Abstract
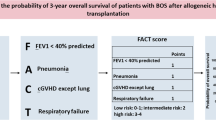
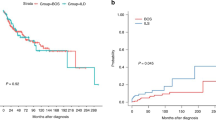
Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) and idiopathic pneumonia syndrome (IPS) cause high mortality and impaired survival after allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). Early recognition of patients at high risk of developing BOS/IPS may lead to improving the outcome of allo-HSCT. We retrospectively analyzed serum surfactant protein A, D (SP-A, -D) and Kerbs von Lungren 6 Ag (KL-6) levels before allo-HSCT in 56 patients who survived more than 90 days after allo-HSCT and compared values of these serum markers and other transplant factors in BOS/IPS patients with those in non-BOS/IPS patients. Five patients developed BOS and two developed IPS at a median interval of 303 and 117 days (range, 100–452 and 95–153) from transplantation. As a result of univariate analysis, pretransplant serum SP-D levels but not SP-A, KL-6 in BOS/IPS patients were significantly lower than those in non-BOS/IPS patients (P=0.03). In multivariate analysis, the patients with lower pretransplant serum SP-D level had a trend toward frequent development of BOS/IPS (P=0.08). Constitutive serum SP-D level before allo-HSCT may be a useful, noninvasive predictor for the development of BOS/IPS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palmas A, Tefferi A, Myers JL, Scott JP, Swensen SJ, Chen MG et al. Late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol 1998; 100: 680–687.
Sakaida E, Nakaseko C, Harima A, Yokota A, Cho R, Saito Y et al. Late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications after allogeneic stem cell transplantation are significantly associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease and with the graft-versus-leukemia effect. Blood 2003; 102: 4236–4242.
Patriarca F, Skert C, Sperotto A, Damiani D, Cerno M, Geromin A et al. Incidence, outcome, and risk factors of late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications after unrelated donor stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 751–758.
Afessa B, Litzow MR, Tefferi A . Bronchiolitis obliterans and other late onset non-infectious pulmonary complications in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 425–434.
Yoshihara S, Yanik G, Cooke KR, Mineishi S . Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS), bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP), and other late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 749–759.
Santo Tomas LH, Loberiza Jr FR, Klein JP, Layde PM, Lipchik RJ, Rizzo JD et al. Risk factors for bronchiolitis obliterans in allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for leukemia. Chest 2005; 128: 153–161.
Fukuda T, Hackman RC, Guthrie KA, Sandmaier BM, Boeckh M, Maris MB et al. Risks and outcomes of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after nonmyeloablative and conventional conditioning regimens for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2003; 102: 2777–2785.
Keates-Baleeiro J, Moore P, Koyama T, Manes B, Calder C, Frangoul H . Incidence and outcome of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome in pediatric stem cell transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 38: 285–289.
Clark H, Reid K . The potential of recombinant surfactant protein D therapy to reduce inflammation in neonatal chronic lung disease, cystic fibrosis, and emphysema. Arch Dis Child 2003; 88: 981–984.
Hartl D, Griese M . Surfactant protein D in human lung diseases. Eur J Clin Invest 2006; 36: 423–435.
Yang S, Milla C, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Hawgood S, Blazar BR, Haddad IY . Surfactant protein A decreases lung injury and mortality after murine marrow transplantation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2002; 27: 297–305.
Walter JN, Fan LL, Bag R, Zhang H, Doan M, Mallory GB et al. Serum KL-6 as a marker for bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation. Transplantation 2006; 82: 709–711.
Clark JG, Crawford SW, Madtes DK, Sullivan KM . Obstructive lung disease after allogeneic marrow transplantation. Clinical presentation and course. Ann Intern Med 1989; 111: 368–376.
Wong R, Rondon G, Saliba RM, Shannon VR, Giralt SA, Champlin RE et al. Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after high-dose chemotherapy and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for high-risk breast cancer. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 31: 1157–1163.
Greene KE, Wright JR, Steinberg KP, Ruzinski JT, Caldwell E, Wong WB et al. Serial changes in surfactant-associated proteins in lung and serum before and after onset of ARDS. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 160: 1843–1850.
Nord M, Schubert K, Cassel TN, Andersson O, Riise GC . Decreased serum and bronchoalveolar lavage levels of Clara cell secretory protein (CC16) are associated with bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome and airway neutrophilia in lung transplant recipients. Transplantation 2002; 73: 1264–1269.
Mattsson J, Remberger M, Andersson O, Sundberg B, Nord M . Decreased serum levels of clara cell secretory protein (CC16) are associated with bronchiolitis obliterans and may permit early diagnosis in patients after allogeneic stem-cell transplantation. Transplantation 2005; 79: 1411–1416.
Struber M, Fischer S, Niedermeyer J, Warnecke G, Gohrbandt B, Gorler A et al. Effects of exogenous surfactant instillation in clinical lung transplantation: a prospective, randomized trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007; 133: 1620–1625.
Kierstein S, Poulain FR, Cao Y, Grous M, Mathias R, Kierstein G et al. Susceptibility to ozone-induced airway inflammation is associated with decreased levels of surfactant protein D. Respir Res 2006; 7: 85–93.
Yang S, Milla C, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Ingbar DH, Blazar BR, Haddad IY . Human surfactant protein a suppresses T cell-dependent inflammation and attenuates the manifestations of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2001; 24: 527–536.
Al-Salmi QA, Walter JN, Colasurdo GN, Sockrider MM, Smith EO, Takahashi H et al. Serum KL-6 and surfactant proteins A and D in pediatric interstitial lung disease. Chest 2005; 127: 403–407.
Takahashi H, Kuroki Y, Tanaka H, Saito T, Kurokawa K, Chiba H et al. Serum levels of surfactant proteins A and D are useful biomarkers for interstitial lung disease in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 162: 258–263.
Husby S, Herskind AM, Jensenius JC, Holmskov U . Heritability estimates for the constitutional levels of the collectins mannan-binding lectin and lung surfactant protein D. A study of unselected like-sexed mono- and dizygotic twins at the age of 6–9 years. Immunology 2002; 106: 389–394.
Sorensen GL, Hjelmborg JB, Kyvik KO, Fenger M, Hoj A, Bendixen C et al. Genetic and environmental influences of surfactant protein D serum levels. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2006; 290: 1010–1017.
Heidinger K, Konig IR, Bohnert A, Kleinsteiber A, Hilgendorff A, Gortner L et al. Polymorphisms in the human surfactant protein-D (SFTPD) gene: strong evidence that serum levels of surfactant protein-D (SP-D) are genetically influenced. Immunogenetics 2005; 57: 1–7.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grant 19591128 from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakane, T., Nakamae, H., Kamoi, H. et al. Prognostic value of serum surfactant protein D level prior to transplant for the development of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome and idiopathic pneumonia syndrome following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 42, 43–49 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.73
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.73
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bortezomib is safe in and stabilizes pulmonary function in patients with allo-HSCT-associated pulmonary CGVHD
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2018)
-
A Call to Arms: a Critical Need for Interventions to Limit Pulmonary Toxicity in the Stem Cell Transplantation Patient Population
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2015)