Abstract
Background:
Gastric cancer (GC) is a leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide. Since the approval of trastuzumab, targeted therapies are emerging as promising treatment options for the disease. This study aimed to explore the molecular segmentation of several known therapeutics targets, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), MET and fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2), within GC using clinically approved or investigational kits and scoring criteria. Knowledge of how these markers are segmented in the same cohort of GC patients could improve future clinical trial designs.
Methods:
Using immunohistochemistry (IHC) and FISH methods, overexpression and amplification of HER2, FGFR2 and MET were profiled in a cohort of Chinese GC samples. The correlations between anti-tumour sensitivity and the molecular segments of HER2, MET and FGFR2 alterations were further tested in a panel of GC cell lines and the patient-derived GC xenograft (PDGCX) model using the targeted inhibitors.
Results:
Of 172 GC patients, positivity for HER2, MET and FGFR2 alternations was found in 23 (13.4%), 21 (12.2%) and 9 (5.2%) patients, respectively. Positivity for MET was found in 3 of 23 HER2-positive GC patients. Co-positivity for FGFR2 and MET was found in 1 GC patient, and amplification of the two genes was found in different tumour cells. Our study in a panel of GC cell lines showed that in most cell lines, amplification or high expression of a particular molecular marker was mutually exclusive and in vitro sensitivity to the targeted agents lapatinib, PD173074 and crizotinib was only observed in cell lines with the corresponding high expression of the drugs’ target protein. SGC031, an MET-positive PDGCX mouse model, responded to crizotinib but not to lapatinib or PD173074.
Conclusions:
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, MET and FGFR2 oncogenic driver alterations (gene amplification and overexpression) occur in three largely distinct molecular segments in GC. A significant proportion of HER2-negative patients may potentially benefit from MET- or FGFR2-targeted therapies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Gastric cancer (GC) is among the leading causes of cancer deaths, and half of the worldwide cases occur within Eastern Asia (Ferlay et al, 2010). The majority of GC patients present with advanced disease with a median overall survival of 8–10 months (Power et al, 2010). Despite significant advances in earlier diagnosis, surgical techniques and standard-of-care therapies, clinical outcome of GC remains dismal with a 5-year survival rate of ∼20% (Kamangar et al, 2006). The development of novel, effective therapeutics for GC represents an urgent priority.
In the last decade, targeted therapies have emerged as a promising strategy for the treatment of GC. Trastuzumab, an mAb against human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) (Fujimoto-Ouchi et al, 2007), was recently approved for the treatment of advanced HER2-positive GC patients as the result of the Trastuzumab for Gastric Cancer (ToGA) study (Bang et al, 2010). Positivity for HER2 in GC is defined by either a score of 3+ by immunohistochemistry (IHC) or with IHC 2+ plus HER2 amplification by FISH. The incidence of HER2 positivity in GC was ∼15% (Janjigian et al, 2012; Kim et al, 2012), leaving a significant proportion whose clinical options are limited to standard chemotherapies. Additionally, a number of other receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), including EGFR, VEGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) and hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET), have been studied intensively to assess their therapeutic potential in GC (Meza-Junco and Sawyer, 2012; Pazo Cid and Anton, 2013). Therapies targeting VEGFR and EGFR have so far failed to translate their preclinical efficacy into prolonged patient survival in several late-stage trials for advanced GC (Ohtsu et al, 2011; Lordick et al, 2013; Waddell et al, 2013). All those trials lacked biomarker-assisted patient selection and post hoc analyses have yet to identify biomarker candidates that could help such selection (Khushalani, 2012). Meanwhile, for agents targeting FGFR2 and MET, predictive biomarkers have been identified in preclinical studies and early development, and the outlook for these inhibitors remains optimistic (Asaoka et al, 2011).
The FGFR2 RTK regulates cell proliferation, differentiation and motility and its frequent dysregulation, like gene amplification, is linked to tumour formation in GC (Turner and Grose, 2010; Xie et al, 2013). Fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors have demonstrated preclinically that FGFR2 amplification confers hypersensitivity to FGFR2 inhibition in GC (Nakamura et al, 2006; Xie et al, 2013). AZD4547 and dovitinib are two such anti-FGFR2 therapies that have progressed to mid-late stage trials in advanced GC patients (NCT01457846 and NCT01719549). Both programs have adopted FGFR2 amplification as patient selection; although the detection techniques are different – the AZD4547 trial employs FISH and the dovitinib trial uses RT–PCR.
MET is also well documented for its role in cell proliferation and invasion, and its dysregulation contributes to tumour growth and metastasis (Sierra and Tsao, 2011). MET amplification and protein overexpression, which can lead to constitutive activation of the MET pathway, are associated with shorter survival in GC patients (Lee et al, 2012). This increased understanding has led to the development of several MET signalling pathway inhibitors including MetMAb, rilotumumab (AMG102) and MET TKIs such as tivantinib (Eder et al, 2009). For these MET signalling pathway inhibitors, finding predictive biomarkers early in clinical development is critical (Brunetto et al, 2010). Earlier phase II trials of tivantinib and MetMAb in NSCLC patients showed that MET overexpression rather than MET amplification could be useful in enriching patients (Spigel et al, 2011; Rodig et al, 2012). Indeed, patients who were negative for MET expression performed worse on MetMAb when compared with chemotherapy alone, highlighting the potential for both positive enrichment and negative exclusion. An ongoing phase III trial (NCT01662869) of MetMAb in HER2-negative GC patients utilises MET protein overexpression by IHC as patient selection. Encouragingly, the HGF-targeted antibody rilotumumab demonstrated clinical benefit when used in combination with chemotherapy in a phase II gastric/oesophageal trial (Oliner et al, 2012). Similarly, patients with tumours scoring ‘MET-high’ by IHC assay (defined as ‘>50% of tumour cells positive’) performed significantly better on drug (OS 11.1 vs 5.7 months, HR=0.29 compared with chemotherapy alone) when compared to patients with tumours scored as ‘MET-low’ (defined as ‘⩽50% tumour cells positive’) who had a trend towards unfavourable survival using the rilotumumab/chemotherapy combination compared with chemotherapy alone (HR=1.84).
The oncogenic alterations in HER2, MET and FGFR2 have rarely been studied simultaneously in the same patient cohort using clinically validated or investigational assays and scoring criteria (Ming, 1998). Previous efforts have mainly focused on the profiling of single biomarkers within individual cohorts (Kim et al, 2012; Lee et al, 2012; Matsumoto et al, 2012). The most comprehensive profiling of GC to date has employed high-resolution single-nucleotide polymorphism arrays (Deng et al, 2012). Unlike most other cancers, mutations and epigenetic changes in HER2, MET and FGFR2 are rarely observed in GC (Asaoka et al, 2011). Furthermore, protein overexpression and/or amplification of HER2, MET and FGFR2 are confirmed as oncogenic driver alterations in GC. Therefore, IHC and FISH are strongly supported as diagnostic platforms for these targeted therapies.
With MET and FGFR2 inhibitors currently progressing into late-stage GC trials, there is a need to better understand molecular segmentation of MET, FGFR2 and HER2 alterations within GC (Nadauld and Ford, 2013). Such knowledge will be particularly useful in the application of patient selection strategies, and also in potentially understanding de novo resistance in response to these targeted therapies (Nadauld and Ford, 2013).
Here, we analysed 172 Chinese GC patients for protein expression and gene amplification of HER2 and MET, using a combination of validated IHC and FISH methods. FGFR2 amplification within the same cohort was recently reported (Xie et al, 2013). Together, we identified HER2-negative GC populations that could potentially benefit from FGFR or MET inhibitors. To further investigate this, we profiled a panel of GC cell lines for high expression and amplification of MET, HER2 and FGFR2, and demonstrated highly selective in vitro growth-inhibitory effects using agents specifically targeting the three proteins. Furthermore, we showed the ability of an MET TKI to potently inhibit tumour growth in a patient-derived GC xenograft (PDGCX) model with MET amplification and overexpression.
Materials and methods
Patients and tumour samples
This study included 253 patients with GC who underwent surgery between 2007 and 2011 at the Renji Hospital, Shanghai, China (Table 1). Adjuvant chemotherapies were administered to 143 patients; 43 patients received no chemotherapy; and chemotherapy status for the remaining 65 patients was not available. Histological subtype according to Lauren’s classification was determined after a review of tumour sections by two trained pathologists. Follow-up data were available from 202 patients, who were assessed at 3, 6 and 12 months and then every 6 months for 5 years or until death. This study was approved by Renji Hospital institutional review board.
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry analyses were performed on tissue microarray (TMA) at 4 μm thickness. For HER2 staining, a HercepTest kit (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark) was used following the manufacturer’s instructions. The MET staining was performed using a rabbit monoclonal anti-total MET antibody (SP44; Ventana Medical Systems, Oro Valley, AZ, USA) on an automatic immunostainer (Discovery XT; Ventana Medical Systems).
The DAKO HercepTest guideline was used to semi-quantitatively score MET and HER2 expression. To minimise the impact of intratumoral heterogeneity of HER2 expression, case-matched whole sections of HER2-negatively scored TMA samples were re-evaluated. All slides were independently evaluated and agreed by two pathologists who were blind to patients’ data.
FISH
The dual-colour FISH assay used the HER2/CEP17 probes from Vysis (Chicago, IL, USA; Cat #30-171060) and the MET probe from labelling BAC (CTD-2270N20) DNA with Red-dUTP (Enzo Biochem, Farmingdale, NY, USA; Cat #02N34-050). CEP10-Spectrum Green probe (Vysis, Cat #32-112010) and CEP7-Spectrum Green probe (Vysis, Cat #32-132007) for the centromeric regions of chromosomes 10 and 7 were used as internal controls of FGFR2 and MET probes, respectively. Detailed procedures were previously described (Xie et al, 2013).
Detailed experimental method for multi-colour FISH was included in Supplementary information.
Criteria for defining biomarker positivity
HER2+ cases were defined by IHC 3+ or IHC 2+ plus HER2 amplification. MET+ cases were defined by IHC 2+/3+ according to the patient selection criteria of the ongoing MetMAb trial in GC (NCT01662869). FGFR2+ cases were defined by FGFR2 amplification according to the ongoing trials of AZD4547 and dovitinib in GC (NCT01457846 and NCT01719549).
In vitro cell proliferation
Anti-proliferative activity was measured as described previously using standard metabolism-based anti-proliferative assays (Davies et al, 2007). Each experiment was carried out in triplicate and data presented as geometric means. All the cell lines were profiled by affymetrix (details in Supplementary information), IHC and FISH.
In vivo anti-tumour efficacy and pharmacodynamics
The PDGCX mouse models were established by implanting fresh surgical human tumour tissue into immunodeficient mice. Animals were housed in a specific pathogen-free animal facility in accordance with the Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (eighth edition) and the regulations of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). All animal studies were approved by the IACUC. Briefly, PDGCX tissue fragments (∼15 mm3) were implanted subcutaneously into 8- to 10-week-old female nude mice (Vital River, Beijing, China). Tumour-bearing mice with a tumour size of 150–250 mm3 were randomly divided into vehicle or treatment groups (five animals per group). Subcutaneous tumours and mice body weight were measured twice a week with caliper and balance. Tumour volumes (TVs) were calculated by the formula: TV=(length × [width]2)/2. The percentage of tumour growth inhibition (%TGI) was calculated by the formula: TGI%=[1−(changes of TV in treatment group/changes of TV in control group)] × 100. For tumour regression, in which the TV after treatment was smaller than the TV at the beginning, the following equation was used: regression%=100 × (T0−Ti)/T0. T0 and Ti are TV in the same group but measured at the different time points. T0 is TV on the day before first treatment and Ti is TV on the last measurement day after treatment. Statistical significance was evaluated using a one-tailed, two sample t-test. P<0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Antibodies and immunoblotting
Primary antibodies for total-MET, p-MET(Tyr1234/1235), p-Erk(Thr202/Tyr204), Erk, AKT, GAPDH, as well as secondary anti-rabbit and mouse antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA). The primary antibody for p-AKT (Ser473) was purchased from DAKO. The vehicle and crizotinib-treated tumours (collected 2-h post treatment) were grinded in liquid nitrogen and lysed in ice-cold RIPA buffer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The protein concentration was determined by BCA (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA). In all, 80 μg of tumour extracts was separated in NuPAGE gel (Invitrogen, Camarillo, CA, USA) under reducing conditions and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes by iBlot gel transfer stack (Invitrogen). After blocking and antibody incubation, the membrane was exposed by ECL followed by western blotting detection system (GE Health, Waukesha, WI, USA). The signals were captured by LAS400 imaging system (Fujifilm Life Science, Valhalla, NY, USA).
Statistical analysis
The analysis was conducted using R version 2.10.1 (http://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/base/old/2.10.1/). Characteristics of the two groups were compared using the χ2-test. Correlation of protein expression and gene amplification of a biomarker is assessed using Kappa statistics. Logistic regression model was applied to interrogate association of biomarker data and individual clinical parameter. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to estimate the survival distributions. The log-rank test was used to compare the survival distributions. Two-sided P-values <0.05 were considered as statistically significant.
Results
Patient information and tumour characteristics
Of the 253 Chinese GC patients evaluated in this study, all had undergone total or subtotal gastrectomy with lymphadenectomy, according to the tumour location. Detailed patient information and tumour characteristics are listed in Table 1. Pathologically, these tumours were all gastric adenocarcinomas representing intestinal and diffused subtypes, according to Lauren’s classification. The percentages of the clinical stages according to WHO TNM classification were stage I, 7%; stage II, 24%; stage III, 51%; stage IV, 19%. Patient survival data were available for 202 patients and the median survival time was 28 months (range 0–55). Patients with more advanced clinicopathological features such as tumour grade and clinical stage were associated with worse survival (data not shown).
HER2 positivity in Chinese GC patients
To evaluate the prevalence of HER2 positivity in these Chinese GC samples, we performed IHC and FISH analysis following the current clinical practice for HER2-targeted therapies in advanced GC patients. A total of 221 patient samples were studied for membranous expression of HER2 by IHC using a ‘HercepTest’ kit. The percentage breakdown of HER2 IHC scores was as follows: 0, 58.4%; 1+, 16.7%; 2+, 14.0%; 3+, 10.9%. Among these, 55 samples exhibited HER2 protein overexpression with IHC scores of 2+ and 3+ (Table 2; Figure 1A). HER2 FISH analysis was also performed on 219 out of the IHC-analysed 221 patient samples, and showed an amplification rate of 15.0% (Table 2; Figure 1B). The remaining two cases that were not evaluated by FISH assay had IHC scores of 0, and hence based on ToGA trial criteria Bang et al (2010) required no further FISH confirmation of their HER2 status. Furthermore, HER2 amplification was found in 25 (45.5%) of 55 patients with HER2 overexpression, but only in 8 (4.9%) of 164 patients with HER2 IHC scores of 0 or 1+. This suggests that HER2 amplification shows a good concordance (κ=0.514) with protein overexpression in these GC samples (Table 2).
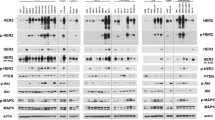
Representative GC cases with overexpression and amplification of HER2, MET and FGFR2. (A and B) Strong membrane staining (IHC 3+) and gene amplification by FISH (red signal, HER2; green signal, CEP17) of HER2. (C) Gene amplification by FISH (red signal, FGFR2; green signal, CEP10) of FGFR2. (D, E) Strong membrane staining (IHC 3+) and gene amplification by FISH (red signal, MET; green signal, CEP7) of MET.
Taken together, HER2+ status was detected in 33 (14.9%) of 221 GC patient samples studied (Table 2). Similar to the findings from the ToGA trial (Bang et al, 2010), a higher incidence of HER2+ was found in the intestinal subtype (28.0%) as compared with the diffuse subtype (8.3%). Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 overexpression and HER2 amplification were not found to be significantly (P>0.1) associated with patient survival.
MET gene amplification and protein overexpression in Chinese GC patients
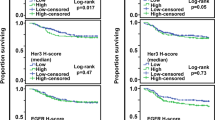
Next, we evaluated the prevalence of MET amplification and overexpression and their concordance correlation in the same Chinese GC cohort. The MET protein overexpression (as defined by IHC 2+ or 3+) was identified in 26 (12.3%) of 212 patients (Table 2; Figure 1D). The FISH analysis detected MET amplification in 12 (6.1%) of 196 patient samples (Table 2; Figure 1E). Among the 176 patient samples analysed by both IHC and FISH, MET overexpression was found in 9 out of the 12 MET-amplified cases, suggesting a markedly high correlation (κ=0.674) between MET gene amplification and protein overexpression (Table 2). In addition, we found that both MET amplification and MET overexpression were significantly associated with more frequent lymph-node metastasis (P=0.01 and 0.02, respectively (X2)) and distant metastasis (P=0.01 and 0.03, respectively (X2)). Patients with MET-amplified tumours had significantly poorer survival than patients with non-amplified tumours (P=0.0012; Figure 2A). Similarly, patients with tumours scoring MET IHC 3+ were also found to be significantly associated with shorter survival time, compared to patients with tumours scoring <IHC3+ (P=0.001; Figure 2B).
MET amplification and overexpression leads to worse survival in GC patients. (A) Association of MET amplification with survival time in 164 GC patients. Median survival time was 10.5 months for patients with MET amplification compared with 48 months for patients with non-amplified MET. The difference was significant in the log-rank test (P=0.0125). (B) Association of MET IHC 3+ with survival time in 167 GC patients. Median survival time was 8 months for patients with MET IHC 3+ compared with 45 months for patients without MET IHC3+. The difference was significant in the log-rank test (P=0.0013).
Chinese GC patient tumours exhibit distinct molecular segments of HER2, FGFR2 and MET alterations
Besides the HER2 and MET oncogenic alterations, abnormal activation of FGFR2 signalling via gene amplification has also been recently identified as a potential oncogenic driver in advanced GC patients (Xie et al, 2013). As we previously observed in the same Chinese GC cohort, FGFR2 amplification (Table 2; Figure 1C) was detected in 10 (5.1%) of 198 patients.
To further evaluate the exclusivity and/or concordance correlation among the three molecular markers within this GC cohort, a total of 172 patients were stratified according to their HER2, MET and FGFR2 positivity status (refer to Materials and methods for criteria of biomarker positivity). As summarised in Figure 3, the percentages of positive patients for each molecular segment were HER2+, 13.4%; MET+, 12.2% and FGFR2+, 5.2%. Among these positive patients, no patient was found to be positive for all three biomarkers. Furthermore, FGFR2+ did not overlap with HER2+ in this cohort. Of particular interest, MET+ overlapped with FGFR2+ in one case from the HER2-negative population, accounting for 11.1% (1 out of 9) of FGFR2+ patients or 0.6% (1 out of 172) of all patients. MET+ also overlapped with HER2+ in 3 cases, accounting for 13.0% (3 out of 23) of HER2+ patients or 1.7% (3 out of 172) of all patients (Figure 3). In summary, the percentage of samples exclusively staining positive for a single marker (i.e., no overlap) is as follows: HER2+ alone, 87.0% (20 out of 23); MET+ alone, 81.0% (17 out of 21); FGFR2+ alone, 88.9% (8 out of 9). Together, our results from 172 Chinese GC patients suggest that HER2, MET and FGFR2 oncogenic alterations occur in three largely distinct molecular segments.
HER2, MET and FGFR2 oncogenic driver alterations occur in distinct molecular segments in GC. The percentages of positive patients for each biomarker are as follows: HER2+, 13.4% (23 out of 172); FGFR2+, 5.2% (9 out of 172); MET+, 12.2% (21 out of 172). No patient was recorded to be positive for all three biomarkers. One case was found to be positive for both MET and FGFR2. Three patients were found to be positive for both HER2 and MET.
FGFR2 and MET gene amplifications exist in different tumour cells from an FGFR2+/MET+ Chinese GC patient
We developed FGFR2/MET multi-colour FISH assay and analysed the whole tumour section from case number GC122T, which is the only case that showed co-amplification of more than one gene among the four overlapping cases (three cases for MET+/HER2+ and one case for FGFR2+/MET+). This case showed gene amplifications for both FGFR2 (average copy number 5.22, FGFR2/CEP10 ratio 2.2) and MET (average copy number >20, MET/CEP7 ratio>4). Both genes exhibited clustered signals, and the two amplifications appeared in different tumour cells (Figure 4).
MET and FGFR2 genes were co-amplified but in different tumour cells from case GC122T. The top lane shows the tumour cell with MET (red signal) amplification (A), FGFR2 (gold signal) trisomy (B) and their merged image (C). The lower lane shows another tumour cell with MET polysomy (D), FGFR2 amplification (E) and their merged image (F). Green and aqua signals represent CEP7 and CEP10, respectively.
GC cell lines carrying HER2, MET and FGFR2 oncogenic alterations are sensitive to drugs targeting the corresponding pathways
To explore in vitro drug sensitivities of cell lines expressing the various molecular aberrations highlighted above, a panel of 24 GC cell lines were exposed to drugs targeting FGFR2 (PD173074, FGFR2 phosphorylation IC50 ∼10 nM) (Kunii et al, 2008), HER2 (Lapatinib, HER2 enzyme IC50 9.2 nM) (Rusnak et al, 2007) and MET (crizotinib, MET enzyme IC50 6 nM) (Timofeevski et al, 2009). Standard metabolism-based anti-proliferative assays were performed following 3 days drug exposure and 50% growth inhibition (GI50) values were determined. In parallel, mRNA expression analysis was performed on HER2, MET and FGFR2, and absolute mRNA probe signal values were used to determine correlations with anti-proliferative responses to these targeted therapies (Table 3). Notably, anti-proliferative response to crizotinib showed an excellent correlation with the levels of MET mRNA and its protein expression, with cell lines GTL16, Hs746t, SNU-5, SNU-620 and SNU-638 displaying crizotinib GI50 values ranging from 6 to 30 nM which all display MET mRNA probe values of >1000, MET amplification and high protein expression (IHC3+). All other cell lines showed minimal response to crizotinib (GI50 values >0.13 μ M) and correspondingly had low MET mRNA expression (probe values <250), no MET amplification and undetectable protein expression (IHC0). Similarly, strong anti-proliferative responses to lapatinib were only achieved in cell lines NCI-N87 and NUGC-4 (GI50 values of 16 and 69 nM, respectively), both of which showed HER2 mRNA probe values of >1000 and high expression of HER2 protein (IHC2+/3+, with NCI-N87 also showing HER2 amplification). Finally, exposure to PD173074 resulted in potent anti-proliferative responses in cell lines KATO-III and SNU-16 (GI50 values of 79 and 92 nM, respectively), both of which are known to be FGFR2 gene amplified and exhibit FGFR2 mRNA probe values of >1000.
Of particular interest, none of the GC cell lines showed strong anti-proliferative responses to all three drugs, and indeed, in each of the responding cell lines, a strong anti-proliferative response was only achieved using a single drug.
MET gene amplification and protein overexpression in a PDGCX mouse model predict selective sensitivity to MET inhibitor
To further explore the translational significance of above findings, we selected a PDGCX mouse model (SGC031) harbouring MET amplification and MET overexpression (IHC 3+), but no gene amplification and/or protein overexpression of FGFR2 and HER2. To assess anti-tumour efficacy of an MET inhibitor in this model, SGC031 tumour-bearing nude mice were treated with crizotinib 50 mg kg−1, Lapatinib 100 mg kg−1, PD173074 50 mg kg−1, docetaxel 10 mg kg−1, or the combination of crizotinib and Docetaxel, respectively. Once-daily administration of crizotinib gave statistically significant tumour regression of 89% (P<0.0001) when compared with vehicle controls (Figure 5A). In contrast, chronic oral treatment with PD173074, an FGFR inhibitor, or lapatinib, an HER2 inhibitor did not result in significant TGI over the same period of treatments (14% and 17% TGI, respectively, all values P⩾0.2). Once weekly intravenous administration of docetaxel showed tumour regression (19% tumour regression, P<0.0001) during treatment period and importantly, combined treatment with crizotinib did not result in antagonism compared with crizotinib monotherapy alone (81% tumour regression, P<0.0001). Downregulation of p-MET (Y1234/1235) as well as its downstream targets, p-AKT (Ser473) and p-ERK (Thr202/Tyr204) in SGC031 tumour post-crizotinib treatment was observed by immunoblotting (Figure 5B).
Crizotinib displays potent anti-tumour efficacy in an MET amplification and overexpression PDGCX model. (A) SGC031-bearing nude mice were treated with vehicle, lapatinib 100 mg kg−1 bid, or crizotinib 50 mg kg−1 qd, or PD173074 50 mg kg−1 qd or docetaxel 20 mg kg−1 twice weekly alone, or the combination of crizotinib and docetaxel, respectively, for 3 weeks. Tumour volume was measured at the time indicated. Statistical analysis of tumour growth inhibition was performed using a Student’s t-test; p<0.0001. (B) Downregulations of p-MET (Y1234/1235), p-AKT (Ser473) and p-ERK (Thr202/Tyr204) were observed in crizotinib-treated SGC031 tumours by immunoblotting. Total-AKT, MET and ERK levels remained unchanged.
Discussion
Since the approval of trastuzumab, it is increasingly clear that targeted therapies can provide survival benefit in advanced GC patients (Bang et al, 2010). Targeted therapies rely on design and execution of a personalised medicine strategy, which depends on a good knowledge of how oncogenic driver markers are expressed in the same set of patient samples (Nadauld and Ford, 2013). To ensure the success of future targeted therapies, it is imperative to understand the molecular segmentation of key ‘druggable’ targets within GC. Currently besides HER2, targeting approaches to MET and FGFR2 are most clinically advanced. MetMAb and rilotumumab, monoclonal antibodies targeting MET and HGF respectively, are currently being tested in phase III GC trials and are utilising MET overexpression by IHC as a patient selection approach; meanwhile, dovitinib and AZD4547, two FGFR TKIs, use FGFR2 amplification by RT–PCR and FISH in their phase II GC trials. Our study here, by using the diagnostic methods that are currently employed for patient selection in MET- and FGFR-targeted GC trials, is the first to comprehensively characterise HER2, MET and FGFR2 oncogenic alterations in a cohort of GC patient samples.
Our data showed that HER2+, MET+ and FGFR2+ represent three largely distinct molecular segments, with slight overlap between HER2+ and MET+ patients (1.7% GC) and between MET+ and FGFR+ (0.6% GC). In addition, our results confirmed the reported findings on Chinese GC patients that HER2+ rate is 10–15% (Shan et al, 2013; Sheng et al, 2013). It is worthwhile to mention that we took consideration of GC tumour heterogeneity, by confirming (on whole tissue sections) the IHC status of those cases (on TMAs) that were HER2 negative. On the other hand, MET protein expression is much less documented in Chinese GC. Recently, Lee et al (2012) analysed a Korean GC population and characterised the incidence of MET overexpression and amplification at 23.7% and 3.4%, respectively. Using identical methodologies, we found a lower protein overexpression rate (12.3%) and a slightly higher amplification rate (6.1%). Despite these slight discrepancies, the findings from these two data sets are largely consistent. Namely, in both data sets MET IHC 3+ and MET amplification were associated with poor prognosis, and MET amplification was highly associated with MET protein overexpression. These data, when combined with our previous FGFR2 amplification results in the same sample cohort (Xie et al, 2013), suggest that ∼15% of HER2-negative GC patients could potentially benefit from FGFR2- or MET-targeted agents. Data from Graziano et al (2011) demonstrate a link between poor prognosis and elevated MET gene copy number (GCN) in radically resected GC patients; however, an absence of robust correlative data between patient tumour MET GCN and protein expression, combined with the prevalence of clinical IHC diagnostic assays suggests that measurement of protein levels appears to be a favoured emerging clinical approach. In addition to the clinical GC responses already described using MetMab and rilotumumab, the small-molecule EML4-ALK and MET inhibitor, crizotinib, has also shown evidence of efficacy in MET-driven tumours (Lennerz et al, 2011). Within a phase I crizotinib expansion study, four patients were identified with focally gene amplified MET gastric or oesophageal junction tumours, two of whom experienced tumour shrinkage upon crizotinib treatment. In keeping with our data, the authors also demonstrated that HER2 and MET were, with one exception, mutually exclusive in a cohort of 489 patient samples. In this instance, co-amplification was observed between MET and EGFR.
Our profiling of a panel of GC cell lines for their DNA, mRNA and/or protein expressions of HER2, MET and FGFR2 revealed a molecular segmentation profile similar to that of the surgical samples. In most cell lines, amplification or high expression of each marker was mutually exclusive and in vitro sensitivity to the targeted agents lapatinib, PD173074 and crizotinib was only observed in cell lines with the corresponding high expression of the drugs’ target. These data support the notion of ‘oncogenic drivers’, whereby tumour cells evolve a reliance on a particular oncogenic pathway. Furthermore, we extended the translational significance of these findings by exploring in vivo sensitivity of an MET amplification and overexpression PDGCX model to drugs targeting the three biomarkers of interest. Our data showed tumour dependence on MET signalling with sensitivity to crizotinib and non-response to drugs targeting HER2 or FGFR2, thus validating targeting of this particular segment through use of a PDGCX model. One exception to above findings is the highly HER2-expressing cell line, SNU-216. Despite showing high expression of HER2 (IHC 3+), this line was relatively unresponsive to lapatinib, likely as a consequence of elevated MET expression. Indeed, co-expression of MET/HER2 proteins was observed in SNU-216 cell and its insensitivity to lapatinib has also been observed by Chen et al (2012), who concluded that MET upregulation abrogates the inhibitory effect of lapatinib.
On the basis of clinical experience, patient selection is critical in ensuring the efficacy of inhibitors targeting oncogenic drivers. Nevertheless, even within biomarker-positive patients, initial response rates can vary (de novo resistance) and more importantly, secondary (acquired) resistance ultimately occurs in the majority of cancer patients. In HER2+ breast cancer patients, the rate of primary resistance to single-agent trastuzumab is around 66–88% and the majority of the responding patients develop secondary resistance within a year (Nahta and Esteva, 2006). In the ToGA trial, HER2+ GC also showed a low complete response rate (Bang et al, 2010). Previous studies (Minuti et al, 2012; Oliveras-Ferraros et al, 2012), together with our results of SNU-216’s poor response to lapatinib or crizotinib, suggest that co-activation of the MET pathway could cause low or no response to HER2-targeted therapies. As our study indicates MET overexpression in 14% of HER2+ patients, we speculate that MET expression could potentially be a contributing factor to the low response rates observed in clinic. In addition, we used multi-colour FISH to analyse the overlapping MET+ and FGFR2+ patient sample and found that the two genes were co-amplified. This is the first reported case of co-amplification of MET and FGFR2 in a GC patient, though such co-amplification event appears rare (0.6% of all GC). In this case, co-amplification found in different tumour cells clearly explains tumour heterogeneity in GC. However, the limitation to this study is that we were unable to verify which class of inhibitor such patient would potentially receive optimal therapeutic benefit from; while future studies aim to identify co-expressing PDGCX models to enable preclinical testing.
In summary, this study profiled the expression of key oncogenic drivers in a cohort of GC patient samples and a panel of GC cell lines. Our data demonstrated that these markers show largely distinct molecular segments within GC and suggest that a significant proportion of HER2-negative GC patients could benefit from FGFR2- and MET-targeted therapies.
Change history
04 March 2014
This paper was modified 12 months after initial publication to switch to Creative Commons licence terms, as noted at publication
References
Asaoka Y, Ikenoue T, Koike K (2011) New targeted therapies for gastric cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 20 (5): 595–604.
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T, Aprile G, Kulikov E, Hill J, Lehle M, Ruschoff J, Kang YK (2010) Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 376 (9742): 687–697.
Brunetto AT, Kristeleit RS, de Bono JS (2010) Early oncology clinical trial design in the era of molecular-targeted agents. Future Oncol 6 (8): 1339–1352.
Chen CT, Kim H, Liska D, Gao S, Christensen JG, Weiser MR (2012) MET activation mediates resistance to lapatinib inhibition of HER2-amplified gastric cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 11 (3): 660–669.
Davies BR, Logie A, McKay JS, Martin P, Steele S, Jenkins R, Cockerill M, Cartlidge S, Smith PD (2007) AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), a potent inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 kinases: mechanism of action in vivo, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship, and potential for combination in preclinical models. Mol Cancer Ther 6 (8): 2209–2219.
Deng N, Goh LK, Wang H, Das K, Tao J, Tan IB, Zhang S, Lee M, Wu J, Lim KH, Lei Z, Goh G, Lim QY, Tan AL, Sin Poh DY, Riahi S, Bell S, Shi MM, Linnartz R, Zhu F, Yeoh KG, Toh HC, Yong WP, Cheong HC, Rha SY, Boussioutas A, Grabsch H, Rozen S, Tan P (2012) A comprehensive survey of genomic alterations in gastric cancer reveals systematic patterns of molecular exclusivity and co-occurrence among distinct therapeutic targets. Gut 61 (5): 673–684.
Eder JP, Vande Woude GF, Boerner SA, LoRusso PM (2009) Novel therapeutic inhibitors of the c-Met signaling pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15 (7): 2207–2214.
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM (2010) Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 127 (12): 2893–2917.
Fujimoto-Ouchi K, Sekiguchi F, Yasuno H, Moriya Y, Mori K, Tanaka Y (2007) Antitumor activity of trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy in human gastric cancer xenograft models. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 59 (6): 795–805.
Graziano F, Galluccio N, Lorenzini P, Ruzzo A, Canestrari E, D'Emidio S, Catalano V, Sisti V, Ligorio C, Andreoni F, Rulli E, Di Oto E, Fiorentini G, Zingaretti C, De Nictolis M, Cappuzzo F, Magnani M (2011) Genetic activation of the MET pathway and prognosis of patients with high-risk, radically resected gastric cancer. J Clin Oncol 29 (36): 4789–4795.
Janjigian YY, Werner D, Pauligk C, Steinmetz K, Kelsen DP, Jager E, Altmannsberger HM, Robinson E, Tafe LJ, Tang LH, Shah MA, Al-Batran SE (2012) Prognosis of metastatic gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer by HER2 status: a European and USA International collaborative analysis. Ann Oncol 23 (10): 2656–2662.
Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF (2006) Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol 24 (14): 2137–2150.
Khushalani NI (2012) Phase I and II clinical trials for gastric cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 21 (1): 113–128.
Kim JW, Im SA, Kim M, Cha Y, Lee KH, Keam B, Kim MA, Han SW, Oh DY, Kim TY, Kim WH, Bang YJ (2012) The prognostic significance of HER2 positivity for advanced gastric cancer patients undergoing first-line modified FOLFOX-6 regimen. Anticancer Res 32 (4): 1547–1553.
Kunii K, Davis L, Gorenstein J, Hatch H, Yashiro M, Di Bacco A, Elbi C, Lutterbach B (2008) FGFR2-amplified gastric cancer cell lines require FGFR2 and Erbb3 signaling for growth and survival. Cancer Res 68 (7): 2340–2348.
Lee HE, Kim MA, Lee HS, Jung EJ, Yang HK, Lee BL, Bang YJ, Kim WH (2012) MET in gastric carcinomas: comparison between protein expression and gene copy number and impact on clinical outcome. Br J Cancer 107 (2): 325–333.
Lennerz JK, Kwak EL, Ackerman A, Michael M, Fox SB, Bergethon K, Lauwers GY, Christensen JG, Wilner KD, Haber DA, Salgia R, Bang YJ, Clark JW, Solomon BJ, Iafrate AJ (2011) MET amplification identifies a small and aggressive subgroup of esophagogastric adenocarcinoma with evidence of responsiveness to crizotinib. J Clin Oncol 29 (36): 4803–4810.
Lordick F, Kang YK, Chung HC, Salman P, Oh SC, Bodoky G, Kurteva G, Volovat C, Moiseyenko VM, Gorbunova V, Park JO, Sawaki A, Celik I, Gotte H, Melezinkova H, Moehler M (2013) Capecitabine and cisplatin with or without cetuximab for patients with previously untreated advanced gastric cancer (EXPAND): a randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 14 (6): 490–499.
Matsumoto K, Arao T, Hamaguchi T, Shimada Y, Kato K, Oda I, Taniguchi H, Koizumi F, Yanagihara K, Sasaki H, Nishio K, Yamada Y (2012) FGFR2 gene amplification and clinicopathological features in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 106 (4): 727–732.
Meza-Junco J, Sawyer MB (2012) Metastatic gastric cancer - focus on targeted therapies. Biologics 6: 137–146.
Ming SC (1998) Cellular and molecular pathology of gastric carcinoma and precursor lesions: A critical review. Gastric Cancer 1 (1): 31–50.
Minuti G, Cappuzzo F, Duchnowska R, Jassem J, Fabi A, O'Brien T, Mendoza AD, Landi L, Biernat W, Czartoryska-Arlukowicz B, Jankowski T, Zuziak D, Zok J, Szostakiewicz B, Foszczynska-Kloda M, Tempinska-Szalach A, Rossi E, Varella-Garcia M (2012) Increased MET and HGF gene copy numbers are associated with trastuzumab failure in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Br J Cancer 107 (5): 793–799.
Nadauld LD, Ford JM (2013) Molecular profiling of gastric cancer: toward personalized cancer medicine. J Clin Oncol 31 (7): 838–839.
Nahta R, Esteva FJ (2006) HER2 therapy: molecular mechanisms of trastuzumab resistance. Breast Cancer Res 8 (6): 215.
Nakamura K, Yashiro M, Matsuoka T, Tendo M, Shimizu T, Miwa A, Hirakawa K (2006) A novel molecular targeting compound as K-samII/FGF-R2 phosphorylation inhibitor, Ki23057, for Scirrhous gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 131 (5): 1530–1541.
Ohtsu A, Shah MA, Van Cutsem E, Rha SY, Sawaki A, Park SR, Lim HY, Yamada Y, Wu J, Langer B, Starnawski M, Kang YK (2011) Bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy as first-line therapy in advanced gastric cancer: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III study. J Clin Oncol 29 (30): 3968–3976.
Oliner K, Tang R, Anderson A, Lan Y, Iveson T, Donehower R, Jiang Y, Dubey S, Loh E (2012) Evaluation of MET pathway biomarkers in a phase II study of rilotumumab (R, AMG 102) or placebo (P) in combination with epirubicin, cisplatin, and capecitabine (ECX) in patients (pts) with locally advanced or metastatic gastric (G) or esophagogastric junction (EGJ) cancer. J Clin Oncol 30 (Suppl)): : abstr 4005.
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Corominas-Faja B, Cufi S, Vazquez-Martin A, Martin-Castillo B, Iglesias JM, Lopez-Bonet E, Martin AG, Menendez JA (2012) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) confers primary resistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin). Cell Cycle 11 (21): 4020–4032.
Pazo Cid RA, Anton A (2013) Advanced HER2-positive gastric cancer: current and future targeted therapies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 85 (3): 350–362.
Power DG, Kelsen DP, Shah MA (2010) Advanced gastric cancer—slow but steady progress. Cancer Treat Rev 36 (5): 384–392.
Rodig S, Sequist LV, Schiller JH, Chen Y, Halim A, Waghorne C, Zahir H, Schwartz B . An exploratory biomarker analysis evaluating the effect of the c-MET inhibitor tivantinib (ARQ 197) and erlotinib in NSCLC patients in a randomized, double-blinded phase 2 study [Abstract] (2012) Proceedings of the 103rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research; 2012 March 31–April 4; Chicago, IL. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res 2012; 72(8 Suppl): Abstract nr 1729. doi:1538-7445.AM2012-1729.
Rusnak DW, Alligood KJ, Mullin RJ, Spehar GM, Arenas-Elliott C, Martin AM, Degenhardt Y, Rudolph SK, Haws Jr TF, Hudson-Curtis BL, Gilmer TM (2007) Assessment of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR, ErbB1) and HER2 (ErbB2) protein expression levels and response to lapatinib (Tykerb, GW572016) in an expanded panel of human normal and tumour cell lines. Cell Prolif 40 (4): 580–594.
Shan L, Ying J, Lu N (2013) HER2 expression and relevant clinicopathological features in gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma in a Chinese population. Diagn Pathol 8: 76.
Sheng WQ, Huang D, Ying JM, Lu N, Wu HM, Liu YH, Liu JP, Bu H, Zhou XY, Du X (2013) HER2 status in gastric cancers: a retrospective analysis from four Chinese representative clinical centers and assessment of its prognostic significance. Ann Oncol 24 (9): 2360–2364.
Sierra JR, Tsao MS (2011) c-MET as a potential therapeutic target and biomarker in cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol 3 (1 Suppl): S21–S35.
Timofeevski SL, McTigue MA, Ryan K, Cui J, Zou HY, Zhu JX, Chau F, Alton G, Karlicek S, Christensen JG, Murray BW (2009) Enzymatic characterization of c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase oncogenic mutants and kinetic studies with aminopyridine and triazolopyrazine inhibitors. Biochemistry 48 (23): 5339–5349.
Spigel DR, Ervin TJ, Ramlau R, Daniel DB, Goldschmidt JH, Blumenschein GR, Krzakowski MJ, Robinet G, Clement-Duchene C, Barlesi F, Govindan R, Patel T, Orlov SV, Wertheim MS, Zha J, Pandita A, Yu W, Yauch RL, Patel PH, Peterson AC (2011) Final efficacy results from OAM4558g, a randomized phase II study evaluating MetMAb or placebo in combination with erlotinib in advanced NSCLC. J Clin Oncol 29 (Suppl)): : abstr 7505.
Turner N, Grose R (2010) Fibroblast growth factor signalling: from development to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10 (2): 116–129.
Waddell T, Chau I, Cunningham D, Gonzalez D, Frances A, Okines C, Wotherspoon A, Saffery C, Middleton G, Wadsley J, Ferry D, Mansoor W, Crosby T, Coxon F, Smith D, Waters J, Iveson T, Falk S, Slater S, Peckitt C, Barbachano Y (2013) Epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine with or without panitumumab for patients with previously untreated advanced oesophagogastric cancer (REAL3): a randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 14 (6): 481–489.
Xie L, Su X, Zhang L, Yin X, Tang L, Zhang X, Xu Y, Gao Z, Liu K, Zhou M, Gao B, Shen D, Ji J, Gavine PR, Zhang J, Kilgour E, Ji Q (2013) FGFR2 gene amplification in gastric cancer predicts sensitivity to the selective FGFR inhibitor AZD4547. Clin Cancer Res 19 (9): 2572–2583.
Acknowledgements
We thank Li Zheng for pathological review, Joan Fan for FISH probes, Lin Zhang and Xie Liang for PDGCX model establishment.
Author contributions
YJL and DS drafted the manuscript. YJL, XY, PG, YG and XN designed and conceived the study. DS, CL and XN acquired and processed the patient samples. XY pathologically reviewed all the patient samples. YX, JQ and YS carried out the in vitro experiment. JL and JZ carried out the in vivo experiments. YJL, DS, TZ, XS, ZQ and PG interpreted and analysed the data. PZ carried out the statistical analysis. YG and XN supervised the whole study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors with the AstraZeneca affiliation are full time employees and/or have stock in AstraZeneca. AstraZeneca sponsored this study.
Additional information
This work is published under the standard license to publish agreement. After 12 months the work will become freely available and the license terms will switch to a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License.
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on British Journal of Cancer website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
From twelve months after its original publication, this work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Shen, D., Yin, X. et al. HER2, MET and FGFR2 oncogenic driver alterations define distinct molecular segments for targeted therapies in gastric carcinoma. Br J Cancer 110, 1169–1178 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.61
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.61
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Transferrin receptor 1 promotes the fibroblast growth factor receptor-mediated oncogenic potential of diffused-type gastric cancer
Oncogene (2022)
-
Clinical difference between fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 subclass, type IIIb and type IIIc, in gastric cancer
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Quantitation of ligand is critical for ligand-dependent MET signalling activation and determines MET-targeted therapeutic response in gastric cancer
Gastric Cancer (2021)
-
The beginning of the era of precision medicine for gastric cancer with fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 aberration
Gastric Cancer (2021)
-
Intratumorale Heterogenität des Magenkarzinoms – Einfluss auf die Biomarkeretablierung
Der Pathologe (2020)