Abstract
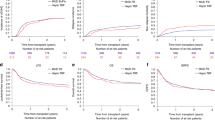
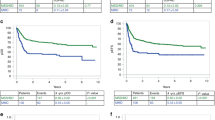
Cell dose is one of the major factors that can be manipulated in unrelated BMT. However, regarding disease-stage-stratified effects of cell dose, data are limited. We analyzed the registry data from 3559 patients with acute leukemia, CML and myelodysplastic syndrome who received T-cell replete unrelated BMT through the Japan Marrow Donor Program. Adjusted effects of cell dose were evaluated for various outcomes separately according to disease stages and children or adults. Acute GVHD and nonrelapse mortality were not affected by cell dose. Among children, a cell dose lower than 3.0 × 108/kg was associated with lower engraftment rates in advanced-stage diseases. Among adults, a cell dose of 3.4 × 108/kg or higher was associated with lower relapse rates and better survival rates only in early-stage diseases, whereas cell dose below 2.3 × 108/kg was associated with lower engraftment rates in advanced-stage diseases. In conclusion, effects of cell dose may differ among disease stages. A cell dose of 3.4 × 108/kg or higher is recommended only for adults with early-stage diseases. With the number of patients available for analysis in this study, we could not show any significant benefits associated with 4.6 × 108/kg or higher in children.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas E, Storb R, Clift RA, Fefer A, Johnson FL, Neiman PE et al. Bone-marrow transplantation (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 1975; 292: 832–843.
Kernan NA, Bartsch G, Ash RC, Beatty PG, Champlin R, Filipovich A et al. Analysis of 462 transplantations from unrelated donors facilitated by the National Marrow Donor Program. N Engl J Med 1993; 328: 593–602.
Sasazuki T, Juji T, Morishima Y, Kinukawa N, Kashiwabara H, Inoko H et al. Effect of matching of class I HLA alleles on clinical outcome after transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells from an unrelated donor. Japan Marrow Donor Program. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: 1177–1185.
Morishima Y, Sasazuki T, Inoko H, Juji T, Akaza T, Yamamoto K et al. The clinical significance of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) allele compatibility in patients receiving a marrow transplant from serologically HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-DR matched unrelated donors. Blood 2002; 99: 4200–4206.
Lee SJ, Klein J, Haagenson M, Baxter-Lowe LA, Confer DL, Eapen M et al. High-resolution donor-recipient HLA matching contributes to the success of unrelated donor marrow transplantation. Blood 2007; 110: 4576–4583.
Davies SM, Kollman C, Anasetti C, Antin JH, Gajewski J, Casper JT et al. Engraftment and survival after unrelated-donor bone marrow transplantation: a report from the national marrow donor program. Blood 2000; 96: 4096–4102.
Sierra J, Storer B, Hansen JA, Bjerke JW, Martin PJ, Petersdorf EW et al. Transplantation of marrow cells from unrelated donors for treatment of high-risk acute leukemia: the effect of leukemic burden, donor HLA-matching, and marrow cell dose. Blood 1997; 89: 4226–4235.
Dominietto A, Lamparelli T, Raiola AM, Van Lint MT, Gualandi F, Berisso G et al. Transplant-related mortality and long-term graft function are significantly influenced by cell dose in patients undergoing allogeneic marrow transplantation. Blood 2002; 100: 3930–3934.
Storb R, Prentice RL, Thomas ED . Marrow transplantation for treatment of aplastic anemia. An analysis of factors associated with graft rejection. N Engl J Med 1977; 296: 61–66.
Deeg HJ, Self S, Storb R, Doney K, Appelbaum FR, Witherspoon RP et al. Decreased incidence of marrow graft rejection in patients with severe aplastic anemia: changing impact of risk factors. Blood 1986; 68: 1363–1368.
Kollman C, Howe CW, Anasetti C, Antin JH, Davies SM, Filipovich AH et al. Donor characteristics as risk factors in recipients after transplantation of bone marrow from unrelated donors: the effect of donor age. Blood 2001; 98: 2043–2051.
Kimura F, Sato K, Kobayashi S, Ikeda T, Sao H, Okamoto S et al. Impact of AB0-blood group incompatibility on the outcome of recipients of bone marrow transplants from unrelated donors in the Japan Marrow Donor Program. Haematologica 2008; 93: 1686–1693.
Rocha V, Labopin M, Gluckman E, Powles R, Arcese W, Bacigalupo A et al. Relevance of bone marrow cell dose on allogeneic transplantation outcomes for patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission: results of a European survey. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 4324–4330.
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues (eds). IARC: Lyon France, 2008.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Sullivan KM, Agura E, Anasetti C, Appelbaum F, Badger C, Bearman S et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease and other late complications of bone marrow transplantation. Semin Hematol 1991; 28: 250–259.
Fine J, Gray R . A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc 1999; 94: 496–497.
Paulin T . Importance of bone marrow cell dose in bone marrow transplantation. Clin Transplant 1992; 6: 48–54.
Byrne JL, Stainer C, Cull G, Haynes AP, Bessell EM, Hale G et al. The effect of the serotherapy regimen used and the marrow cell dose received on rejection, graft-versus-host disease and outcome following unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for leukaemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 411–417.
Barrett AJ, Ringden O, Zhang MJ, Bashey A, Cahn JY, Cairo MS et al. Effect of nucleated marrow cell dose on relapse and survival in identical twin bone marrow transplants for leukemia. Blood 2000; 95: 3323–3327.
Han P, Story C, McDonald T, Mrozik K, Snell L . Immune escape mechanisms of childhood ALL and a potential countering role for DC-like leukemia cells. Cytotherapy 2002; 4: 165–175.
Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Urbani E, Perruccio K, Shlomchik WD, Tosti A et al. Effectiveness of donor natural killer cell alloreactivity in mismatched hematopoietic transplants. Science 2002; 295: 2097–2100.
Weiden PL, Flournoy N, Thomas ED, Prentice R, Fefer A, Buckner CD et al. Antileukemic effect of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of allogeneic-marrow grafts. N Engl J Med 1979; 300: 1068–1073.
Levine JE, Braun T, Penza SL, Beatty P, Cornetta K, Martino R et al. Prospective trial of chemotherapy and donor leukocyte infusions for relapse of advanced myeloid malignancies after allogeneic stem-cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 405–412.
Porter DL, Roth MS, McGarigle C, Ferrara JL, Antin JH . Induction of graft-versus-host disease as immunotherapy for relapsed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 1994; 330: 100–106.
Theilgaard-Monch K, Raaschou-Jensen K, Palm H, Schjodt K, Heilmann C, Vindelov L et al. Flow cytometric assessment of lymphocyte subsets, lymphoid progenitors, and hematopoietic stem cells in allogeneic stem cell grafts. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 1073–1082.
Kolb HJ, Schattenberg A, Goldman JM, Hertenstein B, Jacobsen N, Arcese W et al. Graft-versus-leukemia effect of donor lymphocyte transfusions in marrow grafted patients. Blood 1995; 86: 2041–2050.
Collins Jr RH, Shpilberg O, Drobyski WR, Porter DL, Giralt S, Champlin R et al. Donor leukocyte infusions in 140 patients with relapsed malignancy after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol 1997; 15: 433–444.
Passweg JR, Stern M, Koehl U, Uharek L, Tichelli A . Use of natural killer cells in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 35: 637–643.
Mavroudis D, Read E, Cottler-Fox M, Couriel D, Molldrem J, Carter C et al. CD34+ cell dose predicts survival, posttransplant morbidity, and rate of hematologic recovery after allogeneic marrow transplants for hematologic malignancies. Blood 1996; 88: 3223–3229.
Bittencourt H, Rocha V, Chevret S, Socie G, Esperou H, Devergie A et al. Association of CD34 cell dose with hematopoietic recovery, infections, and other outcomes after HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplantation. Blood 2002; 99: 2726–2733.
Dominietto A, Raiola AM, van Lint MT, Lamparelli T, Gualandi F, Berisso G et al. Factors influencing haematological recovery after allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplants: graft-versus-host disease, donor type, cytomegalovirus infections and cell dose. Br J Haematol 2001; 112: 219–227.
Shiobara S, Nakao S, Ueda M, Yamazaki H, Takahashi S, Asano S et al. Donor leukocyte infusion for Japanese patients with relapsed leukemia after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: indications and dose escalation. Ther Apher 2001; 5: 40–45.
Batinic D, Marusic M, Pavletic Z, Bogdanic V, Uzarevic B, Nemet D et al. Relationship between differing volumes of bone marrow aspirates and their cellular composition. Bone Marrow Transplant 1990; 6: 103–107.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Bone Marrow Transplantation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inamoto, Y., Miyamura, K., Okamoto, S. et al. Disease stage stratified effects of cell dose in unrelated BMT for hematological malignancies: a report from Japan marrow donor program. Bone Marrow Transplant 46, 1192–1202 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2010.281
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2010.281
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bloodstream infections due to Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae in hematological patients: assessment of risk factors for mortality and treatment options
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials (2023)