Abstract
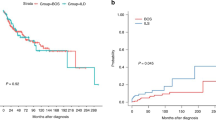
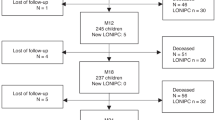
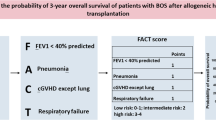
Bronchiolitis obliterans (BrOb) is a well-recognized complication of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). It is associated with substantial morbidity and mortality in adult patients. However, the incidence and morbidity of this complication have not been well described in the pediatric population. We report our experience of BrOb in 216 pediatric allogeneic HSCT patients between 1 January 2001 and 31 December 2005. In total 18 of 216 patients developed BrOb during this time. The diagnosis of BrOb was based on pulmonary function abnormalities, radiographic findings or lung biopsy. In total 14 of 18 patients with BrOb received stem cells from unrelated donors. In total 17 of 18 patients received bone marrow as a stem cell source, and 1 received peripheral blood stem cells. All pediatric patients in this report had a known risk factor for BrOb, most commonly chronic GVHD (l8 of 18 patients). Additionally, 7 of 18 patients had either toxic lung injury or virally mediated pulmonary disease before the diagnosis of BrOb. With a median of 45.1 months of follow-up, the outcomes were 5 of 18 patients died of lung disease, 2 died of other causes, 3 had progressive lung disease, 6 achieved partial resolution of disease and 2 had stable disease. BrOb, while uncommon, is associated with considerable morbidity and mortality in pediatric HSCT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dudek AZ, Mahaseth H, DeFor TE, Weisdorf DJ . Bronchiolitis obliterans in chronic graft-versus-host disease: analysis of risk factors and treatment outcomes. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2003; 9: 657–666.
Clark JG, Crawford SW, Madtes DK, Sullivan KM . Obstructive lung disease after allogeneic marrow transplantation. Clinical presentation and course. Ann Intern Med 1989; 111: 368–376.
Frankovich J, Donaldson SS, Lee Y, Wong RM, Amylon M, Verneris MR . High-dose therapy and autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation in children with primary refractory and relapsed Hodgkin's disease: atopy predicts idiopathic diffuse lung injury syndromes. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2001; 7: 49–57.
Paz HL, Crilley P, Patchefsky A, Schiffman RL, Brodsky I . Bronchiolitis obliterans after autologous bone marrow transplantation. Chest 1992; 101: 775–778.
Yoshihara S, Tateishi U, Ando T, Kunitoh H, Suyama H, Onishi Y et al. Lower incidence of bronchiolitis obliterans in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning compared with myeloablative conditioning. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 35: 1195–1200.
Holland HK, Wingard JR, Beschorner WE, Saral R, Santos GW . Bronchiolitis obliterans in bone marrow transplantation and its relationship to chronic graft-v-host disease and low serum IgG. Blood 1988; 72: 621–627.
Sakaida E, Nakaseko C, Harima A, Yokota A, Cho R, Saito Y et al. Late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications after allogeneic stem cell transplantation are significantly associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease and with the graft-versus-leukemia effect. Blood 2003; 102: 4236–4242.
Griese M, Rampf U, Hofmann D, Fuhrer M, Reinhardt D, Bender-Gotze C . Pulmonary complications after bone marrow transplantation in children: twenty-four years of experience in a single pediatric center. Pediatr Pulmonol 2000; 30: 393–401.
Wieringa J, van Kralingen KW, Sont JK, Bresters D . Pulmonary function impairment in children following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2005; 45: 318–323.
Kurland G, Michelson P . Bronchiolitis obliterans in children. Pediatr Pulmonol 2005; 39: 193–208.
Mauad T, Dolhnikoff M . Histology of childhood bronchiolitis obliterans. Pediatr Pulmonol 2002; 33: 466–474.
Chien JW, Martin PJ, Gooley TA, Flowers ME, Heckbert SR, Nichols WG et al. Airflow obstruction after myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003; 168: 208–214.
Ratjen F, Rjabko O, Kremens B . High-dose corticosteroid therapy for bronchiolitis obliterans after bone marrow transplantation in children. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 36: 135–138.
Santo Tomas LH, Loberiza Jr FR, Klein JP, Layde PM, Lipchik RJ, Rizzo JD et al. Risk factors for bronchiolitis obliterans in allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for leukemia. Chest 2005; 128: 153–161.
Schultz KR, Green GJ, Wensley D, Sargent MA, Magee JF, Spinelli JJ et al. Obstructive lung disease in children after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1994; 84: 3212–3220.
Rovelli A, Pezzini C, Silvestri D, Tana F, Galli MA, Uderzo C . Cardiac and respiratory function after bone marrow transplantation in children with leukaemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 16: 571–576.
Quigley PM, Yeager AM, Loughlin GM . The effects of bone marrow transplantation on pulmonary function in children. Pediatr Pulmonol 1994; 18: 361–367.
Kaplan EB, Wodell RA, Wilmott RW, Leifer B, Lesser ML, August CS . Late effects of bone marrow transplantation on pulmonary function in children. Bone Marrow Transplant 1994; 14: 613–621.
Kaplan EB, Wodell RA, Wilmott RW, Leifer B, Lesser ML, August CS . Chronic graft-versus-host disease and pulmonary function. Pediatr Pulmonol 1992; 14: 141–148.
Nenadov Beck M, Meresse V, Hartmann O, Gaultier C . Long-term pulmonary sequelae after autologous bone marrow transplantation in children without total body irradiation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 16: 771–775.
Frisk P, Arvidson J, Bratteby LE, Hedenstrom H, Lonnerholm G . Pulmonary function after autologous bone marrow transplantation in children: a long-term prospective study. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 645–650.
Arvidson J, Bratteby LE, Carlson K, Hagberg H, Kreuger A, Simonsson B et al. Pulmonary function after autologous bone marrow transplantation in children. Bone Marrow Transplant 1994; 14: 117–123.
Leneveu H, Bremont F, Rubie H, Peyroulet MC, Broue A, Suc A et al. Respiratory function in children undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Pediatr Pulmonol 1999; 28: 31–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duncan, C., Buonanno, M., Barry, E. et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans following pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 41, 971–975 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.19
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.19
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Sleep-related breathing disorder in non-infectious pulmonary complications after pediatric allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Pediatric Research (2023)
-
Late pulmonary complications related to cancer treatment in children
Pediatric Radiology (2022)
-
Imaging of acute and subacute toxicities of cancer therapy in children
Pediatric Radiology (2016)
-
Bronchiolitis obliterans in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic SCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
Bronchiolitis obliterans with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a 10-year experience of the Okayama BMT Group
International Journal of Hematology (2014)