Abstract
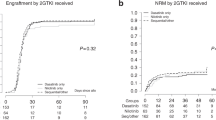
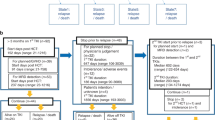
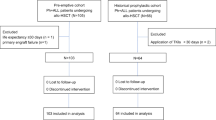
CML treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) has improved many patients’ prognosis, but during the disease’s terminal phase, the blast crisis (CML-BC), has been disappointing. Allo-HSCT is another treatment, but survival rates are still disappointing. Currently, a combination of these two is suggested but with little evidence. This retrospective comparison reports on this combination and TKI alone for treatment of CML-BC. Of the 83 CML-BC patients, 45 received TKIs (imatinib; nilotinb or dasatinib after imatinib resistance; TKIs group) and 38 were treated with allo-HSCT after TKI (TKIs+allo-HSCT group). Treatment success was measured in terms of the hematologic, cytogenic and molecular responses, and subject outcome. Follow-up was 30–126 months or until death. Univariate and multivariate analyses determined EFS and OS predictors. Allo-HSCT significantly improved the 4-year OS (46.7 vs 9.7%, P<0.001) and EFS (47.1 vs 6.7%, P<0.001) compared to TKI treatment alone. Hemoglobin <100 g/L, non-return to chronic phase after TKI therapy and TKI treatment alone are independent adverse predictors of OS and EFS. Allo-HSCT with individualized intervention after TKI therapy is superior to TKI alone for CML-BC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sawyers CL . Chronic myeloid leukemia. New Engl J Med 1999; 340: 1330–1340.
Faderl S, Talpaz M, Estrov Z, Kantarjian HM . Chronic myelogenous leukemia: biology and therapy. Ann Intern Med 1999; 131: 207–219.
Derderian PM, Kantarjian HM, Talpaz M, O'Brien S, Cork A, Estey E et al. Chronic myelogenous leukemia in the lymphoid blastic phase: characteristics, treatment response, and prognosis. Am J Med 1993; 94: 69–74.
Sacchi S, Kantarjian HM, O'Brien S, Cortes J, Rios MB, Giles FJ et al. Chronic myelogenous leukemia in nonlymphoid blastic phase: analysis of the results of first salvage therapy with three different treatment approaches for 162 patients. Cancer 1999; 86: 2632–2641.
Palandri F, Castagnetti F, Testoni N, Luatti S, Marzocchi G, Bassi S et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia in blast crisis treated with imatinib 600 mg: outcome of the patients alive after a 6-year follow-up. Haematologica 2008; 93: 1792–1796.
Nicolini FE, Masszi T, Shen Z, Gallagher NJ, Jootar S, Powell BL et al. Expanding Nilotinib Access in Clinical Trials (ENACT), an open-label multicenter study of oral nilotinib in adult patients with imatinib-resistant or -intolerant chronic myeloid leukemia in accelerated phase or blast crisis. Leuk Lymphoma 2012; 53: 907–914.
Saglio G, Hochhaus A, Goh YT, Masszi T, Pasquini R, Maloisel F et al. Dasatinib in imatinib-resistant or imatinib-intolerant chronic myeloid leukemia in blast phase after 2 years of follow-up in a phase 3 study: efficacy and tolerability of 140 milligrams once daily and 70 milligrams twice daily. Cancer 2010; 116: 3852–3861.
Giles FJ, Kantarjian HM, le Coutre PD, Baccarani M, Mahon FX, Blakesley RE et al. Nilotinib is effective in imatinib-resistant or -intolerant patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in blastic phase. Leukemia 2012; 26: 959–962.
Gratwohl A, Brand R, Apperley J, Crawley C, Ruutu T, Corradini P et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia in Europe 2006: transplant activity, long-term data and current results. An analysis by the Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Haematologica 2006; 91: 513–521.
Luo Y, Zhao Y, Tan Y, Shi J, Han X, Zheng Y et al. Imatinib combined with myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for advanced phases of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res 2011; 35: 1307–1311.
Saussele S, Lauseker M, Gratwohl A, Beelen DW, Bunjes D, Schwerdtfeger R et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo SCT) for chronic myeloid leukemia in the imatinib era: evaluation of its impact within a subgroup of the randomized German CML Study IV. Blood 2010; 115: 1880–1885.
Menzel H, von Bubnoff N, Hochhaus A, Haferlach C, Peschel C, Duyster J . Successful allogeneic stem cell transplantation in second chronic-phase CML induced by the tyrosine kinase inhibitor nilotinib (AMN107) after blast crisis under imatinib. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 40: 83–84.
Baccarani M, Cortes J, Pane F, Niederwieser D, Saglio G, Apperley J et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia: an update of concepts and management recommendations of European LeukemiaNet. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 6041–6051.
Baccarani M, Deininger MW, Rosti G, Hochhaus A, Soverini S, Apperley JF et al. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013; 122: 872–884.
Vardiman JW, Harris NL, Brunning RD . The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of the myeloid neoplasms. Blood 2002; 100: 2292–2302.
Huang XJ, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Chen H, Han W et al. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without in vitro T-cell depletion for the treatment of hematological malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 38: 291–297.
Huang XJ, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Chen H, Han W et al. Treatment of acute leukemia with unmanipulated HLA-mismatched/haploidentical blood and bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 257–265.
Xiao-Jun H, Lan-Ping X, Kai-Yan L, Dai-Hong L, Yu W, Huan C et al. Partially matched related donor transplantation can achieve outcomes comparable with unrelated donor transplantation for patients with hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 4777–4783.
Lu DP, Dong L, Wu T, Huang XJ, Zhang MJ, Han W et al. Conditioning including antithymocyte globulin followed by unmanipulated HLA-mismatched/haploidentical blood and marrow transplantation can achieve comparable outcomes with HLA-identical sibling transplantation. Blood 2006; 107: 3065–3073.
Xiao-Jun H, Lan-Ping X, Kai-Yan L, Dai-Hong L, Huan C, Wei H et al. HLA-mismatched/haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without in vitro T cell depletion for chronic myeloid leukemia: improved outcomes in patients in accelerated phase and blast crisis phase. Ann Med 2008; 40: 444–455.
Huang XJ, Xu LP, Liu KY, Liu DH, Chen H, Liu YR et al. Individualized intervention guided by BCR-ABL transcript levels after HLA-identical sibling donor transplantation improves HSCT outcomes for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 649–656.
Huang XJ, Liu DH, Liu KY, Xu LP, Chen H, Han W . Donor lymphocyte infusion for the treatment of leukemia relapse after HLA-mismatched/haploidentical T-cell-replete hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 2007; 92: 414–417.
Huang XJ, Wang Y, Liu DH, Xu LP, Chen H, Chen YH et al. Modified donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI) for the prophylaxis of leukemia relapse after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with advanced leukemia—feasibility and safety study. J Clin Immunol 2008; 28: 390–397.
Beillard E, Pallisgaard N, van der Velden VH, Bi W, Dee R, van der Schoot E et al. Evaluation of candidate control genes for diagnosis and residual disease detection in leukemic patients using 'real-time' quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR)—a Europe against cancer program. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2474–2486.
Qin YZ, Liu YR, Zhu HH, Li JL, Ruan GR, Zhang Y et al. Different kinetic patterns of BCR-ABL transcript levels in imatinib-treated chronic myeloid leukemia patients after achieving complete cytogenetic response. Int J Lab Hematol 2008; 30: 317–323.
Qin YZ, Jiang Q, Jiang H, Li JL, Li LD, Zhu HH et al. Which method better evaluates the molecular response in newly diagnosed chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients with imatinib treatment, BCR-ABL(IS) or log reduction from the baseline level? Leuk Res 2013; 37: 1035–1040.
Jiang Q, Xu LP, Liu DH, Liu KY, Chen SS, Jiang B et al. Imatinib mesylate versus allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in the accelerated phase. Blood 2011; 117: 3032–3040.
Cross NC, White HE, Muller MC, Saglio G, Hochhaus A . Standardized definitions of molecular response in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2012; 26: 2172–2175.
Sawyers CL, Hochhaus A, Feldman E, Goldman JM, Miller CB, Ottmann OG et al. Imatinib induces hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in myeloid blast crisis: results of a phase II study. Blood 2002; 99: 3530–3539.
Hehlmann R . How I treat CML blast crisis. Blood 2012; 120: 737–747.
Jabbour E, Kantarjian HM, O'Brien S, Shan J, Quintas-Cardama A, Garcia-Manero G et al. Front-line therapy with second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with early chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia: what is the optimal response? J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 4260–4265.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the contributions of all the people who have participated in this research. This includes our laboratory staff, our colleagues and our nurses. The study was supported by the National Outstanding Young Scientists’ Foundation of China (grant no. 30725038) and by the Program for Innovative Research Team at the University of China (grant no. IRT0702). The study was also supported by the Collaborative Innovation Center of Hematology, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, H., Xu, LP., Liu, DH. et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic SCT in combination with tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment compared with TKI treatment alone in CML blast crisis. Bone Marrow Transplant 49, 1146–1154 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.146
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.146
This article is cited by
-
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia in the TKI era: population-based data from the Swedish CML registry
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2019)
-
The consensus on indications, conditioning regimen, and donor selection of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for hematological diseases in China—recommendations from the Chinese Society of Hematology
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2018)
-
A review of hematopoietic cell transplantation in China: data and trends during 2008–2016
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)
-
Donor type, in addition to transplantation in chronic phase and myeloablative conditioning, influence transplant survival for patients with advanced chronic myeloid leukemia in the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Leukemia (2017)
-
All is not lost in accelerated phase/blast crisis and after tyrosine kinase inhibitors fail in chronic myeloid leukaemia: a retrospective study of allogeneic stem cell transplant outcomes in Australia and New Zealand
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2016)