Abstract
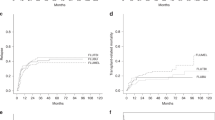
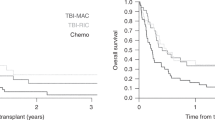
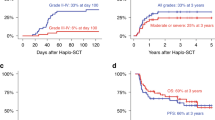
We retrospectively assessed the outcome and pretransplantation predictors of the outcome in 118 patients aged ⩾50 years who received fludarabine-containing reduced-intensity allo-SCT (RIST) for B-cell ALL in the first or second CR. Eighty patients received transplants from unrelated donors. Seventy-eight patients were positive for the Ph chromosome. The median follow-up period was 18 months and the 2-year OS rate was 56%. The 2-year cumulative incidence of relapse and non-relapse mortality was 28% and 26%, respectively. The incidence of grades II–IV and III–IV acute GVHD was 46% and 24%, respectively. After 2 years, the incidence of chronic GVHD was 37%. Multivariate analysis of pretransplant factors showed that a higher white blood cell count (⩾30 × 109/L) at diagnosis (hazard ratio (HR)=2.19, P=0.007) and second CR (HR=2.02, P=0.036) were significantly associated with worse OS, whereas second CR (HR=3.83, P<0.001) and related donor (HR=2.34, P=0.039) were associated with a higher incidence of relapse. Fludarabine-containing RIST may be a promising strategy for older patients with B-cell ALL in their first remission.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
04 December 2013
This article has been corrected since Advance Online Publication and an erratum is also printed in this issue.
References
Kantarjian HM, O’Brien S, Smith TL, Cortes J, Giles FJ, Beran M et al. Results of treatment with hyper-CVAD, a dose-intensive regimen, in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 547–561.
Larson RA, Dodge RK, Burns CP, Lee EJ, Stone RM, Schulman P et al. A five-drug remission induction regimen with intensive consolidation for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: cancer and leukemia group B study 8811. Blood 1995; 85: 2025–2037.
Rowe JM, Buck G, Burnett AK, Chopra R, Wiernik PH, Richards SM et al. Induction therapy for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of more than 1500 patients from the international ALL trial: MRC UKALLXII/ECOG E2993. Blood 2005; 106: 3760–3767.
Goldstone AH, Richards SM, Lazarus HM, Tallman MS, Buck G, Fielding AK et al. In adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the greatest benefit is achieved from a matched sibling allogeneic transplantation in first complete remission, and an autologous transplantation is less effective than conventional consolidation/maintenance chemotherapy in all patients: final results of the International ALL Trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993). Blood 2008; 111: 1827–1833.
Arnold R, Massenkeil G, Bornhäuser M, Ehninger G, Beelen DW, Fauser AA et al. Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation in adults with high-risk ALL may be effective in early but not in advanced disease. Leukemia 2002; 16: 2423–2428.
Martino R, Giralt S, Caballero MD, Mackinnon S, Corradini P, Fernández-Avilés F et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a feasibility study. Haematologica 2003; 88: 555–560.
Mohty M, Labopin M, Tabrizzi R, Theorin N, Fauser AA, Rambaldi A et al. Reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a retrospective study from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica 2008; 93: 303–306.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Sullivan KM, Agura E, Anasetti C, Appelbaum F, Badger C, Bearman S et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease and other late complications of bone marrow transplantation. Semin Hematol 1991; 28: 250–259.
Giralt S, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Bacigalupo A, Horowitz M, Pasquini M et al. Reduced intensity conditioning regimen workshop: defining the dose spectrum. Report of a workshop convened by the center for international blood and marrow transplant research. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 367–369.
Gray RJ . A class of k-sample tests for comparing the cumulative incidence of a competing risk. Ann Stat 1988; 16: 1141–1154.
Fine JP, Gray RJ . A propotional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc 1999; 94: 496–509.
Kanda Y . Investigation of the freely-available easy-to-use software ‘EZR (Easy R) for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 452–458.
Marks DI, Wang T, Pérez WS, Antin JH, Copelan E, Gale RP et al. The outcome of full-intensity and reduced-intensity conditioning matched sibling or unrelated donor transplantation in adults with Philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first and second complete remission. Blood 2010; 116: 366–374.
Mohty M, Labopin M, Volin L, Gratwohl A, Socié G, Esteve J et al. Reduced-intensity versus conventional myeloablative conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a retrospective study from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood 2010; 116: 4439–4443.
Cho BS, Lee S, Kim YJ, Chung NG, Eom KS, Kim HJ et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation is a potential therapeutic approach for adults with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia in remission: result of a prospective phase 2 study. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1763–1770.
Rowe JM . Prognostic factors in adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2010; 150: 389–405.
Faderl S, Jeha S, Kantarjian HM . The biology and therapy of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 2003; 98: 1337–1354.
Yanada M, Takeuchi J, Sugiura I, Akiyama H, Usui N, Yagasaki F et al. High complete remission rate and promising outcome by combination of imatinib and chemotherapy for newly diagnosed BCR-ABL-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a phase II study by the Japan Adult Leukemia Study Group. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 460–466.
Bachanova V, Verneris MR, DeFor T, Brunstein CG, Weisdorf DJ, Vermeris MR . Prolonged survival in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after reduced-intensity conditioning with cord blood or sibling donor transplantation. Blood 2009; 113: 2902–2905.
Acknowledgements
We thank all of the staff from the participating institutions of the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for their assistance and cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Author contributions
HK (Kanamori) designed the study, analyzed the data and wrote the draft version of this manuscript. HN, MT, KI, TY, TF, KM and TE submitted and cleaned the data; T-NI, YM, RS and HS collected and reviewed the data; And SM, SK, HK (Kato), SN, KI, AS and JT interpreted the results and critically revised the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanamori, H., Mizuta, S., Kako, S. et al. Reduced-intensity allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients aged 50 years or older with B-cell ALL in remission: a retrospective study by the Adult ALL Working Group of the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 48, 1513–1518 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.140
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.140
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Newly proposed threshold and validation of white blood cell count at diagnosis for Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: risk assessment of relapse in patients with negative minimal residual disease at transplantation—a report from the Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Working Group of the JSTCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Reduced-intensity conditioning is a reasonable alternative for Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia among elderly patients who have achieved negative minimal residual disease: a report from the Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Working Group of the JSHCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)