Abstract
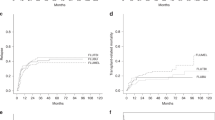
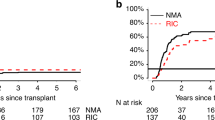
In this study, outcomes for 575 adult ALL patients aged ⩾45 years who underwent first allo-SCT in CR were analyzed according to the type of conditioning regimen (myeloablative conditioning (MAC) for 369 patients vs reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) for 206 patients). Patients in the RIC group were older (median age, 58 vs 51 years, P<0.0001). There were no statistically significant differences in 3-year OS, disease-free survival (DFS) and non-relapse mortality (NRM): 51% vs 53%, 47% vs 39% and 38% vs 36%, respectively. Multivariate analysis showed that CR2 and HLA mismatching were associated with poor OS (P=0.002 and P=0.019, respectively). HLA mismatching was associated with lower rate of relapse (P=0.016), but was associated with higher rate of NRM (P=0.001). RIC was associated with good OS and DFS in patients who received HLA-mismatch transplantation and were aged ⩾55 years compared with MAC by multivariate analysis for each event with interaction (hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval 0.35 and 0.15–0.81, P=0.014 for OS and 0.36 and 0.16–0.81, P=0.013 for DFS). Therefore, patients ⩾55 years of age with HLA-mismatch transplantation should be candidates for RIC rather than MAC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rowe JM, Buck G, Burnett AK, Chopra R, Wiernik PH, Richards SM et al. Induction therapy for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of more than 1500 patients from the international ALL trial: MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993. Blood 2005; 106: 3760–3767.
Hunault M, Harousseau JL, Delain M, Truchan-Graczyk M, Cahn JY, Witz F et al. Better outcome of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia after early genoidentical allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT) than after late high-dose therapy and autologous BMT: a GOELAMS trial. Blood 2004; 104: 3028–3037.
Thomas X, Boiron JM, Huguet F, Dombret H, Bradstock K, Vey N et al. Outcome of treatment in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: analysis of the LALA-94 trial. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 4075–4086.
Goldstone AH, Richards SM, Lazarus HM, Tallman MS, Buck G, Fielding AK et al. In adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the greatest benefit is achieved from a matched sibling allogeneic transplantation in first complete remission, and an autologous transplantation is less effective than conventional consolidation/maintenance chemotherapy in all patients: final results of the International ALL Trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993). Blood 2008; 111: 1827–1833.
Cornelissen JJ, van der Holt B, Verhoef GE, van't Veer MB, van Oers MH, Schouten HC et al. Myeloablative allogeneic versus autologous stem cell transplantation in adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first remission: a prospective sibling donor versus no-donor comparison. Blood 2009; 113: 1375–1382.
Tomblyn MB, Arora M, Baker KS, Blazar BR, Brunstein CG, Burns LJ et al. Myeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: analysis of graft sources and long-term outcome. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 3634–3641.
Marks DI, Pérez WS, He W, Zhang MJ, Bishop MR, Bolwell BJ et al. Unrelated donor transplants in adults with Philadelphia-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission. Blood 2008; 112: 426–434.
Fielding AK, Richards SM, Chopra R, Lazarus HM, Litzow MR, Buck G et al. Outcome of 609 adults after relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL); an MRC UKALL12/ECOG 2993 study. Blood 2007; 109: 944–950.
Bishop MR, Logan BR, Gandham S, Bolwell BJ, Cahn JY, Lazarus HM et al. Long-term outcomes of adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after autologous or unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation: a comparative analysis by the National Marrow Donor Program and Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 41: 635–642.
Marks DI, Forman SJ, Blume KG, Pérez WS, Weisdorf DJ, Keating A et al. A comparison of cyclophosphamide and total body irradiation with etoposide and total body irradiation as conditioning regimens for patients undergoing sibling allografting for acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first or second complete remission. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 438–453.
Marks DI, Aversa F, Lazarus HM . Alternative donor transplants for adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a comparison of the three major options. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 38: 467–475.
Toubai T, Tanaka J, Mori A, Hashino S, Kobayashi S, Ota S et al. Efficacy of etoposide, cyclophosphamide, and total body irradiation in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for adult patients with hematological malignancies. Clin Transplant 2004; 18: 552–557.
Shigematsu A, Kondo T, Yamamoto S, Sugita J, Onozawa M, Kahata K et al. Excellent outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using a conditioning regimen with medium-dose VP-16, cyclophosphamide and total-body irradiation for adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 568–575.
Mohty M, Labopin M, Tabrizzi R, Theorin N, Fauser AA, Rambaldi A et al. Reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a retrospective study from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica 2008; 93: 303–306.
Bachanova V, Verneris MR, DeFor T, Brunstein CG, Weisdorf DJ . Prolonged survival in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after reduced-intensity conditioning with cord blood or sibling donor transplantation. Blood 2009; 113: 2902–2905.
Stein AS, Palmer JM, O'Donnell MR, Kogut NM, Spielberger RT, Slovak ML et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning followed by peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for adult patients with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 1407–1414.
Cho BS, Lee S, Kim YJ, Chung NG, Eom KS, Kim HJ et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation is a potential therapeutic approach for adults with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia in remission: results of a prospective phase 2 study. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1763–1770.
Marks DI, Wang T, Pérez WS, Antin JH, Copelan E, Gale RP et al. The outcome of full-intensity and reduced-intensity conditioning matched sibling or unrelated donor transplantation in adults with Philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first and second complete remission. Blood 2010; 116: 366–374.
Mohty M, Labopin M, Volin L, Gratwohl A, Socié G, Esteve J et al. Reduced-intensity versus conventional myeloablative conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a retrospective study from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood 2010; 116: 4439–4443.
Kim SW, Matsuo K, Fukuda T, Hara M, Matsue K, Taniguchi S et al. Reduced-intensity unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for hematologic malignancies. Int J Hematol 2008; 88: 324–330.
Giralt S, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Bacigalupo A, Horowitz M, Pasquini M et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning regimen workshop: defining the dose spectrum. Report of a workshop convened by the center for international blood and marrow transplant research. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 367–369.
Pepe MS, Mori M . Kaplan-Meier, marginal or conditional probability curves in summarizing competing risks failure time data? Stat Med 1993; 12: 737–751.
Fine JP, Gray RJ . A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc 1999; 94: 496–509.
Martino R, Iacobelli S, Brand R, Jansen T, van Biezen A, Finke J et al. Retrospective comparison of reduced-intensity conditioning and conventional high-dose conditioning for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using HLA-identical sibling donors in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2006; 108: 836–846.
Shimoni A, Hardan I, Shem-Tov N, Yeshurun M, Yerushalmi R, Avigdor A et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in AML and MDS using myeloablative versus reduced-intensity conditioning: the role of dose intensity. Leukemia 2006; 20: 322–328.
Ram R, Storb R, Sandmaier BM, Maloney DG, Woolfrey A, Flowers ME et al. Non-myeloablative conditioning with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for the treatment of high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2011; 96: 1113–1120.
Lee JH, Joo YD, Kim H, Ryoo HM, Kim MK, Lee GW et al. Randomized trial of myeloablative conditioning regimens: busulfan plus cyclophosphamide versus busulfan plus fludarabine. J Clin Oncol 2013 20 31: 701–709.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan and a Japanese Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Author Contributions
JT and NM designed the study and prepared the manuscript; NN and KO performed the statistical analysis; SN, KO, ST, TE, HN, Ke M, Ko M, HS, YM, KK and RS participated in interpretation of data and approval of the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, J., Kanamori, H., Nishiwaki, S. et al. Reduced-intensity vs myeloablative conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic SCT for patients aged over 45 years with ALL in remission: a study from the Adult ALL Working Group of the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (JSHCT). Bone Marrow Transplant 48, 1389–1394 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.68
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.68
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Thiotepa, busulfan and fludarabine conditioning-regimen is a promising approach for older adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)
-
Retrospective institutional analysis of fludarabine/8 Gy TBI reduced intensity conditioning in high risk ALL
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
Reduced-intensity conditioning is a reasonable alternative for Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia among elderly patients who have achieved negative minimal residual disease: a report from the Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Working Group of the JSHCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
Comparison of reduced-intensity conditioning regimens in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia >45 years undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation—a retrospective study by the Acute Leukemia Working Party of EBMT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
Reduced intensity vs. myeloablative conditioning with fludarabine and PK-guided busulfan in allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients with AML/MDS
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2019)