Abstract
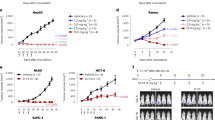
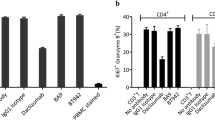
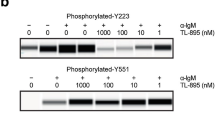
The c-erbB-2 product is thought to be a unique and useful target for antibody therapy of cancers overexpressing the c-erbB-2 gene. In vitro and in vivo anti-tumour effects of a humanised antibody against the extracellular domain of the c-erbB-2 gene product, rhu4D5, were examined. Rhu4D5 was less effective than its murine counterpart, mu4D5, for the direct antiproliferative activity against the c-erbB-2-overexpressing SK-BR-3 cell line. In vivo treatment of severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice carrying the c-erbB-2-overexpressing 4-1ST human gastric carcinoma xenograft with 4hu4D5 revealed that the recombinant protein had potent anti-tumour activity. Furthermore, cytotoxicity of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells against 4-1ST was significantly augmented with rhu4D5, but not with mu4D5. These results indicate that rhu4D5 might perform better in patients than predicted from preclinical studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tokuda, Y., Ohnishi, Y., Shimamura, K. et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-tumour effects of a humanised monoclonal antibody against c-erbB-2 product. Br J Cancer 73, 1362–1365 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1996.259
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1996.259
This article is cited by
-
Ex vivo dual gene therapy using human adipocytes secreting anti-HER2 antibody on HER2-positive xenograft tumor models
Breast Cancer (2023)
-
The role of trastuzumab in the management of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: an updated review
Breast Cancer (2009)
-
Correlation between NK function and response to trastuzumab in metastatic breast cancer patients
Journal of Translational Medicine (2008)
-
The role of hormonal therapy in the management of hormonal-receptor-positive breast cancer with co-expression of HER2
Nature Clinical Practice Oncology (2008)
-
Targeting the function of the HER2 oncogene in human cancer therapeutics
Oncogene (2007)