Abstract
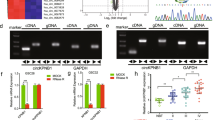
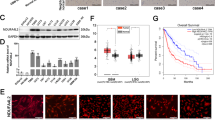
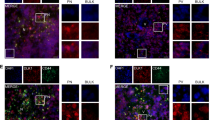
Chimeric tumor suppressor-1 (CTS-1) is based on the sequence of p53 and was designed as a therapeutic tool resisting various mechanisms of p53 inactivation. We previously reported that an adenovirus expressing CTS-1 (Ad-CTS-1) has superior cell death-inducing activity in glioma cells compared with wild-type p53. Here, we used cDNA microarrays to detect changes in gene expression preferentially induced by Ad-CTS-1. The putative serin threonine kinase, PCTAIRE3, and the quinone oxireductase, PIG3, were strongly induced by Ad-CTS-1 compared with wild-type p53. An adenoviral vector encoding PCTAIRE3 (Ad-PCTAIRE3) induced growth arrest and killed a minor proportion of the glioma cells. Ad-PIG3 alone affected neither growth nor viability. However, coinfection with Ad-PCTAIRE3 and Ad-PIG3 resulted in enhanced growth inhibition compared with Ad-PCTAIRE3 infection alone. Ad-CTS1, Ad-PCTAIRE3 or Ad-PIG3 induced the formation of free reactive oxygen species (ROS). However, the prevention of ROS formation induced by Ad-PCTAIRE3 and Ad-CTS-1 did not block growth arrest and cell death, suggesting that ROS formation is not essential for these effects. Altogether, these data identify PCTAIRE3 as one novel growth-inhibitory and death-inducing p53 response gene and suggest that changes in the expression of specific target genes contribute to the superior anti-glioma activity of CTS-1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glioma Meta-Analysis Trialists Group. Chemotherapy in adult high-grade glioma: a systematic review and a meta-analysis of individual patient data from 12 randomised trials. Lancet 2002; 359: 1011–1018.
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 987–996.
Conseiller E, Debussche L, Landais D, Venot C, Maratrat M, Sierra V et al. CTS1: a p53-derived chimeric tumor suppressor gene with enhanced in vitro apoptotic properties. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 120–127.
Naumann U, Kügler S, Wolburg H, Wick W, Rascher G, Schulz JB et al. Chimeric tumor suppressor 1, a p53-derived chimeric tumor suppressor gene, kills p53 mutant and p53 wild-type glioma cells in synergy with irradiation and CD95 ligand. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 5833–5842.
Bougeret C, Virone-Oddos A, Adeline E, Lacroix F, Lefranc C, Ferrero L et al. Cancer gene therapy mediated by CTS1, a p53 derivative: advantage over wild-type p53 in growth inhibition of human tumors overexpressing MDM2. Cancer Gene Ther 2000; 7: 789–798.
Wischhusen J, Melino G, Weller M . p53 and its family members – reporter genes may not see the difference. Cell Death Differ 2004; 10: 1150–1152.
Naumann U, Durka S, Weller M . Dexamethasone-mediated protection from drug cytotoxicity: association with p21WAF1/CIP1 protein accumulation? Oncogene 1998; 17: 1567–1575.
Zhong ZD, Zou P, Huang SA, Hu ZB, Liu LB, Lu YP . A new method for construction of EGFP-labled recombinant adenovirus containing hVEGF(165) and its property in vitro. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2003; 11: 238–242.
Huang H, Colella S, Kurrer M, Yonekawa Y, Kleihues P, Ohgaki H . Gene expression profiling of low-grade diffuse astrocytomas by cDNA arrays. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 6868–6874.
Winkelmeir P . Quantification of cytotoxicity by cell volume and cell proliferation. ALTA 1993; 21: 269–280.
Webb JL . Effect of more than one inhibitor, antagonism, summation, and synergism. In: Enzyme and Metabolic Inhibitors. Academic Press: New York, 1961; 1: 66–79, 487–512.
Polyak K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature 1997; 389: 300–305.
Okuda T, Cleveland JL, Downing JR . PCTAIRE-1 and PCTAIRE-3, two members of a novel cdc2/CDC28-related protein kinase gene family. Oncogene 1992; 7: 2249–2258.
Herskovits AZ, Davies P . Cloning and expression analysis of two novel PCTAIRE 3 transcripts from human brain. Gene 2004; 328: 59–67.
Wischhusen J, Naumann U, Ohgaki H, Rastinejad F, Weller M . CP-31398, a novel p53-stabilizing agent, induces p53-dependent and p53-independent glioma cell death. Oncogene 2003; 22: 8233–8245.
Sander M, Trump BF, Harris CC, Tennant RW . Seventeenth Aspen Cancer Conference: mechanisms of toxicity, carcinogenesis, cancer prevention, and cancer therapy. Mol Carcinog 2003; 36: 101–114.
Venot C, Maratrat M, Dureuil C, Conseiller E, Bracco L, Debussche L . The requirement for the p53 proline-rich functional domain for mediation of apoptosis is correlated with specific PIG3 gene transactivation and with transcriptional repression. EMBO J 1998; 17: 4668–4679.
Kovar H, Jug G, Printz D, Bartl S, Schmid G, Wesierska-Gadek J . Characterization of distinct consecutive phases in non-genotoxic p53-induced apoptosis of Ewing tumor cells and the rate-limiting role of caspase 8. Oncogene 2000; 19: 4096–4107.
Sheng-Tanner X, Bump EA, Hedley DW . An oxidative stress-mediated death pathway in irradiated human leukemia cells mapped using multilaser flow cytometry. Radiat Res 1998; 150: 636–647.
Wu L, Zhu H, Nie L, Maki CG . A link between p73 transcriptional activity and p73 degradation. Oncogene 2004; 23: 4032–4036.
Maisse C, Guerrieri P, Melino G . p73 and p63 protein stability: the way to regulate function? Biochem Pharmacol 2003; 66: 1555–1561.
Michael D, Oren M . The p53 and Mdm2 families in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2002; 12: 53–59.
Okuda T, Valentine VA, Shapiro DN, Downing JR . Cloning of genomic loci and chromosomal localization of the human PCTAIRE-1 and -3 protein kinase genes. Genomics 1994; 21: 217–221.
Iida A, Sekine A, Saito S, Kitamura Y, Kitamoto T, Osawa S et al. Catalog of 320 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 20 quinone oxidoreductase and sulfotransferase genes. J Hum Genet 2001; 46: 225–240.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naumann, U., Huang, H., Wolburg, H. et al. PCTAIRE3: a putative mediator of growth arrest and death induced by CTS-1, a dominant-positive p53-derived synthetic tumor suppressor, in human malignant glioma cells. Cancer Gene Ther 13, 469–478 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700917
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700917
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Limited utility of qPCR-based detection of tumor-specific circulating mRNAs in whole blood from clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients
BMC Urology (2020)
-
Identification of genes regulated by the EWS/NR4A3 fusion protein in extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma
Tumor Biology (2012)
-
Therapeutic effects of the Sp1 inhibitor mithramycin A in glioblastoma
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2011)