Abstract
Aim:
Pregnane X receptor (PXR) is a nuclear receptor that regulates a number of genes encoding drug metabolism enzymes and transporters and plays a key role in xeno- and endobiotic detoxification. Ginkgolide B has shown to increase the activity of PXR. Here we examined whether ginkgolide B activated PXR and attenuated xenobiotic-induced injuries in endothelial cells.
Methods:
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were treated with ginkgolide B. The expression of PXR, CYP3A4, MDR1, VCAM-1, E-selectin and caspase-3 were quantified with qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis. Cell apoptosis was analyzed with flow cytometry. Fluorescently labeled human acute monocytic leukemia cells (THP-1 cells) were used to examine cell adhesion.
Results:
Ginkgolide B (30–300 μmol/L) did not change the mRNA and protein levels of PXR in the cells, but dose-dependently increased nuclear translocation of PXR protein. Ginkgolide B increased the expression of CYP3A4 and MDR1 in the cells, which was partially reversed by pretreatment with the selective PXR signaling antagonist sulforaphane, or transfection with PXR siRNA. Functionally, ginkgolide B dose-dependently attenuated doxorubicin- or staurosporine-induced apoptosis, which was reversed by transfection with PXR siRNA. Moreover, ginkgolide B suppressed TNF-α-induced THP-1 cell adhesion and TNF-α-induced expression of vascular adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) and E-selectin in the cells, which was also reversed by transfection with PXR siRNA.
Conclusion:
Ginkgolide B exerts anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects on endothelial cells via PXR activation, suggesting that a PXR-mediated endothelial detoxification program may be important for protecting endothelial cells from xeno- and endobiotic-induced injuries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The pregnane X receptor (PXR) is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily of ligand-activated transcription factors and has been characterized as a xenobiotic sensor that is activated by structurally diverse compounds including herbal medicines, drugs, environmental contaminants and endogenous compounds like vitamins, oxysterols, and steroid hormones1,2. PXR has been detected in various tissues. Specifically, it is highly expressed in the liver, small intestine and colon and expressed at low levels in the kidney, stomach, testes, skeletal muscle, and adrenal gland3. As a ligand-activated transcriptional factor, PXR regulates a large array of genes that regulate drug metabolism including the Phase I cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP2C9 and CYP3A4, the Phase II enzymes uridine-5-diphosphate glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs), sulfotransferases (SULTs), glutathione S-transferases (GSTs), and drug transporters, such as multidrug resistance 1 (MDR1) and multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1; also known as ABCC1)4,5. Therefore, PXR plays a central role in defending the body from xenobiotic and endobiotic insults by eliminating metabolites. In addition to its defense against chemical insults by transforming and eliminating them from the body, recent studies indicate that PXR plays an endobiotic role by regulating energy homeostasis under various physiological and pathological conditions, including lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, thyroid hormone synthesis, bile acid homeostasis and inflammation6,7. Numerous CYPs are expressed in endothelial cells and are potentially regulated by PXR, which is also expressed in endothelial cells. This regulation of drug-detoxifying enzymes and transporters suggests that PXR may be a novel gatekeeper for endothelial defense8.
Ginkgolide B is a major terpene lactone and an active component of Ginkgo biloba9. Previous studies indicated that ginkgolide B exhibits many pharmacological properties, including anti-oxidant10, anti-inflammatory11,12,13, anti-tumor14, and anti-apoptotic activity12,15,16. Due to the widespread use of Ginkgo biloba extract as a supplement, its effects on drug metabolizing enzymes are of interest. Recent research revealed that Ginkgo biloba extract and ginkgolide A distinctively induced CYP3A2, CYP3A18 and CYP2B1 expression in primary rat hepatocytes17. Moreover, ginkgolide A induced CYP3A expression and enhanced acetaminophen toxicity in rat hepatocytes18. Ginkgolide B increased the expression of several major CYP enzymes (CYP3A4 and CYP2B6) in cultured human hepatocytes19, and it has been reported to activate PXR20,21,22. Our previous work demonstrated that ginkgolide B can increase the transcriptional activity of PXR in vitro in a cell-based reporter gene assay23. However, the pharmacological properties of ginkgolide B, especially the cardiovascular protective effects of ginkgolide B associated with PXR activation, are poorly understood. Thus, we investigated the ability of ginkgolide B to protect endothelial cells via the activation of PXR from injuries induced by xeno- and endobiotics.
Materials and methods
Drugs and reagents
Ginkgolide B (purity: 98% by HPLC) was obtained from the National Institutes for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products (Beijing, China). Rifampicin and staurosporine were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA). Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 medium (RPMI-1640) and fetal bovine serum (FBS) were purchased from HyClone (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Human recombinant TNF-α was obtained from Detroit R&D, Inc (Detroit, MI, USA). TRIzol reagent was obtained from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). TransScript™ First-Step RT-PCR SuperMixFas and SYBR® Green Master Mix were purchased from TransGen Biotech Co Ltd (Beijing, China). Rabbit monoclonal VCAM-1 antibody was purchased from Abcam (Rab MAb, CA, USA). Rabbit monoclonal PXR antibody and rabbit monoclonal E-selectin and histone antibodies were purchased from Millipore Corporation (Millipore, CA, USA). Sheep monoclonal pro-caspase 3 antibody was obtained from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA). Sheep anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody was obtained from Southern Biotech (SBA, Birmingham, AL, USA). BCA was obtained from Applygen Technologies Inc (Beijing, China). Unless otherwise specified, all other reagents were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA).
Cell cultures and treatment
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and THP-1 (a human acute monocytic leukemia cell line) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) (Manassas, VA, USA). The cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS and grown in a humidified incubator containing 5% CO2 at 37 °C. Ginkgolide B or RIF was dissolved in DMSO and diluted with RPMI-1640. The final concentration of DMSO never exceeded 1‰ of the total culture volume. The cells were seeded in 6-, 12-, or 24-well culture plates for each experiment and treated with various concentrations of ginkgolide B for different durations.
RNA isolation and quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR analysis
RNA was isolated, and mRNA expression was assessed using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) as described previously23. Briefly, total RNA was isolated from HUVECs using TRIzol reagent according to the manufacturer's instructions. Total RNA with an OD260/OD280 between 1.8 and 2.0 was used for qRT-PCR. The cDNAs were synthesized using a Transcriptor First-strand cDNA Synthesis Kit. Real-time PCR reactions were performed on a TransScript™ SYBR@ Green Master Mix TransScript™ SYBR@ Green Master Mix in ABI Prism 7500 real-time PCR instrument (Applied Biosystems, Foster, CA, USA), with GAPDH as an internal control. The primer sequences are shown in Table 1.
Preparation of total protein and Western-blot
Western blots were performed as described previously24. Briefly, the cytoplasmic and nuclear protein fractions were extracted using NE-PERTM Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Extraction Reagents (Thermo Scientific, USA). Briefly, cells were harvested and washed twice with PBS, followed by the addition of ice-cold cytoplasmic extraction reagent I. The cells were then vigorously vortexed for 15 s before the addition of ice-cold cytoplasmic extraction reagent II. The samples were centrifuged (500×g) for 5 min and immediately transferred to a pre-chilled tube (cytoplasmic extract). The insoluble fraction, which contained nuclei, was then suspended with ice-cold nuclear extraction reagent, vortexed for 15 s and centrifuged for 10 min (500×g) to obtain a supernatant (nuclear extract). The protein concentration was measured using a BCA protein assay kit. Protein samples were separated using 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (Millipore). Subsequently, membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk for 1 h and incubated overnight at 4 °C with specific primary antibodies. The blots were then incubated with secondary antibody at room temperature for 1 h. Protein bands were revealed with Super Singal West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate (Thermo Scientific, USA) and visualized with ImageQuant LAS 500 (Healthcare Bio-Sciences AB, USA).
RNA Interference
The small interfering (si) RNA against human PXR and negative control non-silencing RNA were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). The target sequences of siPXR are as follows: Forward 5′-GAUGGACGCUCAGAUGAAATT-3′ and Reverse 5′-UUUCAUCUGAGCGUCCAUCTT-3′. The cells were transfected according to a previously described procedure. Briefly, HUVECs were seeded in 24-well plates and incubated overnight in RPMI-1640 medium before being transfected with negative control siRNA or the indicated siRNA (100 nmol/L) for 48 h using the Silencer siRNA Transfection agent II Kit (Invitrogen, USA).
Analysis of apoptosis
HUVECs were trypsinized, washed twice with cold PBS, and resuspended in binding buffer. FITC-conjugated annexin V (0.5 μg/mL) and propidium iodide (50 μg/mL) were added according to the manufacturer's protocol. The samples were then analyzed with a FACStar-Plus flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and the FlowJo (TreeStar) software for acquisition and analysis.
Pro-inflammatory response
HUVECs were pretreated with various concentrations of ginkgolide B or rifampicin (20 μmol/L) for 24 h before exposure to TNF-α (10 ng/mL, 4 h). The HUVECs were then incubated with calcein-AM-labeled THP-1 cells (5×105 cells/mL) for 15–30 min at 37 °C. After washing off the non-adherent cells with PBS, the HUVECs and THP-1 cells were counted under a fluorescent microscope (AXIOVERT 200, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
Statistical analysis
The GraphPad Prism software version 4.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) was used to analyse the results. Data are presented as mean±SEM. A Student's t-test (paired groups) or one-way ANOVA followed by the Newman-Keuls test (multi group comparisons) was used to analyze the significance of differences. P<0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Effect of ginkgolide B on PXR expression
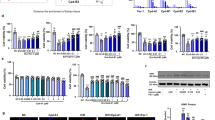
We previously used a transient luciferase expression assay to screen the transcriptional activity of PXR in response to the natural product ginkgolide B. Specifically, 30, 60, and 150 μmol/L ginkgolide B increased luciferase expression at 24 and 48 h23. To confirm the effect of ginkgolide B on PXR expression, HUVECs were treated with ginkgolide B (30, 150, or 300 μmol/L) or rifampicin (10 μmol/L, positive control) for 24 h. The mRNA expression of PXR was analyzed with qRT-PCR. Figures 1A and 1B show that neither treatment affected PXR mRNA expression. However, previous work indicates that PXR, a nuclear receptor, is localized to the cytoplasm and can translocate into the nucleus after ligand treatment25. Thus, the nuclear and cytosolic protein fractions were extracted from HUVECs treated with ginkgolide B and a nuclear translocation assay was performed. The data show that nuclear PXR protein expression increased after treatment with ginkgolide B compared with controls (Figure 1C), suggesting that ginkgolide B can activate PXR, although it does not affect PXR expression.
Ginkgolide B regulates PXR activity in HUVECs. HUVECs were treated with ginkgolide B (30, 150, and 300 μmol/L) for 24 h, and RIF treatment was a positive control. (A) PXR mRNA was measured by qRT-PCR. (B) Protein expression was measured with Western blot. (C) The nuclear and cytosolic PXR protein expression levels were quantified by Western blot analysis. Histone and β-actin were internal controls for nuclear and cytosolic protein, respectively. Data are shown as mean±SEM. n=3. aP>0.05, bP<0.05 vs control group.
Effect of Ginkgolide B on CYP3A4 and MDR1 mRNA expression
To confirm that ginkgolide B can activate PXR, we measured the effect of ginkgolide B on the mRNA expression levels of CYP3A4 and MDR1, which are target genes regulated by PXR. Cells were treated with ginkgolide B (30, 150, or 300 μmol/L) or rifampicin (10 μmol/L, positive control) for 24 and 48 h. qRT-PCR was used to measure CYP3A4 and MDR1 mRNA expression. CYP3A4 mRNA expression increased after 24 h of treatment with ginkgolide B, and this effect was dose-dependent after 48 h (Figure 2A). Likewise, treatment with ginkgolide B induced MDR1 expression at 24 h. Similar changes were observed at 48 h compared with the control group (Figure 2B). The mRNA expression levels of CYP3A4 and MDR1 in response to 150 μmol/L ginkgolide B were measured over time. Specifically, ginkgolide B induced the expression of MDR1 mRNA in a time-dependent manner from 6 to 48 h. Similarly, CYP3A4 expression was increased, peaking at 36 h of incubation and decreasing at 48 h (Figure 2C, 2D).
Ginkgolide B upregulates CYP3A4 and MDR1 mRNA expression via PXR activation. (A, B) Cells were treated with ginkgolide B (30, 150, or 300 μmol/L) for 24 and 48 h; RIF treatment served as a positive control. (C, D) Cells were treated with ginkgolide B (150 μmol/L) for 6 to 48 h. (E, F) HUVECs were pretreated with SFN (10 μmol/L) for 24 h and then treated with ginkgolide B for 24 h. (G, H) Cells were transfected with PXR siRNA and exposed to ginkgolide B for 48 h later. The CYP3A4 and MDR1 mRNA expression levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR. Data are expressed as mean±SEM. n=3–5. aP>0.05, bP<0.05, cP<0.01 vs control group. eP<0.05, fP<0.01 vs SFN group. hP<0.05 vs PXR siRNA group.
To explore whether the effect of ginkgolide B on CYP3A4 and MDR1 expression is associated with PXR activation, cells were pretreated with sulforaphane (SFN, 10 μmol/L), a selective PXR signaling antagonist26 for 24 h and incubated with ginkgolide B (30, 150, or 300 μmol/L) for another 24 h. SFN reduced CYP3A4 and MDR1 expression compared with the controls. Additionally, the ginkgolide B-induced increases in CYP3A4 and MDR1 expression were abolished by SFN (Figure 2E and 2F). Knocking down PXR expression with a specific siRNA, we verified the involvement of PXR in ginkgolide B's ability to increase CYP3A4 and MDR1 expression. Figure 2G and 2H indicted that silencing PXR expression reduced CYP3A4 and MDR1 expression. Moreover, PXR siRNA diminished the ginkgolide B-induced increases in CYP3A4 and MDR1 expression. Therefore, ginkgolide B can induce CYP3A4 and MDR1 mRNA expression by activating PXR.
Ginkgolide B attenuated apoptosis induced by xenobiotics in HUVECs
Ginkgolide B can activate PXR. To characterize how ginkgolide B affects apoptosis via PXR, the functional role of PXR in HUVECs treated with staurosporine (ST) and doxorubicin (DOX), both of which are documented to cause endothelial apoptosis, was examined with flow cytometry27. HUVECs were pretreated with 30, 50, or 150 μmol/L of ginkgolide B for 24 h and then treated with 500 nmol/L of ST for an additional 6 h. The positive control cells for this group were treated with only ST for 6 h. Another group of cells was pretreated with ginkgolide B for 24 h and then treated with 5 μmol/L DOX for 24 h. The positive control cells for this group were treated only with DOX for 24 h. Flow cytometry confirmed that ginkgolide B pretreatment reduced ST-induced apoptosis compared with the positive controls, which exhibited marked apoptosis compared with negative controls (Figure 3A). Figure 3B shows that DOX induced apoptosis (about 12%), but ginkgolide B did not affect this apoptosis.
Ginkgolide B attenuates HUVEC apoptosis. (A) HUVECs were pretreated with ginkgolide B (30, 150, or 300 μmol/L) for 24 h in the presence or absence of PXR siRNA and then treated with 500 nmol/L of ST for an additional 6 h. Positive control cells were treated with ST alone for 6 h. (B) Cells were pretreated with ginkgolide B for 24 h and then treated with 5 μmol/L of DOX for an additional 24 h. Positive control cells were treated with DOX alone for 24 h. (C) Cells were transfected with PXR siRNA and exposed to ginkgolide B for 24 h 48 h later; cells were treated with DOX for an additional 24 h. Apoptosis was assessed with flow cytometry for annexin V-FITC. (D) The intracellular DOX concentration was measured based on the fluorescence intensity in HUVECs pretreated with ginkgolide B in the presence or absence of PXR siRNA before exposure to DOX using flow cytometry. (E, F) Caspase 3 cleavage was measured with Western blotting. Data shown are mean±SEM. n=3–6. bP<0.05, cP<0.01 vs control group. dP>0.05, eP<0.05 vs MOCK group. hP< 0.05 vs PXR siRNA group.
To study the mechanism by which ginkgolide B-induced PXR expression detoxifies cells, PXR expression was silenced with siRNA. This silencing diminished the protective effect of ginkgolide B in HUVECs compared with cells treated with scrambled siRNA (Figure 3A). Knocking down PXR increased DOX-induced apoptosis by ∼25%, and ginkgolide B prevented DOX-mediated apoptosis (Figure 3C). We then evaluated the intracellular accumulation of DOX with flow cytometry and noted that DOX was decreased in HUVECs treated with ginkgolide B and rifampicin; however, DOX accumulation increased after PXR expression was knocked down (Figure 3D). Thus, PXR targets MDR1, which is responsible for DOX efflux. Consistent with earlier findings, a Western blot confirmed that ginkgolide B, as well as rifampicin, decreased caspase-3 cleavage induced by ST or DOX (Figure 3E, 3F).
Ginkgolide B suppressed Pro-inflammatory response in HUVECs
We investigated whether the ginkgolide B exerted a pro-inflammatory effect via PXR activation. HUVECs were pretreated with 30, 50, or 150 μmol/L of ginkgolide B for 24 h and then treated with 10 ng/mL of TNF-α for an additional 4 h. Positive control cells were only treated with TNF-α for 4 h. Figures 4A and 4B show that TNF-α increased the adhesion of THP-1, a human acute monocytic leukemia cell line, by ∼ 8-fold compared with the controls. Conversely, pretreatment with ginkgolide B dose-dependently inhibited the adhesion of THP-1. To rule out a potential PXR-independent anti-inflammatory effect of ginkgolide B, we knocked down PXR expression with a specific siRNA. The data show that silencing PXR expression abolished the ability of ginkgolide B to inhibit the adhesion of THP-1 induced by TNF-α (Figure 4C, 4D).
Ginkgolide B suppresses pro-inflammatory response in HUVECs. HUVECs pretreated with ginkgolide B (30, 150, or 300 μmol/L) for 24 h in the absence (A, B) or presence (C, D) of PXR siRNA before exposure to TNF-α (10 ng/mL). HUVECs were then incubated with fluorescently labeled THP-1 cells (5×105 cells/mL) for 30 min. THP-1 adhesions were counted under a fluorescent microscope. Bar=10 μm. Data shown are as mean±SEM. n=8. cP<0.01 vs control. dP>0.05, eP<0.05 vs MOCK group. AM: under calcein-AM fluorescence; Normal: under normal light.
Finally, we measured the gene expression of vascular adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) and E-selectin using qRT-PCR. Figures 5A and 5B show that treatment with TNF-α alone increased VCAM-1 and E-selectin mRNA expression by ∼3.9- and 5.2-fold, respectively. Pretreatment with different concentrations (30, 150, or 300 μmol/L) of ginkgolide B significantly attenuated the effects of TNF-α. Interestingly, siRNA-mediated PXR knockdown abrogated the suppressive effects of ginkgolide B on E-selectin and VCAM-1 expression (Figure 5A, 5B). Consistent with the changes in mRNA expression, the pretreatment of HUVECs with ginkgolide B inhibited the up-regulation of VCAM-1 and E-selectin protein expression induced by TNF-α (Figure 5C). However, transfection with PXR siRNA diminished ginkgolide B's ability to inhibit VCAM-1 and E-selectin protein expression induced by TNF-α (Figure 5D). Thus, ginkgolide B suppressed the pro-inflammatory response in HUVECs in a PXR-dependent manner.
Ginkgolide B suppresses pro-inflammatory response factors in HUVECs. (A–D) HUVECs pretreated with ginkgolide B (30, 150, or 300 μmol/L) for 24 h in the presence or absence of PXR siRNA before exposure to TNF-α (10 ng/mL). (A, B) VCAM-1 and E-selectin mRNA were measured by qRT-PCR. (C, D) VCAM-1 and E-selectin protein expression was measured with Western blot. Data shown are mean±SEM. n=3. cP<0.01 vs control. dP>0.05, eP<0.05 vs MOCK group. hP<0.05 vs PXR siRNA group. MOCK' group: MOCK+siRNA.
Discussion
In this study, we provide evidence to show that ginkgolide B protects HUVECs from injuries via PXR activation. Ginkgolide B-induced PXR activation facilitates endothelial detoxification by inducing the transcription of phase I and phase II cytochrome P450 enzymes and efflux proteins and may have therapeutic potential for cardiovascular diseases.
PXR has identified as an important therapeutic target28 because of its central role in defending cells against xeno- and endobiotic insults by eliminating metabolites via the modulation of drug-detoxifying enzymes and drug transporters. Recent studies indicate that PXR is important for regulating apoptosis and inflammatory processes. PXR can inhibit xenobiotic-induced apoptosis in mouse epithelium and endothelium cells as well as in PXR transgenic mice27,29. A PXR-KO mouse model exhibited elevated levels of markers of small bowel inflammation compared with wild-type mice, and the expression levels of several key NF-κB target genes were significantly increased, including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), and prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (COX-2)30,31. The ligand-mediated activation of PXR inhibited the LPS-induced expression of pro-inflammatory in human or mouse primary hepatocytes32. Furthermore, PXR regulates glucose and lipid metabolism33 and has been shown to regulate the secretion of and sensitivity to insulin; PXR ligands reduce the levels of lipids and glucose in murine diabetes models34. PXR has also been shown to protect against oxidative stress-induced cytotoxicity by activating total GST and GPx and coordinating an antioxidant response in vascular cells8. However, the role of PXR in the inhibition of the inflammatory response by ginkgolide B has not yet been demonstrated, although a relationship between the two has been established. As previously shown, ginkgolide B protects the endothelium in numerous ways, including by exerting anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects. These effects are predominantly due to the blocking of pathologic signaling pathways activated by xeno- and endotoxins. We show that the anti-inflammatory role of ginkgolide B in the TNF-α-elicited inflammatory response in HUVECs is related to the inhibition of E-selectin and VCAM-1 expression. Moreover, knocking down PXR expression by siRNA completely abolished ginkgolide B's ability to attenuate inflammation (Figure 4). This PXR activation is key to the inhibition of inflammation in HUVECs by ginkgolide B.
Multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1 or ABCB1), which belongs to the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily, has been demonstrated to act as an efficient toxin efflux molecule to protect human tissues from drugs and other xenobiotics35. Here, we show that ginkgolide B increased MDR1 mRNA expression (Figure 2B, 2D). Previous work confirmed that Ginkgo biloba extract was able to induce the mRNA and protein expression of MDR1 and increase its functional activity20. PXR has been shown to directly regulate the transcriptional activation of MDR136. Moreover, we observed that SFN diminished the ginkgolides B-induced expression of MDR1 mRNA, a selective PXR signaling antagonist (Figure 2F). PXR knockdown with PXR siRNA also significantly attenuated the ginkgolide B-induced expression of MDR1 (Figure 2H), indicating that MDR1 is regulated by PXR in HUVECs. In this study, ginkgolide B likely protected endothelial cells from DOX-induced apoptosis by activating the PXR target MDR1 because MDR1 plays a critical role in multidrug resistance. Ginkgolide B also significantly reduced HUVEC apoptosis induced by ST (Figure 3A) but did not significantly affect DOX-induced apoptosis (Figure 3B). DOX is an anthracycline antibiotic commonly used in cancer chemotherapy and a substrate for ABC-mediated drug efflux37, and enhanced DOX-induced apoptosis via the down-regulation of PXR and MDR1 has been reported to be a novel therapeutic approach for cancer38,39. Thus, we suspected that MDR1 protein promotes the intracellular efflux of DOX in HUVECs and ginkgolide B enhanced this effect. We further measured the intracellular accumulation of DOX with flow cytometry and noted it was decreased in HUVECs treated with ginkgolide B compared with controls (Figure 3D). This reduced accumulation may be responsible for the modest DOX-induced apoptosis and the lack of effect of ginkgolide B on this apoptosis. Importantly, siRNA-mediated PXR knockdown abrogated the intracellular efflux of DOX in HUVECs (Figure 3D) and increased DOX-induced apoptosis by ∼25% but ginkgolide B prevented this apoptosis (Figure 3C). Therefore, another signaling pathway or transcription factor may participate in the effects of ginkgolide B on apoptosis. For example, Ginkgo biloba extract can activate several nuclear hormone receptors, including PXR, the constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR)21. Ginkgolides B may affect inflammation, apoptosis and lipid metabolism and trafficking via any of these receptors. However, PXR siRNA significantly attenuated the ability of ginkgolide B to reduce ST-induced apoptosis (Figure 3A), indicating that PXR, at least in part, plays a functional role in ginkgolide B-mediated detoxification. The details of this process warrant further investigation.
The mechanism by which ginkgolide B activates PXR in HUVECs is poorly understood. TNF-α signaling was previously reported to increase the SUMOylation of the PXR ligand via the incorporation of SUMO3 chains in hepatocytes, and the SUMOylated form of the PXR protein inhibits NF-κB target gene expression40. Recently, PXR was reported to be cytoplasmic and undergo nuclear translocation upon ligand activation to bind to the promoter region of target genes, increasing gene transcription in mouse hepatocytes41. Similarly, we found that after activation by ginkgolide B, PXR translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus (Figure 1C). A nuclear localization signal was also observed in PXR42, although the molecular mechanism responsible for this signal is unknown. We also observed that ginkgolide B did not significantly affect PXR mRNA and protein expression (Figure 1A, 1B). In addition, PXR activity can be regulated by a series of posttranscriptional modifications, such as phosphorylation, acetylation and sumoylation. The contributions of these modifications to the regulation of PXR activity by ginkgolide B in HUVECs will be a topic of future research.
In conclusion, we confirmed that ginkgolide B activates an important nuclear hormone receptor PXR, and that ginkgolide B induced the expression of CYP3A4 and MDR1 in a PXR-dependent manner. The anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of ginkgolide B in endothelial cells depend on PXR activation, providing further evidence that a PXR-mediated endothelial detoxification program may protect endothelial cells from xeno- and endobiotic injury and may be a potential therapeutic target. More studies are needed to assess the physiological significance of ginkgolide B-activated PXR in animal models using PXR overexpression or a knockout approach.
Author contribution
Tao ZHOU and Wen-ting YOU performed most of the experiments, analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript; Zeng-chun MA and Yu-guang WANG performed some of the experiments and statistical analysis; Qian-de LIANG, Xiang-lin TANG, Hong-ling TAN and Cheng-rong XIAO assisted in the experiments; Bo-li ZHANG and Yue GAO designed the study and reviewed the manuscript.
References
Lehmann JM, Mckee DD, Watson MA, Willson TM, Moore JT, Kliewer SA . The human orphan nuclear receptor PXR is activated by compounds that regulate CYP3A4 gene expression and cause drug interactions. J Clin Invest 1998; 102: 1016–23.
Mani S, Dou W, Redinbo MR . PXR antagonists and implication in drug metabolism. Drug Metab Rev 2013; 45: 60–72.
Nishimura M, Naito S, Yokoi T . Tissue-specific mRNA expression profiles of human nuclear receptor subfamilies. Drug Metab Pharmacokin 2004; 19: 135–49.
Kliewer SA, Goodwin B, Willson TM . The nuclear pregnane X receptor: a key regulator of xenobiotic metabolism. Endocrine Rev 2002; 23: 687–702.
Verma S, Tabb MM, Blumberg B . Activation of the steroid and xenobiotic receptor, SXR, induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2009; 9: 3.
Zhou C, Verma S, Blumberg B . The steroid and xenobiotic receptor (SXR), beyond xenobiotic metabolism. Nucl Recept Signal 2009; 7: e001.
Gao J, Xie W . Targeting xenobiotic receptors PXR and CAR for metabolic diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2012; 33: 552–8.
Swales KE, Moore R, Truss NJ, Tucker A, Warner TD, Negishi M, et al. Pregnane X receptor regulates drug metabolism and transport in the vasculature and protects from oxidative stress. Cardiovasc Res 2012; 93: 674–81.
Maclennan KM, Darlington CL, Smith PF . The CNS effects of Ginkgo biloba extracts and ginkgolide B. Prog Neurobiol 2002; 67: 235–57.
Wang GG, Chen QY, Li W, Lu XH, Zhao X . Ginkgolide B increases hydrogen sulfide and protects against endothelial dysfunction in diabetic rats. Croatian Med J 2015; 56: 4–13.
Chu X, Ci X, He J, Wei M, Yang X, Cao Q, et al. A novel anti-inflammatory role for ginkgolide B in asthma via inhibition of the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. Molecules 2011, 16: 7634–48.
Gu JH, Ge JB, Li M, Wu F, Zhang W, Qin ZH . Inhibition of NF-kappaB activation is associated with anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of Ginkgolide B in a mouse model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur J Pharm Sci 2012; 47: 652–60.
Zhang S, Chen B, Wu W, Bao L, Qi R . Ginkgolide B reduces inflammatory protein expression in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-stimulated human vascular endothelial cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2011; 57: 721–7.
Chan WH, Hsuuw YD . Dosage effects of Ginkgolide B on ethanol-induced cell death in human hepatoma G2 cells. N Y Acad Sci U S A 2007; 1095: 388–98.
Qin XF, Lu XJ, Ge JB, Xu HZ, Qin HD, Xu F . Ginkgolide B prevents cathepsin-mediated cell death following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neuroreport 2014; 25: 267–73.
Wu X, Zhou C, Du F, Lu Y, Peng B, Chen L, et al. Ginkgolide B preconditioning on astrocytes promotes neuronal survival in ischemic injury via up-regulating erythropoietin secretion. Neurochem Int 2013; 62: 157–64.
Thomas KH, Chen J, Teng XW . Distinct role of bilobalide and Ginkgolide a in the modulation of rat CYP2B1 and CYP3A23 gene expression by ginkgo bilobae extract in cultured hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos 2005; 34: 234–42.
Rajaraman G, Chen J, Thomas KH . Ginkgolide A contributes to the potentiation of acetaminophen toxicity by Ginkgo biloba extract in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2006; 217: 225–33.
Deng Y, Bi HC, Zhao LZ, Wang XD, Chen J, OU ZM, et al. Induction of cytochrome P450 3A by the Ginkgo biloba extract and bilobalides in human and rat primary hepatocytes. Drug Metab Lett 2008; 2: 60–6.
Satsu H, Hiura Y, Mochizuki K, Hamada M, Shimizu M . Activation of pregnane X receptor and induction of MDR1 by dietary phytochemicals. J Agric Food Chem 2008; 56: 5366–73.
Li L, Stanton JD, Tolson AH, Luo Y, Wang H . Bioactive terpenoids and flavonoids from Ginkgo biloba extract induce the expression of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes through pregnane X receptor, constitutive androstane receptor, and aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated pathways. Pharm Res 2009; 26: 872–82.
Lau AJ, Yang G, Yap CW, Chang TK . Selective agonism of human pregnane X receptor by individual ginkgolides. Drug Metab Dispos 2012; 40: 1113–21.
Zhou T, Wang YG, Xiao Y, Tang XL, Liang QD, Xiao CR, et al. Ginkgolide B induces CYP3A4 expression through activation of human pregnane X receptor. Chin Pharmacol Bull 2014; 30: 926–31.
Wang YG, Zhou JM, Ma ZC, Li H, Liang QD, Tan HL, et al. Pregnane X receptor mediated-transcription regulation of CYP3A by glycyrrhizin: a possible mechanism for its hepatoprotective property against lithocholic acid-induced injury. Chem Biol Interact 2012; 200: 11–20.
Yang J, Hao C, Yang D, Shi D, Song X, Luan X, et al. Pregnane X receptor is required for interleukin-6-mediated down-regulation of cytochrome P450 3A4 in human hepatocytes. Toxicol Lett 2010; 197: 219–26.
Poulton EJ, Levy L, Lampe JW, Shen DD, Tracy J, Shuhart MC, et al. Sulforaphane is not an effective antagonist of the human pregnane X-receptor in vivo. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2013; 266: 122–31.
Wang XH, Fang X, Zhou J, Chen Z, Zhao BL, Xiao L, et al. Shear stress activation of nuclear receptor PXR in endothelial detoxification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013; 110: 13174–9.
Levi M, Wang XX, Choudhury D . Nuclear hormone receptors as therapeutic targets. Contrib Nephrol 2011; 170: 209–16.
Zhou J, Liu M, Zhai Y, Xie W . The antiapoptotic role of pregnane X receptor in human colon cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol 2008; 22: 868–80.
Zhou C, Tabb MM, Nelson EL, Grun F, Verma S, Sadatrafiei A, et al. Mutual repression between steroid and xenobiotic receptor and NF-kappaB signaling pathways links xenobiotic metabolism and inflammation. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 2280–9.
Sun M, Cui W, Woody SK, Staudinger JL . Pregnane X receptor modulates the inflammatory response in primary cultures of hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos 2015; 43: 335–43.
Kittayaruksakul S, Zhao W, Xu M, Ren S, Lu J, Wang J, et al. Identification of three novel natural product compounds that activate PXR and CAR and inhibit inflammation. Pharm Res 2013; 30: 2199–208.
Francis GA, Fayard E, Picard F, Auwerx J . Nuclear receptors and the control of metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol 2003; 65: 261–311.
Gao J, Xie W . Pregnane X receptor and constitutive androstane receptor at the crossroads of drug metabolism and energy metabolism. Drug Metab Dispos 2010; 38: 2091–5.
Ueda K, Cardarelli C, Gottesman MM, Pastan I . Expression of a full-length cDNA for the human “MDRI” gene confers resistance to colchicine, doxorubicin, and vinblastine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1987; 84: 3004–8.
Synold TW, Dussault I, Forman BM . The orphan nuclear receptor SXR coordinately regulates drug metabolism and efflux. Nat Med 2001; 7: 584–90.
Peetla C, Bhave R, Vijayaraghavalu S, Stine A, Kooijman E, Labhasetwar V . Drug resistance in breast cancer cells: biophysical characterization of and doxorubicin interactions with membrane lipids. Mol Pharm 2010; 7: 2334–48.
Masuyama H, Nakatsukasa H, Takamoto N, Hiramatsu Y . Down-regulation of pregnane X receptor contributes to cell growth inhibition and apoptosis by anticancer agents in endometrial cancer cells. Mol Pharm 2007; 72: 1045–73.
Wang Z, Yang L, Xia Y, Guo C, Kong L . Icariin enhances cytotoxicity of doxorubicin in human multidrug-resistant osteosarcoma cells by inhibition of ABCB1 and down-regulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Biol Pharm Bull 2015; 38: 277–84.
Hu G, Xu C, Staudinger JL . Pregnane X receptor is SUMOylated to repress the inflammatory response. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2010; 335: 342–50.
Kawana K, Ikuta T, Kobayashi Y, Gotoh O, Takede K, Kawajiri K . Molecular mechanism of nuclear translocation of an orphan nuclear receptor, SXR. Mol Pharm 2003; 63: 524–31.
Biswas A, Pasquel D, Tyagi RK, Mani S . Acetylation of pregnane X receptor protein determines selective function independent of ligand activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011; 406: 371–6.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (“973 Program”, No 2011CB505304 and 2012CB518402) and the Scientific and Technological “New Drug Creation” Major Project (Grant No 2009ZX09501-304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, T., You, Wt., Ma, Zc. et al. Ginkgolide B protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells against xenobiotic injuries via PXR activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37, 177–186 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.124
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.124
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Ginkgolide B Suppresses TPA-induced Metastatic Potential in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells by Inhibiting MAPK/AP-1 Signaling
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering (2022)
-
Functions of pregnane X receptor in self-detoxification
Amino Acids (2017)