Abstract
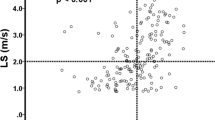
Hepatic complications contribute to morbidity and mortality after allogeneic hemopoietic SCT. Liver Doppler ultrasound and elastography represent promising methods for pretransplant risk assessment and early detection of complications. Ultrasound (liver and spleen size, liver perfusion) and elastography (transient elastography (TE); right liver lobe acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (r-ARFI); left liver lobe ARFI (l-ARFI)) were prospectively evaluated in patients with indications for allo-SCT. Measurements were performed before and repeatedly after SCT. Results were compared with the incidence of life-threatening complications and death during the first 150 days after SCT. Of 59 included patients, 16 suffered from major complications and 9 of them died within the follow-up period. At baseline, liver and spleen size, liver perfusion, TE and r-ARFI did not differ significantly between patients with and without severe complications. In contrast, l-ARFI was significantly elevated in patients who later developed severe complications (1.58±0.30 m/s vs 1.37±0.27 m/s, P=0.030). After SCT, l-ARFI values remained elevated and TE showed increasing liver stiffness in patients with complications. The value of conventional liver ultrasound for prediction of severe SCT complications is limited. Increased values for TE and l-ARFI are associated with severe SCT complications and demand further evaluation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
McDonald GB . Hepatobiliary complications of hematopoietic cell transplantation, 40 years on. Hepatology 2010; 51: 1450–1460.
Sorror ML . How I assess comorbidities before hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood 2013; 121: 2854–2863.
Berzigotti A, Castera L . Update on ultrasound imaging of liver fibrosis. J Hepatol 2013; 59: 180–182.
Song M, Chung J, Kim S, Seol Y, Kim S, Shin H et al. Hepatic artery resistance index at doppler ultrasonography is a useful parameter of hepatic graft-vs-host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Transplant Proc 2010; 42: 3717–3722.
Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storb R, Baron F, Sandmaier BM, Maloney DG et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: a new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood 2005; 106: 2912–2919.
Castera L . Noninvasive methods to assess liver disease in patients with hepatitis B or C. Gastroenterology 2012; 142: e4.
Bota S, Herkner H, Sporea I, Salzl P, Sirli R, Neghina AM et al. Meta-analysis: ARFI elastography versus transient elastography for the evaluation of liver fibrosis. Liver Int 2013; 33: 1138–1147.
Talwalkar JA . Chronic inflammation, liver stiffness, and clinical decision making: an unavoidable partnership. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 10: 938–940.
Karlas TF, Pfrepper C, Rosendahl J, Benckert C, Wittekind C, Jonas S et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography in acute liver failure: necrosis mimics cirrhosis. Z Gastroenterol 2011; 49: 443–448.
Millonig G, Reimann FM, Friedrich S, Fonouni H, Mehrabi A, Büchler MW et al. Extrahepatic cholestasis increases liver stiffness (FibroScan) irrespective of fibrosis. Hepatology 2008; 48: 1718–1723.
Auberger J, Graziadei I, Clausen J, Vogel W, Nachbaur D . Non-invasive transient elastography for the prediction of liver toxicity following hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 159–160.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Filipovich AH . Diagnosis and manifestations of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2008; 21: 251–257.
Fontana RJ, Seeff LB, Andrade RJ, Björnsson E, Day CP, Serrano J et al. Standardization of nomenclature and causality assessment in drug-induced liver injury: summary of a clinical research workshop. Hepatology 2010; 52: 730–742.
McDonald GB, Sharma P, Matthews DE, Shulman HM, Thomas ED . Venocclusive disease of the liver after bone marrow transplantation: diagnosis, incidence, and predisposing factors. Hepatology 1984; 4: 116–122.
Pai RK, van Besien K, Hart J, Artz AS, O'Donnell PH . Clinicopathologic features of late-onset veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome after high dose intravenous busulfan and hematopoietic cell transplant. Leuk Lymphoma 2012; 53: 1552–1557.
NCI Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 4. Available from http://evs.nci.nih.gov/ftp1/CTCAE/About.html (Last accessed 12th November 2013).
Rifkin MD, Needleman L, Pasto ME, Kurtz AB, Foy PM, McGlynn E et al. Evaluation of renal transplant rejection by duplex Doppler examination: value of the resistive index. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1987; 148: 759–762.
Karlas T, Pfrepper C, Wiegand J, Wittekind C, Neuschulz M, Mössner J et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI) for non-invasive detection of liver fibrosis: examination standards and evaluation of interlobe differences in healthy subjects and chronic liver disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 2011; 46: 1458–1467.
Castéra L, Foucher J, Bernard P, Carvalho F, Allaix D, Merrouche W et al. Pitfalls of liver stiffness measurement: a 5-year prospective study of 13,369 examinations. Hepatology 2010; 51: 828–835.
Lédinghen V de, Wong VW, Vergniol J, Wong GL, Foucher J, Chu SH et al. Diagnosis of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis using liver stiffness measurement: comparison between M and XL probe of FibroScan®. J Hepatol 2012; 56: 833–839.
Copelan EA . Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. New Engl J Med 2006; 354: 1813–1826.
Cosgrove D, Piscaglia F, Bamber J, Bojunga J, Correas J, Gilja OH et al. EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 2: Clinical applications. Ultraschall Med 2013; 34: 238–253.
Stebbing J, Farouk L, Panos G, Anderson M, Jiao LR, Mandalia S et al. A meta-analysis of transient elastography for the detection of hepatic fibrosis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2010; 44: 214–219.
Toshima T, Shirabe K, Takeishi K, Motomura T, Mano Y, Uchiyama H et al. New method for assessing liver fibrosis based on acoustic radiation force impulse: a special reference to the difference between right and left liver. J Gastroenterol 2011; 46: 705–711.
Millonig G, Friedrich S, Adolf S, Fonouni H, Golriz M, Mehrabi A et al. Liver stiffness is directly influenced by central venous pressure. J Hepatol 2010; 52: 206–210.
Arena U, Vizzutti F, Corti G, Ambu S, Stasi C, Bresci S et al. Acute viral hepatitis increases liver stiffness values measured by transient elastography. Hepatology 2008; 47: 380–384.
Koch A, Horn A, Dückers H, Yagmur E, Sanson E, Bruensing J et al. Increased liver stiffness denotes hepatic dysfunction and mortality risk in critically ill non-cirrhotic patients at a medical ICU. Crit Care 2011; 15: R266.
Sagir A, Erhardt A, Schmitt M, Häussinger D . Transient elastography is unreliable for detection of cirrhosis in patients with acute liver damage. Hepatology 2008; 47: 592–595.
Myers RP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Kirsch R, Pollett A, Beaton M, Levstik M et al. Discordance in fibrosis staging between liver biopsy and transient elastography using the FibroScan XL probe. J Hepatol 2012; 56: 564–570.
Fontanilla T, Hernando CG, Claros JCV, Bautista G, Minaya J, Del Carmen Vega M et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography and contrast-enhanced sonography of sinusoidal obstructive syndrome (Veno-occlusive Disease): preliminary results. J Ultrasound Med 2011; 30: 1593–1598.
Acknowledgements
We thank Katrin Moritz for her dedicated support in coordinating the study.
This work was supported by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Germany, FKZ: 01EO1001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
TK received travel grants from Echosens/France. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlas, T., Weber, J., Nehring, C. et al. Value of liver elastography and abdominal ultrasound for detection of complications of allogeneic hemopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 49, 806–811 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.61
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.61
This article is cited by
-
Predicting hepatic complications of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using liver stiffness measurement
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2019)
-
Evaluation of liver tissue by ultrasound elastography and clinical parameters in children with multiple blood cell transfusions
Pediatric Radiology (2019)
-
Usefulness of liver stiffness measurement in predicting hepatic veno-occlusive disease development in patients who undergo HSCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)