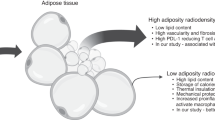
Abstract
Obesity, increasing worldwide, is common in patients undergoing hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). This complex physiological state may alter the outcome of cancer therapies by many mechanisms including direct effects on pathogenesis, host responses to disease and altered pharmacology of chemotherapy. Obesity has been associated with multiple adverse health outcomes. Reports of obese patients undergoing HCT are challenging to interpret because of the heterogeneity of obesity definitions, underlying diseases, graft sources and chemotherapy regimens employed. Compared with normal-weight patients, it appears that obese patients undergoing allogeneic HCT have a higher risk of non-relapse mortality and inferior survival whereas those receiving autologous HCT appear to have equivalent outcomes. These findings are also difficult to interpret because there is no consistent standard for calculating chemotherapy dose in this group and future studies on specific regimens in this population are urgently needed. Patients who have undergone bariatric surgery may be at risk for unexpected events because of impaired nutritional state and altered pharmacokinetics of oral drugs. We recommend that future studies utilize more consistent and biologically relevant definitions of obesity and that the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of specific conditioning regimens be studied. Until more evidence is available, a rationale is presented for dosing based on adjusted body weight. Moreover, recommendations are provided to guide future research efforts based on more definitive measurements of body fat and its distribution available through modern quantitative imaging techniques using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry or magnetic resonance imaging scanning.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL . Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA 2002; 288: 1723–1727.
Finkelstein EA, Khavjou OA, Thompson H, Trogdon JG, Pan L, Sherry B et al. Obesity and severe obesity forecasts through 2030. Am J Prev Med 2012; 42: 563–570.
Allison DB, Fontaine KR, Manson JE, Stevens J, VanItallie TB . Annual deaths attributable to obesity in the United States. JAMA 1999; 282: 1530–1538.
Calle EE, Thun MJ, Petrelli JM, Rodriguez C, Heath CW . Body-mass index and mortality in a prospective cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 1097–1105.
Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ . Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1625–1638.
Chiu BC, Gapstur SM, Greenland P, Wang R, Dyer A . Body mass index, abnormal glucose metabolism, and mortality from hematopoietic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2006; 15: 2348–2354.
Engeland A, Tretli S, Hansen S, Bjorge T . Height and body mass index and risk of lymphohematopoietic malignancies in two million Norwegian men and women. Am J Epidemiol 2007; 165: 44–52.
Merchav S . The haematopoietic effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 1998; 11: 677–685.
Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, Heller RF, Zwahlen M . Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studiess. Lancet 2008; 371: 569–578.
Birmann BM, Giovannucci E, Rosner B, Anderson KC, Colditz GA . Body mass index, physical activity, and risk of multiple myeloma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2007; 16: 1474–1478.
Friedman GD, Herrinton LJ . Obesity and multiple myeloma. Cancer Causes Control 1994; 5: 479–483.
Navaro WH, Loberiza Jr FR . The impact of obesity on stem cell transplant. In: Mittelman SD, Berger NA (ed.) Energy Balance and Hematologic Malignancies. Springer: New York, 2012, pp 129–140.
Wyatt SB, Winters KP, Dubbert PM . Overweight and obesity: prevalence, consequences, and causes of a growing public health problem. Am J Med Sci 2006; 331: 166–174.
Storfer-Isser A, Patel SR, Babineau DC, Redline S . Relation between sleep duration and BMI varies by age and sex in youth age 8-19. Pediatr Obes 2012; 7: 53–64.
Tchoukalova YD, Koutsari C, Karpyak MV, Votruba SB, Wendland E, Jensen MD . Subcutaneous adipocyte size and body fat distribution. Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 87: 56–63.
Mundi MS, Karyak MV, Koutsari C, Votruba SB, O'Brien PC, Jensen MD . Body fat distribution, adipocyte size, and metabolic characteristics of nondiabetic adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 95: 67–73.
Calle EE, Kaaks R . Overweight, obesity and cancer: epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 579–591.
Han J, Koh YJ, Moon HR, Ryoo HG, Cho CH, Kim I et al. Adipose tissue is an extramedullary reservoir for functional hematopoeietic stem and progenitor cells. Blood 2010; 115: 957–964.
Cousin B, Andre M, Arnaud E, Penicaud L, Casteilla L . Reconstitution of lethally irradiated mice by cells isolated from adipose tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 301: 1016–1022.
Horng T, Hotamisligil GS . Linking the inflammasome to obesity-related disease. Nat Med 2011; 17: 164–165.
Vanadanmagasar B, Ravussin A, Gimble JM, Greenway F, Stephens JM, Mynatt RL et al. Obesity increase the production of proinflammatory mediators in adipose tissue T cells and compromises TCR repertoire diversity: implications for systemic inflammation and insulin resistance. J Immunol 2010; 185: 1836–1845.
Feurer ML, Herrero D, Cipoletta A, Naaz J, Wong A, Nayer J et al. Lean but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T-cells that affect metabolic parameters. Nat Med 2009; 15: 930–939.
Villaret A, Galitzky J, Decaunes P, Estéve D, Marques MA, Sengenés C et al. Adipose tissue endothelial cells from obese human subjects: differences among depots in angiogenic, metabolic, and inflammatory gene expression and cellular senescence. Diabetes 2010; 59: 2755–2763.
Ali AH, Koutsari C, Mundi M, Stegall MD, Heimbach JK, Taler SJ et al. Free fatty acid storage in human visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue: role of adipocyte proteins. Diabetes 2011; 60: 2300–2307.
McTernan PG, Anderson LA, Anwar AJ, Eggo MC, Crocker J, Barnett AH et al. Glucocorticoid regulation of p450 aromatase activity in human adipose tissue: gender and site differences. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 1327–1336.
Gimble JM . The function of adipocytes in the bone marrow stroma. New Biol 1990; 2: 304–3012.
Behan JW, Yun JP, Proektor MP, Ehsanipour EA, Arutyunyan A, Moses AS et al. Adipocytes impair leukemia treatment in mice. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 7867–7874.
World Cancer Research Fund and American Institute for Cancer Research. Determinants of weight gain, overweight, and obesity. Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity and the Prevention of Cancer: A Global Perspective. AICR: Washington DC, 2007, pp 322–341.
Wen CP, vid Cheng GY, Tsay SP, Chan HT, Hsu HL, Hsu CC et al. Are Asians at greater mortality risks for being overweight than Caucasians? Redefining obesity for Asians. Public Health Nutr 2009; 12: 497–506.
Despres JP, Lemieux I . Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 2006; 444: 881–885.
Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Ross R . Body mass index, waist circumference, and health risk: evidence in support of current National Institutes of Health guidelines. Arch Intern Med 2002; 162: 2074–2079.
World Health Organization. International Association for the Study of Obesity and International Obesity Task Force. The Asia-Pacific Perspective: Redefining Obesity and its Treatment. Health Communications: Geneva, 2000.
Perissinotto E, Pisent C, Sergi G, Grigoletto F, ILSA Working Group. (Italian Longitudinal Study on Ageing). Anthropometric measurements in the elderly: age and gender differences. Br J Nutr 2002; 87: 177–186.
Kullberg J, Brandberg J, Angelhed JE, Frimmel H, Bergelin E, Strid L et al. Whole-body adipose tissue analysis: comparison of MRI, CT and dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. Br J Radiol 2009; 82: 123–130.
Müller HP, Raudies F, Unrath A, Neumann H, Ludolph AC, Kassubek J . Quantification of human body fat tissue percentage by MRI. NMR Biomed 2011; 24: 17–24.
Nock N, Berger NA . Obesity and Cancer, Overview of Mechanisms. In: Berger NA (ed). Energy Balance and Cancer. Springer: New York, 2010, pp 129–179.
Hursting SD, Berger NA . Energy balance, host-related factors, and cancer progression. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 4058–4065.
Pollak M . Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 915–928.
Renehan AG, Frystyk J, Flyvbjerg A . Obesity and cancer risk: the role of the insulin-IGF axis. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2006; 17: 328–336.
Foster KG, Fingar DC . Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): Conducting the cellular signaling symphony. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 14071–14076.
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 1996; 334: 292–295.
Gil-Campos M, Canete RR, Gil A. . Adiponectin the missing link in insulin resistance and obesity. Clin Nutr 2004; 23: 963–974.
Vona-Davis L, Rose DP . Adipokines as endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine factors in breast cancer risk and progression. Endocr Relat Cancer 2007; 14: 189–206.
Cirillo D, Rachiglio AM, la Montagna R, Giordano A, Normanno N . Leptin signaling in breast cancer: an overview. J Cell Biochem 2008; 105: 956–64.
Saxena NK, Taliaferro-Smith L, Knight BB, Merlin D, Anania FA, O’Regan RM et al. Bidirectional crosstalk between leptin and insulin-like growth factor -1 signaling promotes invasion and migration of breast cancer cells via transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 9712–9722.
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, Tsuchida A, Yokomizo T, Kita S et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003; 423: 762–769.
Cong L, Gasser J, Zhao J, Yang B, Li F, Zhao AZ . Human adiponectin inhibits cell growth and induced apoptosis in human endometrial carcinoma cells, HEC-1-A and RL95-2. Endocr Relat Cancer 2007; 14: 713–720.
Chen PM, Kwan SH, Hwang TS, Chou CK . Insulin receptors on leukemia and lymphoma cells. Blood 1983; 62: 251–255.
Saiya-Cork K, Collins R, Parkin B, Ouillette P, Kuizon E, Kujawski L et al. A pathobiological role of the insulin receptor in chronic lymphocitic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 2679–2692.
Shimon I, Shpilberg O . The insulin-like growth factor system in regulation of normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Leuk Res 1995; 19: 233–240.
Tamurini J, Chapois N, Bardet V, Park S, Sujorber P, Willems L et al. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibition activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt by up-regulating insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling in acute myeloid leukemia: rationale for therapeutic inhibition of both pathways. Blood 2008; 111: 379–382.
Chapuis N, Tamourini J, Cornillet-Lefebvre P, Gillot L, Bardet V, Willems L et al. Autocrine IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling is responsible for constitutive PI2K/Akt activation in acute myeloid leukemia: therapeutic value of neutralizing anti IGF-1R antibody. Haematologia 2010; 95: 415–423.
Ozturk K, Avcu F, Ural AU . Aberrant expressions of leptin and adiponectin receptor isoforms in chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Cytokine 2012; 57: 61–67.
Nakao T, Hino M, Yamane T, Nishizawa Y, Morii H, Tatsumi N . Expression of the leptin receptor in human leukaemic blast cells. Br J Haematol 1998; 102: 740–745.
Konopleva M, Mikhail A, Estrov Z, Zhao S, Harris D, Sanchez-Williams G et al. Expression and function of leptin receptor isoforms in myeloid leukemia and myelodysplasticsydromes: proliferative and anti-apoptotic activities. Blood 1999; 93: 1668–1676.
Bruserud Ø, Huang T-S, Glenjen N, Gjertsen BT, Foss B . Leptin in human acute myelogenous leukemia: studies of in vivo levels and in vitro effects on native functional leukemic blasts. Haematologica 2002; 87: 584–595.
Martelli AM, Tazzari PL, Tabellini G, Bortul R, Billi AM, Manzoli L et al. A new selective AKT pharmacological inhibitor reduces resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs, TRAIL, all-trans-retinoic acid, and ionizing radiation of human leukemia cells. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1794–1805.
Yu C, Mao X, Li WX . Inhibition of the PI3K pathway sensitizes fludarabine-induced apoptosis in human leukemic cells through an inactivation of MAPK-dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 331: 391–397.
Wong KK, Engelman JA, Cantley LC . Targeting the P13K signaling pathway in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2010; 20: 87–90.
Brown LM, Gridley G, Pottern LM, Baris D, Swanso CA, Silverman DT et al. Diet and nutrition as risk factors for multiple myeloma among blacks and whites in the United States. Cancer Causes Control 2001; 12: 117–125.
Landgren O, Rajkumar SV, Pfeiffer RM, Kyle RA, Katzmann JA, Dispenzieri A et al. Obesity is associated with an increased risk of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance among black and white women. Blood 2010; 116: 1056–1059.
Eder BN, Falus A, Fuloop A . The major inflammatory mediator interleukin-6 and obesity. Inflamm Res 2009; 58: 727–736.
Zhang XG, Kelin B, Balaille R . Interleukin-6 is a potent myeloma-cell growth factor in patients with aggressive multiple myeloma. Blood 1989; 74: 11–13.
Wrighting DM, Andrews NC . Interleukin-6 induces hepcidin expression through STAT3. Blood 2006; 108: 3204–3209.
Sprynski AC, Hose D, Kassambara A, Vincent L, Jourdan M, Rossi JF et al. Insulin is a potent myeloma cell growth factor through insulin/IGF-1 hybrid receptor activation. Leukemia 2010; 24: 1940–1950.
Reseland JE, Reppe S, Olstad OK, Hjorth-Hansen H, Brenne AT, Sylersen U et al. Abnormal adipokine levels and leptin-induced changes in gene expression profiles in multiple myeloma. Eur J Haematol 2009; 83: 460–470.
Barb D, Williams CJ, Neuwirth AK, Mantzoros CS . Adiponectin in relation to malignancies: a review of existing basic research and clinical evidence. Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 86 (suppl): 858S–866S.
Fowler JA, Lwin ST, Drake MT, Edwards JR, Kyle RB, Mundy GR et al. Host-derived adiponectin is tumor-suppressive and a novel therapeutic target for multiple myeloma and the associated bone disease. Blood 2011; 118: 5872–5882.
Blouin RA, Kolpek JH, Mann HJ . Influence of obesity on drug disposition. Clin Pharm 1987; 6: 706–714.
Tisdale MJ . Mechanisms of cancer cachexia. Physiol Rev 2009; 89: 381–410.
Clarke B, Engler H . Patients with morbid obesity don't get life-saving bone marrow transplants. Obes Surg 1999; 9: 77–79.
Field KM, Kosmider S, Jefford M, Michael M, Jennens R, Green M et al. Chemotherapy dosing strategies in the obese, elderly, and thin patient: results of a nationwide survey. J Oncol Pract 2008; 4: 108–113.
Grigg A, Harun MH, Szer J . Variability in determination of body weight used for dosing busulphan and cyclophosphamide in adult patients: results of an international survey. Leuk Lymphoma 1997; 25: 487–491.
Fuji S, Kim SW, Yoshimura K, Akiyama H, Okamoto S, Sao H et al. Possible association between obesity and posttransplantation complications including infectious diseases and acute graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 73–82.
Fleming DR, Rayens MK, Garrison J . Impact of obesity on allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant cell transplant patients: a matched case-controlled study. Am J Med 1997; 102: 265–268.
Hansen JA, Gooley TA, Martin PJ, Appelbaum F, Chauncey TR, Clift RA et al. Bone marrow transplants from unrelated donors for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 962–968.
Sriharsha L, Lipton JH, Pond G, Ma C, Raybardhan S, Messner HA et al. Examining the safety and efficacy of a chemotherapy dosing method in allogeneic stem cell transplant patients of extreme body size. J Oncol Pharm Pract 2009; 15: 201–210.
Navarro WH, Agovi MA, Logan BR, Ballen K, Bolwell BJ, Frangoul H et al. Obesity does not preclude safe and effective myeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) for acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) in adults. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010; 16: 1442–1450.
Nikolousis E, Nagra S, Paneesha S, Delgado J, Holder K, Bratby L et al. Allogeneic transplant outcomes are not affected by body mass index (BMI) in patients with haematological malignancies. Ann Hematol 2010; 89: 1141–1145.
Barker CC, Agovi MA, Logan B, Lazarus HM, Ballen KK, Gupta V et al. Childhood obesity and outcomes after bone marrow transplantation for patients with severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 737–744.
Dickson TM, Kusnierz-Glaz CR, Blume KG, Negrin RS, Hu WW, Shizuru JA et al. Impact of admission body weight and chemotherapy dose adjustment on the outcome of autologous bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 1999; 5: 299–305.
Meloni G, Proia A, Capria S, Romano A, Trapé G, Trisolini SM et al. Obesity and autologous hematopoietic cell transplant cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 365–367.
Tarella C, Caracciolo D, Gavarotti P, Argentino C, Zallio F, Corradini P et al. Overweight as an adverse prognostic factor for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma patients receiving high-dose chemotherapy and autograft. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26: 1185–1191.
Navarro WH, Loberiza FR, Bajorunaite R, van Besien K, Vose JM, Lazarus HM et al. Effect of body mass index on mortality of patients with lymphoma undergoing autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 541–551.
Vogl DT, Wang T, Perez WS, Stadtamauer EA, Heitjan DF, Lazarus HM et al. Effect of obesity on outcomes after autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 1765–1774.
Griggs JJ, Mangu PB, Anderson H, Balaban EP, Dignam JJ, Hryniuk WM et al. Appropriate chemotherapy dosing for obese adult patients with cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 1553–1561.
Powis G, Reece P, Ahmann DL, Ingle JN . Effect of bodyweight on the pharmacokinetics of cyclophosphamide in breast cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1987; 20: 219–222.
Lind MJ, Margison JM, Cerny T, Thatcher N, Wilkinson PM . Prolongation of ifosfamide elimination half-life in obese patients due to altered drug distrubution. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1989; 25: 139–142.
Gibbs JP, Gooley T, Corneau B, Murray G, Stewart P, Appelbaum FR et al. The impact of obesity and disease on busulfan oral clearance in adults. Blood 1999; 93: 4436–4440.
Rodvold KA, Rushing DA, Tewksbury DA . Doxorubicin clearance in the obese. J Clin Oncol 1988; 6: 1321–1327.
Whiteman MK, Hillis SD, Curtis KM, McDonald JA, Wingo PA, Marchbanks PA . Body mass and mortality after breast cancer diagnosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2005; 14: 2009–2014.
Rosner GL, Hargis JB, Hollis DR, Budman DR, Weiss RB, Henderson IC et al. Relationship between toxicity and obesity in women receiving adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: Results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study 8541. J Clin Oncol 1996; 14: 3000–3008.
Poikonen P, Blomqvist C, Joensuu H . Effect of obesity on the leukocyte nadir in women treated with adjuvant cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil dosed according to body surface area. Acta Oncol 2001; 40: 67–71.
Loi S, Milne RL, Friedlander ML, McCredie MR, Giles GG, Hopper JL et al. Obesity and outcomes in premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2005; 14: 1686–1691.
Kroenke CH, Chen WY, Rosner B, Holmes MD . Weight, weight gain, and survival after breast cancer diagnosis. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 1370–1378.
Griggs JJ, Sorbero MES, Lyman GH . Undertreatment of obese women receiving breast cancer chemotherapy. Arch Intern Med 2005; 165: 1267–1273.
Findlay B, Myles J, Levine M, Bramwell V, Pritchard K, Ottoway J . Using ideal vs. actual weights to calculate chemotherapy doses in premenopausal women with stage 2 breast cancer (abstract #63). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 1994; 12.
Bastarrachea J, Hortobagyi GN, Smith TL, Kau SW, Buzdar AU . Obesity as an adverse prognostic factor for patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Ann Intern Med 1994; 120: 18–25.
Berclaz G, Li S, Price KN, Coates AS, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Rudenstam CM et al. Body mass index as a prognostic feature in operable breast cancer: the International Breast Cancer Study Group experience. Ann Oncol 2004; 15: 875–884.
Meyerhardt JA, Tepper JE, Niedzwiecki D, Hollis DR, McCollum AD, Brady D et al. Impact of body mass index on outcomes and treatment-related toxicity in patients with stage II and III rectal cancer: Findings from Intergroup Trial 0114. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 648–657.
Meyerhardt JA, Catalano PJ, Haller DG, Mayer RJ, Benson AB, Macdonald JS et al. Influence of body mass index on outcomes and treatment-related toxicity in patients with colon carcinoma. Cancer 2003; 98: 484–495.
Georgiadis MS, Steinberg SM, Hankins LA, Ihde DC, Johnson BE . Obesity and therapy-related toxicity in patients treated for small-cell lung cancer. JNCI 1995; 87: 361–366.
Medeiros BC, Othus M, Estey E, Fang M, Appelbaum FR . Impact of body-mass index on the outcome of adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2012; 97: 1401–1404.
Vogl DT, Stoopler E, Davis L, Paul TM, Salazar G, Raguza-Lopez M et al. Effect of pharmacokinetic variability on the toxicity and efficacy of high-dose melphalan for multiple myeloma (abstract #1349). Blood 2010; 116 (suppl)).
Vogl DT, Paul TM, Stoopler E, Salazar G, Davis L, Kapoor S et al. Effect of obesity and renal insufficiency on toxicity of high-dose melphalan for multiple myeloma (abstract #1177). Blood 2009; 114 (suppl).
Vogl DT, Mick R, Stoopler E, Davis LE, Paul TM, Salazar G et al. Effect of body composition and renal function on the pharmacokinetics of high-dose melphalan for multiple myeloma (abstract #S248). Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18 (suppl)).
Millar JA . The Cockroft and Gault formula for estimation of creatinine clearance: a friendly deconstruction. NZ Med J 2012; 125: 119–122.
Taylor K . Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery 2011. http://s3.amazonaws.com/publicASMBS/MediaPressKit/MetabolicBariatricSurgeryOverviewJuly2011.pdf.
Sjöström L, Gummesson A, Sjöström CD, Narbro K, Peltonen M, Wedel H et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on cancer incidence in obese patients in Sweden (Swedish Obese Subjects Study): a prospective, controlled intervention trial. Lancet Oncol 2009; 10: 653–662.
Adams TD, Hunt SC . Cancer and obesity: effect of bariatric surgery. World J Surg 2009; 33: 2028–2033.
Darwich AS, Pade D, Ammori BJ, Jamei M, Ashcroft DM, Rostami-Hodjegan A . Amechanistic pharmacokinetic model to assess modified oral drug bioavailabilitypost bariatric surgery in morbidly obese patients: interplay between CYP3A gutwall metabolism, permeability and dissolution. J Pharm Pharmacol 2012; 64: 1008–1024.
Rogers CC, Alloway RR, Alexander JW, Cardi M, Trofe J, Vinks AA . Pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid, tacrolimus and sirolimus after gastricbypass surgery in end-stage renal disease and transplant patients: a pilot study. Clin Transplant 2008; 22: 281–291.
Fong T, Vij R, Vijayan A, DiPersio J, Blinder M . Copper deficiency: animportant consideration in the differential diagnosis of myelodysplasticsyndrome. Haematologica 2007; 92: 1429–1430.
Badros A, Goloubeva O, Terpos E . Prevalence and significance of vitamin D deficiency in multiple myeloma patients. Br J Haematol 2008; 142: 492–494.
Ng AC, Sk Kumar, Rajkumar SV, Drake MT . Impact of vitamin D deficiency on the clinical presentation and prognosis of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients. Am J Hematol 2009; 84: 397–400.
Soares-Miranda L, Fiuza-Luces C, Lucia A . Physical activity and recovery from hematological malignancy. In: Mittelman SD, Berger NA (ed). Energy Balance and Hematologic Malignancies. Springer: New York, 2012, pp 159–175.
Dimeo F, Schwartz S, Fietz T, Wanjura T, Boning D, Thiel E . Effects of endurance training on the physical performance of patients with hematological malignancies during chemotherapy. Support Care Cancer 2003; 11: 623–628.
DeFor TE, Burns LJ, Gold EM, Weisdorf DJ . A randomized trial of the effect of a walking regimen on the functional status of 100 adult allogeneic donor hematopoietic cell transplant patients. Biol Blood Marrow Translplant 2007; 13: 948–955.
Wiskemann J, Dreger P, Schwerdtfeger R, Bondong A, Huber G, Kleindienst N et al. Effects of a partly self-administered exercise program before, during, and after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2011; 117: 2604–2613.
Hayes S, Davies PS, Parker T, Bashford J . Total energy expenditure and body composition changes following peripheral blood stem cell transplantation and participation in an exercise programme. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 31: 331–338.
Dimeo F, Bertz H, FInke J, Fetscher S, Mertelsmann R, Keul J . An aerobic exercise program for patients with haematological malignancies after bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 18: 1157–1160.
Mello M, Tanaka C, Dulley FL . Effects of an exercise program on muscle performance in patients undergoing allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 32: 723–728.
Hayes S, Davies PS, Parker T, Bashford J, Newman B . Quality of life changes following peripheral blood stem cell transplantation and participation in a mixed-type, moderate-intensity, exercise program. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 553–558.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported, in part, by the Transdisciplinary Research on Energetics and Cancer grants no. U54 CA116867 to NAB; and P20 103736 from the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiss, B., Vogl, D., Berger, N. et al. Trimming the fat: obesity and hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 48, 1152–1160 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.201
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.201
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The impact of pre-transplantation diabetes and obesity on acute graft-versus-host disease, relapse and death after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a study from the EBMT Transplant Complications Working Party
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2024)
-
Role for Leptin and Leptin Receptors in Stem Cells During Health and Diseases
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2021)
-
Pretransplant body mass index on outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
Pharmacokinetic and clinical outcomes when ideal body weight is used to dose busulfan in obese hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2019)
-
Bone marrow lympho-myeloid malfunction in obesity requires precursor cell-autonomous TLR4
Nature Communications (2018)