Abstract
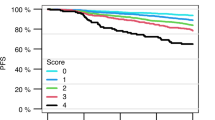
Systematic, standardised pretransplant risk assessment is an important tool for predicting patient outcomes following allogeneic haematopoietic SCT (HSCT). To assess the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) risk score capacities for predicting patient outcomes following unmanipulated haploidentical blood and marrow transplantation (HBMT), we analysed 502 leukaemia patients who received transplants at our centre between 2008 and 2010. The cohort OS and leukaemia-free survival (LFS) were 72.1% and 68.1%, whereas the cumulative non-relapse mortality (NRM) and relapse incidences were 16.5% and 16.1%. According to univariate analysis, the values for OS, LFS and NRM were worse for an EBMT risk score of 6 (40.0, 40.0, 50.0%) than a score of 1 (83.1, 78.3, 8.4%). Hazard ratios steadily increased for each additional score point. Likewise, a higher EBMT risk score was associated with an increased relapse incidence. Importantly, the EBMT risk score prognostic value regarding OS, LFS, NRM and relapse was maintained in the multivariate analysis. Moreover, we also made a haploidentical EBMT (haplo-EBMT) risk score, which used number of HLA disparity instead of donor type, and the haplo-EBMT risk scores can also be used to predict patient outcomes following unmanipulated HBMT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin PJ, Counts GW Jr, Appelbaum FR, Lee SJ, Sanders JE, Deeg HJ et al. Life expectancy in patients surviving more than 5 years after hematopoietic cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 1011–1016.
Wingard JR, Majhail NS, Brazauskas R, Wang Z, Sobocinski KA, Jacobsohn D et al. Long-term survival and late deaths after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 2230–2239.
Gratwohl A . The EBMT risk score. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 749–756.
Gratwohl A, Hermans J, Goldman JM, Arcese W, Carreras E, Devergie A et al. Risk assessment for patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia before allogeneic blood or marrow transplantation. Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Lancet 1998; 352: 1087–1092.
Gratwohl A, Stern M, Brand R, Apperley J, Baldomero H, de Witte T et al. Risk score for outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a retrospective analysis. Cancer 2009; 115: 4715–4726.
Huang XJ, Chang YJ . Unmanipulated HLA-mismatched/haploidentical blood and marrow hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 197–204.
Chang YJ, Huang XJ . Haploidentical bone marrow transplantation without T-cell depletion. Semin Oncol 2012; 39: 653–663.
Huang XJ, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Chen H, Han W et al. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without in vitro T-cell depletion for the treatment of hematological malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 38: 291–297.
Huang XJ, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Chen H, Han W et al. Treatment of acute leukemia with unmanipulated HLA-mismatched/haploidentical blood and bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 257–265.
Liu D, Huang X, Liu K, Xu L, Chen H, Han W et al. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without in vitro T cell depletion for treatment of hematological malignancies in children. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 469–477.
Lu DP, Dong L, Wu T, Huang XJ, Zhang MJ, Han W et al. Conditioning including antithymocyte globulin followed by unmanipulated HLA-mismatched/haploidentical blood and marrow transplantation can achieve comparable outcomes with HLA-identical sibling transplantation. Blood 2006; 107: 3065–3073.
Xiao-Jun H, Lan-Ping X, Kai-Yan L, Dai-Hong L, Huan C, Wei H et al. HLA-mismatched/haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without in vitro T cell depletion for chronic myeloid leukemia: improved outcomes in patients in accelerated phase and blast crisis phase. Ann Med 2008; 40: 444–455.
Xiao-Jun H, Lan-Ping X, Kai-Yan L, Dai-Hong L, Yu W, Huan C et al. Partially matched related donor transplantation can achieve outcomes comparable with unrelated donor transplantation for patients with hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 4777–4783.
Wang Y, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Zhang XH, Han W et al. Long-term follow-up of haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without in vitro T cell depletion for the treatment of leukemia: nine years of experience at a single center. Cancer 2013; 119: 978–985.
Vogelsang GB . How I treat chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2001; 97: 1196–1201.
Zhao XS, Jin S, Zhu HH, Xu LP, Liu DH, Chen H et al. Wilms' tumor gene 1 expression: an independent acute leukemia prognostic indicator following allogeneic hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 499–507.
Zhao XS, Liu YR, Zhu HH, Xu LP, Liu DH, Liu KY et al. Monitoring MRD with flow cytometry: an effective method to predict relapse for ALL patients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol 2012; 91: 183–192.
Yan CH, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Liu YR, Chen H et al. Risk stratification-directed donor lymphocyte infusion could reduce relapse of standard-risk acute leukemia patients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2012; 119: 3256–3262.
Huang XJ, Wang Y, Liu DH, Xu LP, Liu KY, Chen H et al. Administration of short-term immunosuppressive agents after DLI reduces the incidence of DLI-associated acute GVHD without influencing the GVL effect. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 44: 309–316.
Huang XJ, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Chen H, Han W . Donor lymphocyte infusion for the treatment of leukemia relapse after HLA-mismatched/haploidentical T-cell-replete hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 2007; 92: 414–417.
Rezvani K, Kanfer EJ, Marin D, Gabriel I, Rahemtulla A, Taylor A et al. EBMT risk score predicts outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients who have failed a previous transplantation procedure. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18: 235–240.
Terwey TH, Hemmati PG, Martus P, Dietz E, Vuong LG, Massenkeil G et al. A modified EBMT risk score and the hematopoietic cell transplantation-specific comorbidity index for pre-transplant risk assessment in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2010; 95: 810–818.
Lodewyck T, Oudshoorn M, van der Holt B, Petersen E, Spierings E, von dem Borne PA et al. Predictive impact of allele-matching and EBMT risk score for outcome after T-cell depleted unrelated donor transplantation in poor-risk acute leukemia and myelodysplasia. Leukemia 2011; 25: 1548–1554.
De Souza CA, Vigorito AC, Ruiz MA, Nucci M, Dulley FL, Funcke V et al. Validation of the EBMT risk score in chronic myeloid leukemia in Brazil and allogeneic transplant outcome. Haematologica 2005; 90: 232–237.
Passweg JR, Walker I, Sobocinski KA, Klein JP, Horowitz MM, Giralt SA . Validation and extension of the EBMT Risk Score for patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) receiving allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplants. Br J Haematol 2004; 125: 613–620.
Hemmati PG, Terwey TH, le Coutre P, Vuong LG, Massenkeil G, Dorken B et al. A modified EBMT risk score predicts the outcome of patients with acute myeloid leukemia receiving allogeneic stem cell transplants. Eur J Haematol 2011; 86: 305–316.
Wang Y, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Zhang XH, Han W et al. Impact of pretransplantation risk factors on post transplantation outcome of patients with acute myeloid leukemia in remission after haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 283–290.
Gorin NC, Labopin M, Polge E, Cordonnier C, Jouet JP, Michallet M et al. Risk assessment in adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia before early haemopoietic stem cell transplantation with a geno-identical donor: an easy clinical prognostic score to identify patients who benefit most from allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1596–1599.
Qazilbash MH, Devetten MP, Abraham J, Lynch JP, Beall CL, Weisenborn R et al. Utility of a prognostic scoring system for allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Acta Haematol 2003; 109: 119–123.
Klingebiel T, Cornish J, Labopin M, Locatelli F, Darbyshire P, Handgretinger R et al. Results and factors influencing outcome after fully haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children with very high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: impact of center size: an analysis on behalf of the Acute Leukemia and Pediatric Disease Working Parties of the European Blood and Marrow Transplant group. Blood 2010; 115: 3437–3446.
Ciceri F, Labopin M, Aversa F, Rowe JM, Bunjes D, Lewalle P et al. A survey of fully haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adults with high-risk acute leukemia: a risk factor analysis of outcomes for patients in remission at transplantation. Blood 2008; 112: 3574–3581.
Ciurea SO, Champlin RE . Donor selection in T cell-replete haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: knowns, unknowns, and controversies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 180–184.
Huo MR, Xu LP, Li D, Liu DH, Liu KY, Chen H et al. The effect of HLA disparity on clinical outcome after HLA-haploidentical blood and marrow transplantation. Clin Transplant 2012; 26: 284–291.
Mo XD, Xu LP, Liu DH, Zhang XH, Chen H, Chen YH et al. The hematopoietic cell transplantation-specific comorbidity index (HCT-CI) is an outcome predictor for partially matched related donor transplantation. Am J Hematol 2013; 88: 497–502.
Barba P, Martino R, Perez-Simon JA, Fernandez-Aviles F, Castillo N, Pinana JL et al. Combination of the Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Comorbidity Index and the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Score allows a better stratification of high-risk patients undergoing reduced-toxicity allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 20: 66–72.
Marek A, Stern M, Chalandon Y, Ansari M, Ozsahin H, Gungor T et al. The impact of T-cell depletion techniques on the outcome after haploidentical hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 49: 55–61.
Ciurea SO, Mulanovich V, Saliba RM, Bayraktar UD, Jiang Y, Bassett R et al. Improved early outcomes using a T cell replete graft compared with T cell depleted haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18: 1835–1844.
Chang YJ, Zhao XY, Huang XJ . Immune reconstitution after haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 20: 440–449.
Mo XD, Xu LP, Liu DH, Chen YH, Han W, Zhang XH et al. Patients receiving HLA-haploidentical/partially matched related allo-HSCT can achieve desirable health-related QoL that is comparable to that of patients receiving HLA-identical sibling allo-HSCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 1201–1205.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81230013), Scientific Research Foundation for Capital Medicine Development (2011-4022-08), Chang Jiang Scholars Program, Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission (No. Z121107002612035), Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission (No. Z111107067311070) and Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission (No. Z121107002812033). We thank Rachel G and Cara B, medical editors at the American Journal Experts, for providing editing assistance to the authors during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Ht., Chang, Yj., Xu, Lp. et al. EBMT risk score can predict the outcome of leukaemia after unmanipulated haploidentical blood and marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 49, 927–933 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.80
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.80
This article is cited by
-
Fludarabine melphalan versus fludarabine treosulfan for reduced intensity conditioning regimen in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a retrospective analysis
International Journal of Hematology (2024)
-
The prognostic value of patient-reported outcomes in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: exploratory analysis of a randomized nutrition intervention trial
Annals of Hematology (2023)
-
Unrelated umbilical cord blood can improve the prognosis of haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2022)
-
The consensus from The Chinese Society of Hematology on indications, conditioning regimens and donor selection for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: 2021 update
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2021)
-
Beneficial role of CD8+ T-cell reconstitution after HLA-haploidentical stem cell transplantation for high-risk acute leukaemias: results from a clinico-biological EBMT registry study mostly in the T-cell-depleted setting
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2019)