Abstract
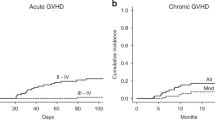
GVHD is a recognized complication of autologous hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation (HPCT), but has typically been reported to respond well to primary therapy with corticosteroids. In this study, we report the development of severe autologous GVHD in five patients who underwent HPCT for multiple myeloma. In all cases, response to corticosteroids was unsatisfactory and three of these patients ultimately died from complications that ensued from prolonged immunosuppressive therapy. Severe autologous GVHD occurred only in patients transplanted for multiple myeloma and was observed at a much higher frequency in patients undergoing their second HPCT. The severity of this syndrome primarily in patients undergoing second HPCTs suggests that repetitive exposure to high-dose therapy may compromise endogenous peripheral regulatory mechanisms and predispose these patients to autoimmunity. Given the evolving role of second autologous transplantations in the therapeutic armamentarium for multiple myeloma, consideration of this potential toxicity may be appropriate when considering treatment options for these patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shlomchik WD, Couzens MS, Tang CB, McNiff J, Robert ME, Liu J et al. Prevention of graft versus host disease by inactivation of host antigen-presenting cells. Science 1999; 285: 412–415.
Zhang Y, Shlomchik WD, Joe G, Louboutin JP, Zhu J, Rivera A et al. APCs in the liver and spleen recruit activated allogeneic CD8+ T cells to elicit hepatic graft-versus-host disease. J Immunol 2002; 169: 7111–7118.
Schmaltz C, Alpdogan O, Muriglan SJ, Kappel BJ, Rotolo JA, Ricchetti ET et al. Donor T cell-derived TNF is required for graft-versus-host disease and graft-versus-tumor activity after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 2002; 97: 2886–2895.
Van den Brink MR, Burakoff SJ . Cytolytic pathways in hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Nat Rev Immunol 2002; 2: 273–281.
Graubert TA, DiPersio JF, Russell JH, Ley TJ . Perforin/granzyme-dependent and independent mechanisms are both important for the development of graft-versus-host disease after murine bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 904–911.
Hess A, Jones R . Autologous graft vs host disease. In: Blume K, Froman SJ, Appelbaum F (eds). Thomas' Hematpoietic Cell Transplantation, 3rd edn. Blackwell Scientific Publishing: Malden, MA, 2004 pp 405–413.
Tzung S-P, Hackman RC, Hockenberry DM, Bensinger W, Schiffman K, McDonald GB . Lymphocytic gastritis resembling graft versus host disease following autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 1998; 4: 43–48.
Saunders MD, Shulman HM, Murakami CS, Chauncey TR, Bensinger WI, McDonald GB et al. Bile duct apoptosis and cholestasis resembling acute graft versus host disease after autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation. Am J Surg Pathol 2000; 24: 1004–1008.
Hood AF, Vogelsang GB, Black LP, Farmer ER, Santos GW . Acute graft versus host disease: development following autologous and syngeneic bone marrow transplantation. Arch Dermatol 1987; 123: 745–750.
Jones RJ, Vogelsang GB, Hess AD, Farmer ER, Mann RB, Geller RB et al. induction of graft versus host disease after autologous bone marrow transplantation. Lancet 1989; 1: 754–757.
Yeager AM, Vogelsang GB, Jones RJ, Farmer ER, Altomonte V, Hess AD et al. Induction of cutaneous graft versus host disease by administration of cyclosporine to patients undergoing autologous bone marrow transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 1992; 80: 2948–2950.
Giralt S, Weber D, Colome M, Dimopoulos M, Mehra R, Van Besien K et al. Phase I trial of cyclosporine-induced autologous graft versus host disease in patients with multiple myeloma undergoing high dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell rescue. J Clin Oncol 1997; 15: 667–673.
Fischer AC, Ruvolo PP, Burt R, Horwitz LR, Bright EC, Hess JM et al. Characterization of the autoreactive T cell repertoire in cyclosporine-induced syngeneic graft versus host disease, a highly conserved repertoire mediates autoaggression. J Immunol 1995; 154: 3713–3725.
Chen W, Thoburn C, Hess AD . Characterization of the pathogenic autoreactive T cells in cyclosporine-induced syngeneic graft versus host disease. J Immunol 1998; 161: 7040–7046.
Hess AD, Thoburn CJ, Chen W, Horwitz LR . Complexity of effector mechanisms in cyclosporine-induced syngeneic graft versus host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2000; 6: 13–24.
Hess AD, Thoburn CJ . Immune tolerance to self major histocompatibility complex class II antigens after bone marrow transplantation: role of regulatory T cells. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 518–529.
Holmberg L, Kikuchi K, Gooley TA, Adams KM, Hockenberry DM, Flowers MED et al. Gastrointestinal graft versus host disease in recipients of autologous hematopoietic stem cells: Incidence, risk factors and outcome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 226–234.
Piqueras B, Lavenu-Bombled C, Galicier L, Bergeron-van der Cruyssen F, Mouthon L et al. Common variable immunodeficiency patient classification based on impaired B cell memory differentiation correlates with clinical aspects. J Clin Immunol 2003; 23: 385–400.
Wehr C, Kivioja T, Schmitt C, Ferry B, Witte T, Eren E et al. The EUROclass trial: defining subgroups in common variable immunodeficiency. Blood 2007; 111: 77–85.
Baecher-Allan C, Brown JA, Freeman GJ, Hafler DA . CD4+ CD25+ regulatory cells from human peripheral blood express very high levels of CD25 ex vivo. Novartis Found Symp 2003; 252: 67–88.
Miura Y, Thoburn CJ, Bright EC, Hess AD . Cytolytic effector mechanisms and gene expression in autologous graft versus host disease: distinct roles of perforin and fas ligand. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2004; 10: 156–170.
Busca A, Locatelli F, Lovisone E, Ottobrelli A, Boggio D, Novero D et al. Treatment of severe refractory acute graft versus host disease of the gastrointestinal tract with Campath-1H. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 734–736.
Wandroo F, Auguston B, Cook M, Craddock C, Mahendra P . Successful use of Campath-1H in the treatment of steroid refractory liver GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 34: 285–287.
Carella AM, Beltrami G, Scalzulli PR, Carella Jr AM, Corsetti MT . Alemtuzumab can successfully treat steroid-refractory acute graft versus host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 131–132.
Richardson PG, Sonneveld P, Schuster MW, Irwin D, Stadtmauer EA, Facon T et al. Bortezomib or high dose dexamethasone for relapsed multiple myeloma. N J Engl Med 2005; 352: 2487–2498.
Rajkumar SV, Blood E, Vesole D, Fonseca R, Greipp PR . Phase III clinical trial of thalidomide plus dexamethasone compared with dexamethasone alone in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: a clinical trial coordinated by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 1–6.
Richardson PG, Blood E, Mitsiades CS, Jagannath S, Zeldenrust SR, Alsina M et al. A randomized phase 2 study of lenalidomide therapy for patients with relapsed or relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2006; 108: 3458–3464.
Condomines M, Quittet P, Lu Z-Y, Nadal L, Latry P, Lopez E et al. Functional regulatory T cells are collected in stem cell autografts by mobilization with high dose cyclophosphamide and granulocyte colony stimulating factor. J Immunol 2006; 176: 6631–6639.
Ahmad I, Haider K, Kanthan R . Autoimmune thrombocytopenia following tandem autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for refractory germ cell tumor. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 34: 279–280.
Lambertenghi Deliers G, Annaloro C, Della Volpe A, Oriani A, Pozzoli E, Soligo D . Multiple autoimmune events after autologous bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 19: 745–747.
Ishikawa F, Shigematsu H, Gondo H, Okamura T, Niho Y . Autoreactive antibodies following autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 22: 729–731.
Isshiki I, Okamoto S, Kakimoto T, Chen CK, Mori T, Yokoyama K et al. Recurrence of autoimmune disease after autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. Int J Hematol 2006; 84: 354–358.
Anderson BE, McNiff JM, Matte C, Athanasiadis I, Shlomchik WD, Shlomchik MJ . Recipient CD4+ T cells that survive irradiation regulate graft versus host disease. Blood 2004; 104: 1565–1573.
Sanchorawala V, Wright DC, Quillen K, Finn KT, Dember LM, Berk JL et al. Tandem cycles of high dose melphalan and autologous stem cell transplantation increases the response rate in AL amyloidosis. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 110: 3561–3563.
Fung HC, Stiff P, Schriber J, Toor A, Smith E, Rodriguez T et al. Tandem autologous stem cell transplantation for patients with primary refractory or poor risk recurrent Hodgkin's lymphoma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 594–600.
Tiersten A, Selleck M, Smith DH, Wertheim I, Kaufman E, Hershman D et al. Phase I/II study of tandem cycles of high dose chemotherapy followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell support in women with advanced ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer 2006; 16: 57–64.
Kroger N, Frick M, Gluz O, Mohrmann S, Metzner B, Jackisch C et al. Randomized trial of single compared with tandem high dose chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation with chemotherapy-sensitive metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 3919–3926.
Attal M, Harousseau J-L, Facon T, Guilhot F, Doyen C, Fuzibet JG et al. Single versus double autologous stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. N Eng J Med 2003; 349: 2495–2502.
Moreau P, Hullin C, Garban F, Yakoub-Agha I, Benboubker L, Attal M et al. Tandem autologous stem cell transplantation in high risk de novo multiple myeloma: final results of the prospective and randomized ZIFM 99-04 protocol. Blood 2006; 107: 397–403.
Barlogie B, Tricot GJ, van Rhee F, Angtuaco E, Walker R, Epstein J et al. Long term results of the first tandem autotransplant trial for multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 2006; 135: 158–164.
Acknowledgements
We thank Gwen Werra for performing all flow cytometry acquisitions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drobyski, W., Hari, P., Keever-Taylor, C. et al. Severe autologous GVHD after hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. Bone Marrow Transplant 43, 169–177 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.295
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.295
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Colonic graft-vs.-host disease in autologous versus allogeneic transplant patients: earlier onset, more apoptosis, and lack of regulatory T-cell attenuation
Modern Pathology (2018)
-
Late recurrence of autologous GvHD in a myeloma patient: a myth or diagnostic challenge?
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)
-
Autologous GVHD?
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
Cellular immunotherapy for plasma cell myeloma
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2013)
-
Gastrointestinal pathology of autologous graft-versus-host disease following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a clinicopathological study of 17 cases
Modern Pathology (2011)