Abstract
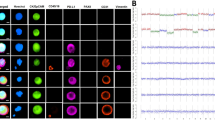
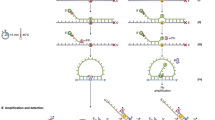
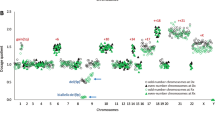
Detection of loss of heterozygosity (LOH) is usually performed on homogenised tumour specimens. In this type of analysis samples with a low percentage of tumour cells have to be excluded and possible intra-tumour heterogeneity is obscured. In this study we report the application of polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-driven LOH detection with in total 22 microsatellite markers for chromosome 1q, 3p, 3q, 4p, 6p, 6q, 11p, 11q, 17p, 17q, 18p, 18q, Xp and Xq on flow-sorted cells from fresh and paraffin-embedded ovarian tumour tissue. Titration experiments showed that LOH can be detected with as few as 100 cell equivalents of DNA. Clear examples of LOH could be detected in the sorted aneuploid fractions from one unilateral and two bilateral ovarian tumours from three patients. In two samples the sorted fraction was less than 10% of the total sample. The bilateral tumours from the same patient showed loss of identical alleles for one marker (case OV64) and two markers (case OV69), indicative of their monoclonal origin. Multiparameter flow cytometry using two different ovarian tumour markers (MOv18 and BMA180), an anti-cytokeratin monoclonal antibody (MAb) (M9), an anti-vimentin MAb (V9) and a MAb against the panepithelial antigen 17-1A on the fresh ascites cells of the fourth ovarian cancer patient was used to investigate possible intra-tumour heterogeneity. We showed the presence of at least three phenotypically different populations, of which the diploid, keratin-positive, vimentin-negative population showed a similar LOH pattern as the aneuploid population (DNA index = 1.7), indicative of its neoplastic origin. The same LOH pattern was shown in an omentum metastasis from this patient also having the same aneuploid DNA index of 1.7. The sharing of the same LOH pattern by the diploid and aneuploid tumour cell populations suggests that the observed allele loss events occurred before the development of aneuploidy. PCR on flow-sorted cells is thus an important tool to study clonal diversity in tumours.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abeln, E., Corver, W., Kuipers-Dijkshoorn, N. et al. Molecular genetic analysis of flow-sorted ovarian tumour cells: improved detection of loss of heterozygosity. Br J Cancer 70, 255–262 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1994.289
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1994.289
This article is cited by
-
Evolutionary perspectives, heterogeneity and ovarian cancer: a complicated tale from past to present
Journal of Ovarian Research (2022)
-
Novel cell enrichment technique for robust genetic analysis of archival classical Hodgkin lymphoma tissues
Laboratory Investigation (2018)
-
Cervical carcinoma-associated fibroblasts are DNA diploid and do not show evidence for somatic genetic alterations
Cellular Oncology (2011)
-
Expression of Smad2 and Smad4 in cervical cancer: absent nuclear Smad4 expression correlates with poor survival
Modern Pathology (2008)
-
Somatic loss of maternal chromosome 11 causes parent-of-origin-dependent inheritance in SDHD-linked paraganglioma and phaeochromocytoma families
Oncogene (2004)