Abstract
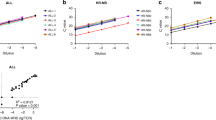
Several reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assays have been described for the detection of circulating tumour cells in blood and bone marrow. Target mRNA sequences for this purpose are the cytokeratins (CK) 19 and 20, the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), and the prostate-specific antigen messages. In this study, we investigated biological factors influencing the specificity of the CK19 and CEA RT-PCR assays. Bone marrow, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)-mobilized blood stem cells and peripheral blood samples obtained from healthy volunteers (n = 15; CEA n = 7), from patients with epithelial (n = 29) and haematological (n = 23) cancer and from patients with chronic inflammatory diseases (n = 16) were examined. Neither CEA nor cytokeratin 19 messages could be amplified from bone marrow samples from healthy subjects and from patients with haematological malignancies. In contrast, specimens from patients with inflammatory diseases scored positive up to 60%. To investigate the influence of inflammation on target mRNA expression, haemopoietic cells were cultured with and without cytokine stimulation in vitro. CK19 messages could be easily detected in cultured marrow cells without further stimulation, CEA messages only after gamma-interferon (gamma-INF) stimulation. In contrast, G-CSF-mobilized peripheral blood stem cells were positive for CK19 messages only after stem cell factor (SCF) or interleukin stimulation. We conclude that transcription of so-called tissue-specific genes is inductible in haemopoietic tissues under certain conditions. These factors have to be considered in future applications of RT-PCR for the detection of minimal residual disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, R., Krüger, W., Hosch, S. et al. Specificity of reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction assays designed for the detection of circulating cancer cells is influenced by cytokines in vivo and in vitro. Br J Cancer 78, 1194–1198 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1998.653
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1998.653
This article is cited by
-
Prognostic significance of CEACAM5mRNA-positive circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2018)
-
Digital-Direct-RT-PCR: a sensitive and specific method for quantification of CTC in patients with cervical carcinoma
Scientific Reports (2014)
-
Nucleic acid aptamers for clinical diagnosis: cell detection and molecular imaging
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2011)
-
Heterogeneous detection of circulating tumor cells in patients with colorectal cancer by immunomagnetic enrichment using different EpCAM-specific antibodies
BMC Biotechnology (2010)
-
Systemic inflammation as a confounding factor in cancer biomarker discovery and validation
Nature Reviews Cancer (2010)