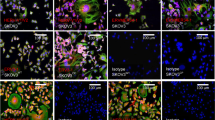
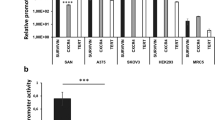
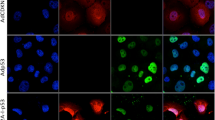
Abstract
Tight regulation of the therapeutic gene expression is critical in gene therapy. In this report, a doxycycline (Dox)-regulated retrovirus-mediated gene expression system was used to study the effects of suicide gene therapy on human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 and the nude mice model of implanted human breast cancer. To render the expression of suicide gene under control, we used two pseudoviruses simultaneously, RevTRE/HSVtk and RevTet-On, to infect MCF-7 cells or xenografts of nude mice. When infected by the pseudoviruses and followed by Dox and Ganciclovir (GCV) treatment, MCF-7 cells were arrested at S phase and the growth was suppressed. We then evaluated the antitumor efficiency of this system in vivo through studying the mice bearing human breast cancer xenografts. Compared with control groups, the HSVtk mRNA level increased significantly in tumor tissues, mass of the tumors shrank remarkably, and tumor necrosis features occurred after treatment with Dox and GCV. These data suggest that suicide gene therapy using the Dox-induced Tet-On-controlled HSVtk gene expression system is a feasible method to treat human breast cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiewrodt R, Amin K, Kiefer M, Jovanovic VP, Kapoor V, Force S et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of enhanced Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase mutants improves prodrug-mediated tumor cell killing. Cancer Gene Ther 2003; 10 (5): 353–364.
Asklund T, Appelskog IB, Ammerpohl O, Langmoen IA, Dilber MS, Aints A et al. Gap junction-mediated bystander effect in primary cultures of human malignant gliomas with recombinant expression of the HSVtk gene. Exp Cell Res 2003; 284 (2): 185–195.
Zhong Q, Kolls JK, Schwarzenberger P . Retrovirus molecular conjugates. A novel, high transduction efficiency, potentially safety-improved, gene transfer system. J Biol Chem 2001; 276 (27): 24601–24607.
Bai Y, Soda Y, Izawa K, Tanabe T, Kang X, Tojo A et al. Effective transduction and stable transgene expression in human blood cells by a third-generation lentiviral vector. Gene Therapy 2003; 10 (17): 1446–1457.
Hillman GG, Slos P, Wang Y, Wright JL, Layer A, De Meyer M et al. Tumor irradiation followed by intratumoral cytokine gene therapy for murine renal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther 2004; 11: 61–72.
Zabala M, Wang L, Hernandez-Alcoceba R, Hillen W, Qian C, Prieto J et al. Optimization of the Tet-On system to regulate interleukin 12 expression in the liver for the treatment of hepatic tumors. Cancer Res 2004; 64 (8): 2799–2804.
Koponen JK, Kankkonen H, Kannasto J, Wirth T, Hillen W, Bujard H et al. Doxycycline-regulated lentiviral vector system with a novel reverse transactivator rtTA2S-M2 shows a tight control of gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Gene Therapy 2003; 10 (6): 459–466.
Tang Y, Jackson M, Qian K, Phillips MI . Hypoxia inducible double plasmid system for myocardial ischemia gene therapy. Hypertension 2002; 39 (2, Part 2): 695–698.
Dalle B, Payen E, Beuzard Y . Modulation of transduced erythropoietin expression by iron. Exp Hematol 2000; 28 (7): 760–764.
Worthington J, McCarthy HO, Barrett E, Adams C, Robson T, Hirst DG . Use of the radiation-inducible WAF1 promoter to drive iNOS gene therapy as a novel anti-cancer treatment. J Gene Med 2004; 6 (6): 673–680.
Schmeisser F, Donohue M, Weir JP . Tetracycline-regulated gene expression in replication-incompetent herpes simplex virus vectors. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13 (18): 2113–2124.
A-Mohammadi S, Hawkins RE . Efficient transgene regulation from a single tetracycline-controlled positive feedback regulatory system. Gene therapy 1998; 5 (1): 76–84.
Kim HJ, Gatz C, Hillen W, Jones TR . Tetracycline repressor-regulated gene repression in recombinant human cytomegalovirus. J Virol 1995; 69 (4): 2565–2573.
Chtarto A, Bender HU, Hanemann CO, Kemp T, Lehtonen E, Levivier M et al. Tetracycline-inducible transgene expression mediated by a single AAV vector. Gene Therapy 2003; 10 (1): 84–94.
Ginhoux F, Turbant S, Gross DA, Poupiot J, Marais T, Lone Y et al. HLA-A*0201-restricted cytolytic responses to the rtTA transactivator dominant and cryptic epitopes compromise transgene expression induced by the tetracycline on system. Mol Ther 2004; 10 (2): 279–289.
Gimenez E, Lavado A, Giraldo P, Cozar P, Jeffery G, Montoliu L . A transgenic mouse model with inducible Tyrosinase gene expression using the tetracycline (Tet-On) system allows regulated rescue of abnormal chiasmatic projections found in albinism. Pigment Cell Res 2004; 17 (4): 363–370.
Laposa RR, Henderson JT, Wells PG . Tetracycline-dependent regulation of formamidopyrimidine DNA glycosylase in transgenic mice conditionally reduces oxidative DNA damage in vivo. FASEB J 2003; 17 (10): 1343–1345.
Hu WX, Zeng ZJ, Luo SQ, Chen Q . Suicide gene therapy of human breast cancer in SCID mice model by the regulation of Tet-On. Chin Med J (Engl) 2004; 117 (3): 434–439.
Sheridan PL, Bodner M, Lynn A, Phuong TK, DePolo NJ, de la Vega Jr DJ et al. Generation of retroviral packaging and producer cell lines for large-scale vector production and clinical application: improved safety and high titer. Mol Ther 2000; 2 (3): 262–275.
Jordan M, Wurm F . Transfection of adherent and suspended cells by calcium phosphate. Methods 2004; 33 (2): 136–143.
Lake DE, Hudis CA . High-dose chemotherapy in breast cancer. Drugs 2004; 64 (17): 1851–1860.
Kim KB, Eton O, East MJ, Hodges C, Papadopoulos NE, Grimm EA et al. Pilot study of high-dose, concurrent biochemotherapy for advanced melanoma. Cancer 2004; 101 (3): 596–603.
Brade AM, Szmitko P, Ngo D, Liu FF, Klamut HJ . Heat-directed suicide gene therapy for breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 2003; 10 (4): 294–301.
Kanazawa T, Mizukami H, Okada T, Hanazono Y, Kume A, Nishino H et al. Suicide gene therapy using AAV-HSVtk/ganciclovir in combination with irradiation results in regression of human head and neck cancer xenografts in nude mice. Gene Therapy 2003; 10 (1): 51–58.
Zerrouqi A, Rixe O, Ghoumari AM, Yarovoi SV, Mouawad R, Khayat D et al. Liposomal delivery of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene in glioma: improvement of cell sensitization to ganciclovir. Cancer Gene Ther 1996; 3 (6): 385–392.
Kashima Y, Miki T, Minami K, Seino S . Establishment of a tet-on gene expression system in glucose-responsive and -unresponsive MIN6 cells. Diabetes 2001; 50 (Suppl): S133.
Mizuguchi H, Xu ZL, Sakurai F, Mayumi T, Hayakawa T . Tight positive regulation of transgene expression by a single adenovirus vector containing the rtTA and tTS expression cassettes in separate genome regions. Hum Gene Ther 2003; 14 (13): 1265–1277.
Kugawa F, Matsumoto K, Aoki M . Apoptosis-like cell death of human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 induced by buprenorphine hydrochloride. Life Sci 2004; 75 (3): 287–299.
Simoes-Wust AP, Schurpf T, Hall J, Stahel RA, Zangemeister-Wittke U . Bcl-2/bcl-xL bispecific antisense treatment sensitizes breast carcinoma cells to doxorubicin, paclitaxel and cyclophosphamide. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2002; 76 (2): 157–166.
Harwell RM, Mull BB, Porter DC, Keyomarsi K . Activation of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 by full length and low molecular weight forms of cyclin E in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2004; 279 (13): 12695–12705.
Keyomarsi K, Tucker SL, Buchholz TA, Callister M, Ding Y, Hortobagyi GN et al. Cyclin E and survival in patients with breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2002; 347 (20): 1566–1575.
Paulovich AG, Toczyski DP, Hartwell LH . When checkpoints fail. Cell 1997; 88 (3): 315–321.
Agami R, Bernards R . Convergence of mitogenic and DNA damage signaling in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cancer Lett 2002; 177 (2): 111–118.
Nagle DG, Zhou YD, Mora FD, Mohammed KA, Kim YP . Mechanism targeted discovery of antitumor marine natural products. Curr Med Chem 2004; 11 (13): 1725–1756.
Tu LC, Melendy T, Beerman TA . DNA damage responses triggered by a highly cytotoxic monofunctional DNA alkylator, hedamycin, a pluramycin antitumor antibiotic. Mol Cancer Ther 2004; 3 (5): 577–585.
Corban-Wilhelm H, Ehemann V, Becker G, Greulich D, Braun K, Debus J . Comparison of different methods to assess the cytotoxic effects of cytosine deaminase and thymidine kinase gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 2004; 11: 208–214.
Wang Y, Hu JK, Krol A, Li YP, Li CY, Yuan F . Systemic dissemination of viral vectors during intratumoral injection. Mol Cancer Ther 2003; 2 (11): 1233–1242.
Patil R, Chavez JB, Yee D . Inducible expression of herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase increases sensitivity to ganciclovir but does not enhance bystander effect in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2000; 62 (2): 109–115.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the grant from CMB (China Medical Board of New York Inc., Grant # 99-698).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, ZJ., Li, ZB., Luo, SQ. et al. Retrovirus-mediated tk gene therapy of implanted human breast cancer in nude mice under the regulation of Tet-On. Cancer Gene Ther 13, 290–297 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700889
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700889
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The novel gene HA117 promotes in vitro and in vivo drug resistance in mouse colon tumor cells
Cancer Gene Therapy (2017)
-
A Novel Double-Enhanced Suicide Gene Therapy in a Colon Cancer Cell Line Mediated by Gef and Apoptin
BioDrugs (2014)
-
HIV vector-mediated targeted suicide gene therapy for adult T-cell leukemia
Gene Therapy (2007)
-
Recombinant AAV-mediated HSVtk gene transfer with direct intratumoral injections and Tet-On regulation for implanted human breast cancer
BMC Cancer (2006)