Abstract
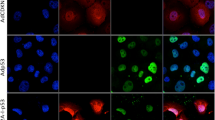
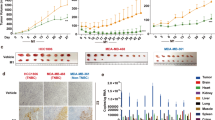
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising anticancer agent, which selectively induces apoptosis in many transformed cells without apparent toxic side effects in normal tissue. We recently described the construction and characterization of a lentiviral vector for expression of TRAIL. In this report, we evaluate its suitability for therapeutic application. In vitro, we observed specific induction of apoptosis upon transduction in human lung cancer cells. Cell death was partially dependent on successful integration and TRAIL expression by the vectors, but was to some extent mediated by protein carryover, as we found TRAIL protein associated with virus particles. Transduction of subcutaneously growing lung tumors on nude mice with lentiviral TRAIL mediated a transient suppression of tumor growth. Analysis of tumor sections revealed that transduction efficiency of lentiviral control vector but not of lentiviral TRAIL vector was high. This was because of the direct cytotoxic activity of recombinant TRAIL present in viral particles, which prevented efficient tumor transduction. These data therefore suggest that enveloped viral vectors constitutively expressing TRAIL are well suited for ex vivo applications, such as the transduction of tumor-homing cells, but may have a lower effect when used directly for the transduction of tumor cells in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smyth MJ, Takeda K, Hayakawa Y, Peschon JJ, van den Brink MR, Yagita H . Nature's TRAIL – on a path to cancer immunotherapy. Immunity 2003; 18: 1–6.
LeBlanc HN, Ashkenazi A . Apo2L/TRAIL and its death and decoy receptors. Cell Death Differ 2003; 10: 66–75.
Sprick MR, Rieser E, Stahl H, Grosse-Wilde A, Weigand MA, Walczak H . Caspase-10 is recruited to and activated at the native TRAIL and CD95 death-inducing signalling complexes in a FADD-dependent manner but can not functionally substitute caspase-8. EMBO J 2002; 21: 4520– 4530.
Almasan A, Ashkenazi A . Apo2L/TRAIL: apoptosis signaling, biology, and potential for cancer therapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2003; 14: 337–348.
Roth W, Isenmann S, Naumann U, Kugler S, Bahr M, Dichgans J et al. Locoregional Apo2L/TRAIL eradicates intracranial human malignant glioma xenografts in athymic mice in the absence of neurotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999; 265: 479–483.
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B, Griffith TS, Kubin M et al. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med 1999; 5: 157–163.
Chinnaiyan AM, Prasad U, Shankar S, Hamstra DA, Shanaiah M, Chenevert TL et al. Combined effect of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and ionizing radiation in breast cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 1754–1759.
Lawrence D, Shahrokh Z, Marsters S, Achilles K, Shih D, Mounho B et al. Differential hepatocyte toxicity of recombinant Apo2L/TRAIL versions. Nat Med 2001; 7: 383–385.
Mori E, Thomas M, Motoki K, Nakazawa K, Tahara T, Tomizuka K et al. Human normal hepatocytes are susceptible to apoptosis signal mediated by both TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2. Cell Death Differ 2004; 11: 203–207.
Kerr D . Clinical development of gene therapy for colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 615–622.
Lang FF, Bruner JM, Fuller GN, Aldape K, Prados MD, Chang S et al. Phase I trial of adenovirus-mediated p53 gene therapy for recurrent glioma: biological and clinical results. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 2508–2518.
Rainov NG, Ren H . Gene therapy for human malignant brain tumors. Cancer J 2003; 9: 180–188.
Hughes RM . Strategies for cancer gene therapy. J Surg Oncol 2004; 85: 28–35.
McNeish IA, Bell SJ, Lemoine NR . Gene therapy progress and prospects: cancer gene therapy using tumour suppressor genes. Gene Therapy 2004; 11: 497–503.
Griffith TS, Broghammer EL . Suppression of tumor growth following intralesional therapy with TRAIL recombinant adenovirus. Mol Ther 2001; 4: 257–266.
Kagawa S, He C, Gu J, Koch P, Rha SJ, Roth JA et al. Antitumor activity and bystander effects of the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) gene. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 3330–3338.
Mohr A, Henderson G, Dudus L, Herr I, Debatin K-M, Weiher H et al. AAV-encoded expression of TRAIL in experimental human colorectal cancer leads to tumor regression. Gene Therapy 2004; 11: 534–543.
Jacob D, Davis J, Zhu H, Zhang L, Teraishi F, Wu S et al. Suppressing orthotopic pancreatic tumor growth with a fiber-modified adenovector expressing the TRAIL gene from the human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 3535–3541.
Lin T, Huang X, Gu J, Zhang L, Roth JA, Xiong M et al. Long-term tumor-free survival from treatment with the GFP-TRAIL fusion gene expressed from the hTERT promoter in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2002; 21: 8020–8028.
Ehtesham M, Kabos P, Gutierrez MA, Chung NH, Griffith TS, Black KL et al. Induction of glioblastoma apoptosis using neural stem cell-mediated delivery of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 7170–7174.
Ucur E, Mattern J, Wenger T, Okouoyo S, Schroth A, Debatin KM et al. Induction of apoptosis in experimental human B cell lymphomas by conditional TRAIL-expressing T cells. Br J Cancer 2003; 89: 2155–2162.
Trono D . Lentiviral vectors: turning a deadly foe into a therapeutic agent. Gene Therapy 2000; 7: 20–23.
Wiznerowicz M, Trono D . Harnessing HIV for therapy, basic research and biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 2005; 23: 42–47.
Wenger T, Mattern J, Penzel R, Gassler N, Haas TL, Sprick MR et al. Resistance by intracellular retention of TRAIL receptors by lentiviral TRAIL transfer. Cell Death and Diff 2006; 13: 1740–1751.
Herr I, Ucur E, Herzer K, Okouoyo S, Ridder R, Krammer PH et al. Glucocorticoid co-treatment induces apoptosis resistance toward cancer therapy in carcinomas. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 3112–3120.
DuBridge RB, Tang P, Hsia HC, Leong PM, Miller JH, Calos MP . Analysis of mutation in human cells by using an Epstein–Barr virus shuttle system. Mol Cell Biol 1987; 7: 379–387.
Walczak H, Degli-Esposti MA, Johnson RS, Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Boiani N et al. TRAIL-R2: a novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for TRAIL. EMBO J 1997; 16: 5386–5397.
Naldini L, Blomer U, Gage FH, Trono D, Verma IM . Efficient transfer, integration, and sustained long-term expression of the transgene in adult rat brains injected with a lentiviral vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 11382–11388.
Zufferey R, Dull T, Mandel RJ, Bukovsky A, Quiroz D, Naldini L et al. Self-inactivating lentivirus vector for safe and efficient in vivo gene delivery. J Virol 1998; 72: 9873–9880.
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F, Riccardi C . A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 1991; 139: 271–279.
Herr I, Wilhelm D, Boehler T, Angel P, Debatin K-M . Activation of CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling by ceramide mediates cancer therapy-induced apoptosis. EMBO J 1997; 16: 6200–6208.
Ghosh SK, Wood C, Boise LH, Mian AM, Deyev VV, Feuer G et al. Potentiation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in primary effusion lymphoma through azidothymidine-mediated inhibition of NF-kappa B. Blood 2003; 101: 2321–2327.
Rohn TA, Wagenknecht B, Roth W, Naumann U, Gulbins E, Krammer PH et al. CCNU-dependent potentiation of TRAIL/Apo2L-induced apoptosis in human glioma cells is p53-independent but may involve enhanced cytochrome c release. Oncogene 2001; 20: 4128–4137.
Mariani SM, Krammer PH . Differential regulation of TRAIL and CD95 ligand in transformed cells of the T and B lymphocyte lineage. Eur J Immunol 1998; 28: 973–982.
Monleon I, Martinez-Lorenzo MJ, Monteagudo L, Lasierra P, Taules M, Iturralde M et al. Differential secretion of Fas ligand- or APO2 ligand/TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-carrying microvesicles during activation-induced death of human T cells. J Immunol 2001; 167: 6736–6744.
Van Maele B, De Rijck J, De Clercq E, Debyser Z . Impact of the central polypurine tract on the kinetics of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vector transduction. J Virol 2003; 77: 4685–4694.
Strehlow D, Jodo S, Ju ST . Retroviral membrane display of apoptotic effector molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 4209–4214.
Kemp TJ, Ludwig AT, Earel JK, Moore JM, Vanoosten RL, Moses B et al. Neutrophil stimulation with Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) results in the release of functional soluble TRAIL/Apo-2L. Blood 2005; 106: 3474–3482.
Janssen EM, Droin NM, Lemmens EE, Pinkoski MJ, Bensinger SJ, Ehst BD et al. CD4+ T-cell help controls CD8+ T-cell memory via TRAIL-mediated activation-induced cell death. Nature 2005; 434: 88–93.
Okouoyo S, Herzer K, Ucur E, Mattern J, Krammer PH, Debatin K-M et al. Rescue of death receptor and mitochondrial apoptosis signaling in resistant human NSCLC in vivo. Int J Cancer 2004; 108: 580–587.
Acknowledgements
We thank Peter H Krammer for helpful discussion, Didier Trono for providing lentiviral plasmids, Elisabeth Klimczak, Marlene Roth and Jessica Gabler for excellent technical assistance and the Tumorzentrum Heidelberg for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wenger, T., Mattern, J., Haas, T. et al. Apoptosis mediated by lentiviral TRAIL transfer involves transduction-dependent and -independent effects. Cancer Gene Ther 14, 316–326 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7701016
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7701016