Abstract
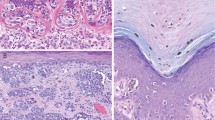
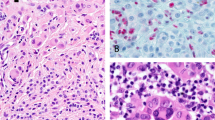
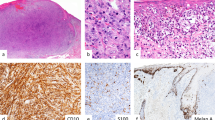
Clinical-pathologic-genetic studies were performed on 3 kindreds showing the familial atypical multiple mole-melanoma syndrome (FAMMM). Findings showed vertical transmission, including father-to-son, of cutaneous malignant melanoma and/or FAMMM moles with no sex predilection. A broad spectrum of clinical signs characterizing the phenotype ranged from an apparent lack of disease expression through minimal, moderate, and florid manifestations. An extreme example was a patient with 9 separate primary melanomas in 18 years. The FAMMM moles were histologically compound nevocellular nevi with varying degrees of dysplasia of the melanocytes, an increased occurrence of fibroplasia, and chronic inflammation within the papillary dermis. Of further interest was marked variation in the degree of dysplasia in moles between and within families. These observations, when coupled with recent reports by others, are consistent with an autosomal dominant gene showing markedly variable expressivity. Management of these patients is difficult, as one cannot be certain which moles require biopsy and then, following histological study, which will require wider excision. Studies of the FAMMM syndrome should deal carefully with its natural history, including the patient's lifelong susceptibility to multiply malignant melanomas, and the possibility that cancer of other anatomic sites may be integral components of this hereditary cancer syndrome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lynch, H., Fusaro, R., Pester, J. et al. Familial atypical multiple mole melanoma (FAMMM) syndrome: genetic heterogeneity and malignant melanoma. Br J Cancer 42, 58–70 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1980.203
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1980.203
This article is cited by
-
Präkanzerosen und Malignome des Gastrointestinaltrakts
coloproctology (2021)
-
Familial atypical multiple mole melanoma (FAMMM) syndrome: history, genetics, and heterogeneity
Familial Cancer (2016)
-
Melanoma susceptibility as a complex trait: genetic variation controls all stages of tumor progression
Oncogene (2015)