Abstract
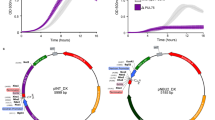
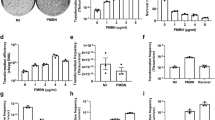
To utilize Bifidobacterium longum (B. longum) as a safe and stable delivery system for endostatin in cancer gene therapy, we constructed pBV22210 vector combining a chloramphenicol-resistance gene (Cmr) from pBCSK(+) plasmid, a cryptic plasmid pMB1 from B. longum strain with pBV222. Endostatin was cloned directly downstream of an N terminal His6-tag sequence in the pBV22210, so that the endostatin protein expressed in B. longum could be purified with Ni-binding resin. The results indicated that the plasmid electroporated into B. longum was maintained stably in the absence of selective antibiotics and did not significantly affect biological characteristics of B. longum. In addition, the plasmid in B. longum showed a strong inhibitory effect on the growth of mouse solid liver tumor in vivo. These results suggested that this new plasmid may be a stable vector in B. longum for transporting anti-cancer genes in cancer gene therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kimura NT, Taniguchi S, Aoki K, Baba T . Selective localization and growth of Bifidobacterium bifidum in mouse tumors following intravenous administration. Cancer Res 1980; 40: 2061–2068.
Missich R, Sgorbati B, LeBlanc DJ . Transformation of Bifidobacterium longum with pRM2, a constructed Escherichia coli-B.longum shuttle vector. Plasmid 1994; 32: 208–211.
Rossi M, Brigidi P, Matteuzzi D . An efficient transformation system for Bifidobacterium spp. Lett Appl Microbiol 1997; 24: 33–36.
Rossi M, Brigidi P, Matteuzzi D . Improved cloning vectors for Bifidobacterium spp. Lett Appl Microbiol 1998; 26: 101–104.
Rossi M, Brigidi P, Gonzalez Vara y Rodriguez A, Matteuzzi D . Characterization of the plasmid pMB1 from Bifidobacterium longum and its use for shuttle vector construction. Res Microbiol 1996; 147: 133–143.
Park MS, Shin DW, Lee KH, Ji GE . Sequence analysis of plasmid pKJ50 from Bifidobacterium longum. Microbiology 1999; 145: 585–592.
Yazawa K, Fujimori M, Nakamura T, Sasaki T, Amano J, Kano Y et al. Bifidobacterium longum as a delivery system for gene therapy of chemically induced rat mammary tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2001; 66: 165–170.
Nakamura T, Sasaki T, Fujimori M, Yazawa K, Kano Y, Amano J et al. Cloned cytosine deaminase gene expression of Bifidobacterium longum and application to enzyme/pro-drug therapy of hypoxic solid tumors. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2002; 66: 2362–2366.
Li X, Fu GF, Fan YR, Liu WH, Liu XJ, Wang JJ et al. Bifidobacterium adolescentis as a delivery system of endostatin for cancer gene therapy: selective inhibitor of angiogenesis and hypoxic tumor growth. Cancer Gene Ther 2003; 10: 105–111.
Fu GF, Li X, Hou YY, Fan YR, Liu WH, Xu GX . Bifidobacterium longum as an oral delivery system of endostatin for gene therapy on solid liver cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 2005; 12: 133–140.
Yi C, Huang Y, Guo ZY, Wang SR . Antitumor effect of cytosine deaminase/5-fluorocytosine suicide gene therapy system mediated by Bifidobacterium infantis on melanoma. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2005; 26: 629–634.
Wei YQ, Wang QR, Zhao X, Yang L, Tian L, Lu Y et al. Immunotherapy of tumors with xenogeneic endothelial cells as a vaccine. Nat Med 2000; 6: 1160–1166.
Wei YQ, Huang MJ, Yang L, Zhao X, Tian L, Lu Y et al. Immunogene therapy of tumors with vaccine based on Xenopus homologous vascular endothelial growth factor as a model antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2001; 98: 11545–11550.
Wang J, Chen C, Li B, Yu H, Zhao Y, Sun J et al. Antioxidative function and biodistribution of [Gd@C82(OH)22]n nanoparticles in tumor-bearing mice. Biochem Pharmacol 2006; 71: 872–881.
Boehm T, Folkman J, Browder T, O'Reilly MS . Antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance. Nature 1997; 390: 404–407.
Smeianov VV, Efimov BA, Korschunov VM, Steele JL . Characterization of plasmid p4M from Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum. GenBank 2002; Accession No AF359574.
Kaufmann P, Pfefferkorn A, Teuber M, Meile L . Complete nucleotide sequence of the 2.1 kb plasmid pAP1 isolated from Bifidobacterium asteroides. GenBank 1997; Accession No Y11549.
O'Riordan K, Fitzgerald GF . Molecular characterisation of a 5.75-kb cryptic plasmid from Bifidobacterium breve NCFB 2258 and determination of mode of replication. FEMS Microbiol Lett 1999; 174: 285–294.
Park MS, Lee KH, Ji GE . Isolation and characterization of two plasmids from Bifidobacterium longum. Lett Appl Microbiol 1997; 25: 5–7.
Tanaka K, Samura K, Kano Y . Structural and functional analysis of pTB6 from Bifidobacterium longum. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2005; 69: 422–455.
Gonzalez Vara A, Rossi M, Altomare L, Eikmanns B, Matteuzzi D . Stability of recombinant plasmids on the continuous culture of Bifidobacterium animalis ATCC 27536. Biotechnol Bioeng 2003; 84: 145–150.
Zhu L, Li W, Dong X . Species identification of genus Bifidobacterium based on partial HSP60 gene sequences and proposal of Bifidobacterium thermacidophilum subsp. porcinum subsp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2003; 53: 1619–1623.
O'Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS et al. Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell 1997; 88: 277–285.
Tjin Tham Sjin RM, Satchi-Fainaro R, Birsner AE, Ramanujam VM, Folkman J, Javaherian K . A 27-amino-acid synthetic peptide corresponding to the NH2-terminal zinc-binding domain of endostatin is responsible for its antitumor activity. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 3656–3663.
Rothbard JB, Garlington S, Lin Q, Kirschberg T, Kreider E, McGrane PL et al. Conjugation of arginine oligomers to cyclosporin A facilitates topical delivery and inhibition of inflammation. Nat Med 2000; 6: 1253–1257.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants BM 2002009 from the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China to GXX, and Grants 30370462 and the NSFC/RGC Joint Research Scheme 30318004 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, RFDP Grant 20050284025 from the State Educational Ministry of China and Grant BK2006713 from the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China to JJW. We thank Prof. Zhi-Wei Wu (Center for Public Health Research, Nanjing University) for reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, YF., Zhu, LP., Hu, B. et al. A new expression plasmid in Bifidobacterium longum as a delivery system of endostatin for cancer gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 14, 151–157 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7701003
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7701003
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bacteria-cancer interactions: bacteria-based cancer therapy
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2019)
-
The role of bacteria in cancer therapy – enemies in the past, but allies at present
Infectious Agents and Cancer (2018)
-
Bifidobacterial recombinant thymidine kinase-ganciclovir gene therapy system induces FasL and TNFR2 mediated antitumor apoptosis in solid tumors
BMC Cancer (2016)
-
Engineering of bacterial strains and their products for cancer therapy
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2013)
-
Gene therapy for cancer: bacteria-mediated anti-angiogenesis therapy
Gene Therapy (2011)