Abstract
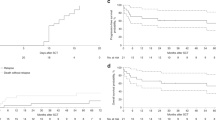
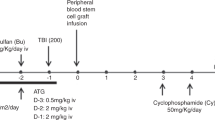
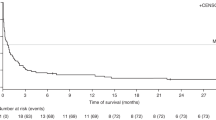
We reviewed the incidence and risk factors for EBV-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (EBV-PTLD) in 89 patients with acquired aplastic anaemia (AAA) receiving allogeneic transplants between 1989 and 2006. The overall incidence of EBV-PTLD was 6.3% (5/89) with no cases in those receiving an allograft for constitutional BM failure syndromes (n=30) during the same period. There was no impact of age, gender, donor status, CMV seropositivity, GVHD and graft cell dose on the occurrence of PTLD. Although both reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) and the prior use of antithymocyte globulin (ATG), as immunosuppressive therapy (IST), were identified as the risk factors for PTLD, only prior use of ATG strongly influenced the development of PTLD with an incidence of 13.38±5.6% (5/43), compared with none in those not exposed to ATG before transplantation (P=0.01) with a relative risk of 10.39 for each course of prior ATG. This is the first study in patients with AAA documenting that those receiving multiple prior courses of ATG are at the highest risk of developing EBV-PTLD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta V, Ball SE, Yi QL, Sage D, McCann SR, Lawler M et al. Favorable effect on acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease with cyclophosphamide and in vivo anti-CD52 monoclonal antibodies for marrow transplantation from HLA-identical sibling donors for acquired aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2004; 10: 867–876.
Scheinberg P, Fischer SH, Li L, Nunez O, Wu CO, Sloand EM et al. Distinct EBV and CMV reactivation patterns following antibody-based immunosuppressive regimens in patients with severe aplastic anemia. Blood 2007; 109: 3219–3224.
Tichelli A, Passweg J, Nissen C, Bargetzi M, Hoffmann T, Wodnar-Filipowicz A et al. Repeated treatment with horse antilymphocyte globulin for severe aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol 1998; 100: 393–400.
Chakrabarti S, Milligan DW, Pillay D, Mackinnon S, Holder K, Kaur N et al. Reconstitution of the Epstein–Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response following T-cell-depleted myeloablative and nonmyeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2003; 102: 839–842.
Brunstein CG, Weisdorf DJ, DeFor T, Barker JN, Tolar J, van Burik JA et al. Marked increased risk of Epstein–Barr virus-related complications with the addition of antithymocyte globulin to a nonmyeloablative conditioning prior to unrelated umbilical cord blood transplantation. Blood 2006; 108: 2874–2880.
Loren AW, Porter DL, Stadtmauer EA, Tsai DE . Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder: a review. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 31: 145–155.
Cesaro S, Murrone A, Mengoli C, Pillon M, Biasolo MA, Calore E et al. The real-time polymerase chain reaction-guided modulation of immunosuppression enables the pre-emptive management of Epstein–Barr virus reactivation after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol 2005; 128: 224–233.
Kinch A, Oberg G, Arvidson J, Falk KI, Linde A, Pauksens K . Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease and other Epstein–Barr virus diseases in allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation after introduction of monitoring of viral load by polymerase chain reaction. Scand J Infect Dis 2007; 39: 235–244.
Cohen JM, Cooper N, Chakrabarti S, Thomson K, Samarasinghe S, Cubitt D et al. EBV-related disease following haematopoietic stem cell transplantation with reduced intensity conditioning. Leuk Lymphoma 2007; 48: 256–269.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buyck, H., Ball, S., Junagade, P. et al. Prior immunosuppressive therapy with antithymocyte globulin increases the risk of EBV-related lymphoproliferative disorder following allo-SCT for acquired aplastic anaemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 43, 813–816 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.394
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.394
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Impact of antithymocyte globulin usage and risk stratification for posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders in aplastic anemia patients after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2024)
-
Epstein–Barr virus-positive lymphoproliferative disorder manifesting as pulmonary disease in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia: a case report
Journal of Medical Case Reports (2021)
-
Epstein-Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (EBV-PTLD) in the setting of allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a comprehensive review from pathogenesis to forthcoming treatment modalities
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
EBV-induced post transplant lymphoproliferative disorders: a persisting challenge in allogeneic hematopoetic SCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
Epstein–Barr virus-related lymphoproliferative disorder induced by equine anti-thymocyte globulin therapy
Medical Oncology (2011)