Abstract
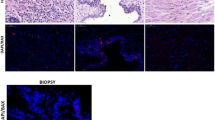
To explore the relationship between short-term effects of castration therapy and clinical response, biopsies obtained before and a week after castration therapy from 15 responding and 13 non-responding patients with prostate cancer were investigated. The biopsies were assessed for regressive morphology, apoptotic index by morphological criteria, nuclear area, and immunoreactivity (IR) for Ki-67, p53, bcl-2, bax and Fas. The index was defined as the percentage of immunoreactive cells in a tumour. Regressive morphology was observed in 14 out of 15 responding tumours after therapy, compared with 4 out of 13 non-responders (P < 0.001). Median tumour epithelial cell nuclear area and Ki-67 index decreased equally in both groups. The median apoptotic index increased from 2.6 to 3.5 after castration among responders (P < 0.05), whereas it remained at 2.8 among non-responders. p53 IR was present in three tumours before castration; after therapy p53 reactivity was seen in three additional tumours belonging to the responding group. Median bcl-2 index increased in responders from 1.5 to 10.0 (P < 0.05), and in non-responders from 0.08 to 2.7 (P < 0.05). Bax IR and Fas IR were present in all tumours before therapy and unchanged after therapy. Thus, regressive morphology and an increase in apoptotic index were related to a favourable clinical response. These data suggest that it might be possible to predict the effect of castration therapy by examining tumour biopsies shortly after treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stattin, P., Westin, P., Damber, JE. et al. Short-term cellular effects induced by castration therapy in relation to clinical outcome in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 77, 670–675 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1998.107
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1998.107