-risk karyotype as a predictor of outcome for patients with myelodysplastic syndrome following myeloablative stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 205–213.
Armand P, Kim HT, DeAngelo DJ, Ho VT, Cutler CS, Stone RM et al. Impact of cytogenetics on outcome of de novo and therapy related AML and MDS after allogeneic transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 655–664.
Armand P, Deeg HJ, Kim HT, Lee H, Armistead P, de Lima M et al. Multicenter validation study of a transplantation-specific cytogenetics grouping scheme for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Bone Marrow Transplant 2010; 45: 877–885.
Deeg HJ, Scott BL, Fang M, Shulman HM, Gyurkocza B, Myerson D et al. Five-group cytogenetic risk classification, monosomal karyotype, and outcome after hematopoietic cell transplantation for MDS or acute leukemia evolving from MDS. Blood 2012; 120: 1398–1408.
Van Gelder M, de Wreede LC, Schetelig J, van Biezen A, Volin L, Maertens J et al. Monosomal karyotype predicts poor survival after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in chromosome 7 abnormal myelodysplastic syndrome and secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2013; 27: 879–888.
Wang SA, Jabbar K, Chen SS, Galili N, Vega F, Jones D et al. Trisomy 11 in myelodysplastic syndromes defines a unique group of disease with aggressive clinicopathologic features. Leukemia 2010; 24: 740–747.
CIBMTR Forms manual: pre-TED (Form2400). Document number A00413 version 2.4.
Kaplan E, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observation. J Am Stat Assoc 1958; 53: 457–481.
Peto R, Peto J . Asymptotically efficient rank invariant test procedures. J R Stat Soc A 1972; 135: 185–198.
Fine J, Gray R . A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc 1999; 94: 496–509.
Cox DR . Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc B 1972; 34: 187–220.
Middeke JM, Beelen D, Stadler M, Göhring G, Schlegelberger B, Baurmann H et al. Outcome of high-risk acute myeloid leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: negative impact of abnl(17p) and -5/5q-. Blood 2012; 120: 2521–2528.
Valcárcel D, Ademà V, Solé F, Ortega M, Nomdedeu B, Sanz G et al. Complex, not monosomal, karyotype is the cytogenetic marker of poorest prognosis in patients with primary myelodysplastic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31: 916–922.
Patnaik MM, Hanson CA, Hodnefield JM, Knudson R, Van Dyke DL, Tefferi A et al. Monosomal karyotype in myelodysplastic syndromes, with or without monosomy 7 or 5, is prognostically worse than an otherwise complex karyotype. Leukemia 2011; 25: 266–270.
Belli CB, Bengió R, Aranguren PN, Sakamoto F, Flores MG, Watman N et al. Partial and total monosomal karyotypes in myelodysplastic syndromes: comparative prognostic relevance among 421 patients. Am J Hematol 2011; 86: 540–545.
Itzykson R, Thépot S, Eclache V, Quesnel B, Dreyfus F, Beyne-Rauzy O et al. Prognostic significance of monosomal karyotype in higher risk myelodysplastic syndrome treated with azacitidine. Leukemia 2011; 25: 1207–1209.
Schanz J, Tüchler H, Solé F, Mallo M, Luño E, Cervera J et al. Monosomal karyotype in MDS: Explaining the poor prognosis? Leukemia 2013; 27: 1988–1995.
Nevill TJ, Shepherd JD, Sutherland HJ et al. IPSS poor-risk karyotype as a predictor of outcome for patients with myelodysplastic syndrome following myeloablative stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 205–213.
Damaj G, Duhamel A, Robin M, Beguin Y, Michallet M, Mohty M et al. Impact of azacitidine before allogeneic stem-cell transplantation for myelodysplastic syndromes: a study by the Société Française de Greffe de Moelle et de Thérapie-Cellulaire and the Groupe-Francophone des Myélodysplasies. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 4533–4540.
Acknowledgements
CK is indebted to Professor Pierre Fenaux for critical reviewing of the manuscript
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Bone Marrow Transplantation website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelaidi, C., Tzannou, I., Baltadakis, I. et al. Specific abnormalities versus number of abnormalities and cytogenetic scoring systems for outcome prediction after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT for myelodysplastic syndromes. Bone Marrow Transplant 49, 1022–1028 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.87
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.87