Abstract
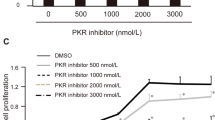
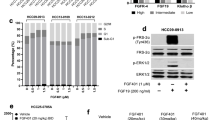
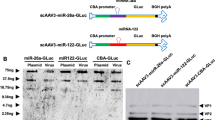
NK4 is an hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-antagonist and a broad angiogenesis inhibitor. NK4 gene therapy has confirmed antitumor efficacy on cancers with intact HGF-cMET signaling pathway. However, the feasibility to treat tumors in which the effect of the HGF-cMET signaling pathway is less unambiguous or may even be inhibitory on carcinogenesis, such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with NK4 needs further assessment. Therefore, we evaluated the effects of adenoviral vector-mediated expression of NK4 on the biological behavior of a series of HCC cell lines in vitro and on HepG2 xenografts in vivo. In vitro, transduction of HCC cell lines with the replication-deficient recombinant adenoviral vector AdCMV.NK4 resulted in significant inhibition of proliferation over and above the antimitogenic effects of HGF. In addition, HGF-induced scattering and invasion through matrigel were inhibited effectively. Moreover, transduced HCC cells produced sufficient amounts of NK4 protein to achieve bystander effects involving reduced migration of nontransduced tumor cells and reduced proliferation of endothelial cells. Finally, treatment of established HepG2 xenografts with AdCMV.NK4 resulted in significant tumor growth delay and significant reduction of intratumoral microvessel density. In conclusion, NK4 gene therapy is a promising strategy to treat HCC based on the pleiotropic functions of NK4 interfering with tumor growth, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curley SA, Jones DV . Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. In: Meyers MA ed. Neoplasms of the digestive tract: imaging, staging and management. 1st edn. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1998: 93–109.
Prieto J, Herraiz M, Sangro B, et al. The promise of gene therapy in gastrointestinal and liver diseases. Gut. 2003;52 (Suppl 2):49–54.
Date K, Matsumoto K, Shimura H, et al. HGF/NK4 is a specific antagonist for pleiotrophic actions of hepatocyte growth factor. FEBS Lett. 1997;420:1–6.
Kuba K, Matsumoto K, Date K, et al. HGF/NK4, a four-kringle antagonist of hepatocyte growth factor, is an angiogenesis inhibitor that suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in mice. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6737–6743.
Date K, Matsumoto K, Kuba K, et al. Inhibition of tumor growth and invasion by a four-kringle antagonist (HGF/NK4) for hepatocyte growth factor. Oncogene. 1998;17:3045–3054.
Jiang WG, Hiscox SE, Parr C, et al. Antagonistic effect of NK4, a novel hepatocyte growth factor variant, on in vitro angiogenesis of human vascular endothelial cells. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:3695–3703.
Matsumoto K, Nakamura T . NK4 (HGF-antagonist/ angiogenesis inhibitor) in cancer biology and therapeutics. Cancer Sci. 2003;94:321–327.
Maemondo M, Narumi K, Saijo Y, et al. Targeting angiogenesis and HGF function using an adenoviral vector expressing the HGF antagonist NK4 for cancer therapy. Mol Ther. 2002;5:177–185.
Hirao S, Yamada Y, Koyama F, et al. Tumor suppression effect using NK4, a molecule acting as an antagonist of HGF, on human gastric carcinomas. Cancer Gene Ther. 2002;9:700–707.
Maehara N, Nagai E, Mizumoto K, et al. Gene transduction of NK4, HGF antagonist, inhibits in vitro invasion and in vivo growth of human pancreatic cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2002;19:417–426.
Saimura M, Nagai E, Mizumoto K, et al. Intraperitoneal injection of adenovirus-mediated NK4 gene suppresses peritoneal dissemination of pancreatic cancer cell line AsPC-1 in nude mice. Cancer Gene Ther. 2002;9:799–806.
Heideman DAM, van Beusechem VW, Bloemena E, et al. Suppression of tumor growth, invasion and angiogenesis of human gastric cancer by adenovirus-mediated expression of NK4. J Gene Med. 2004;6:317–327.
Fujiwara H, Kubota T, Amaike H, et al. Suppression of peritoneal implantation of gastric cancer cells by adenovirus vector-mediated NK4 expression. Cancer Gene Ther. 2005;12:206–216.
Ueda K, Iwahashi M, Matsuura I, et al. Adenoviral-mediated gene transduction of the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) antagonist, NK4, suppresses peritoneal metastases of gastric cancer in nude mice. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:2135–2142.
Kushibiki T, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Tabata Y . Suppression of the progress of disseminated pancreatic cancer cells by NK4 plasmid DNA released from cationized gelatin microspheres. Pharm Res. 2004;21:1109–1118.
Tanaka T, Shimura H, Sasaki T, et al. Gallbladder cancer treatment using adenovirus expressing the HGF/NK4 gene in a peritoneal implantation model. Cancer Gene Ther. 2004;11:431–440.
Wen J, Matsumoto K, Taniura N, Tomioka D, Nakamura T . Hepatic gene expression of NK4, an HGF-antagonist/angiogenesis inhibitor, suppresses liver metastasis and invasive growth of colon cancer in mice. Cancer Gene Ther. 2004;11:419–430.
Brockmann MA, Papadimitriou A, Brandt M, et al. Inhibition of intracerebral glioblastoma growth by local treatment with the scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor-antagonist NK4. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:4578–4585.
Davies G, Mason MD, Martin TA, et al. The HGF/SF antagonist NK4 reverses fibroblast- and HGF-induced prostate tumor growth and angiogenesis in vivo. Int J Cancer. 2003;106:348–354.
Martin TA, Parr C, Davies G, et al. Growth and angiogenesis of human breast cancer in a nude mouse tumour model is reduced by NK4, a HGF/SF antagonist. Carcinogenesis. 2003;24:1317–1323.
Luo YQ, Wu MC, Cong WM . Gene expression of hepatocyte growth factor and its receptor in HCC and nontumorous liver tissues. World J Gastroenterol. 1999;5:119–121.
Tavian D, De Petro G, Benetti A, et al. u-PA and c-MET mRNA expression is co-ordinately enhanced while hepatocyte growth factor mRNA is down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2000;87:644–649.
Okano J, Shiota G, Kawasaki H . Expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and HGF receptor (c-met) proteins in liver diseases: an immunohistochemical study. Liver. 1999;19:151–159.
Ljubimova JY, Petrovic LM, Wilson SE, et al. Expression of HGF, its receptor c-met, c-myc and albumin in cirrhotic and neoplastic human liver tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 1997;45:79–87.
Ueki T, Fujimoto J, Suzuki T, et al. Expression of hepatocyte growth factor and its receptor c-met proto-oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1997;25:619–623.
Sakata H, Takayama H, Sharp R, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor overexpression induces growth, abnormal development, and tumor formation in transgenic mouse livers. Cell Growth Differ.. 1996;7:1513–1523.
Horiguchi N, Takayama H, Toyoda M, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor promotes hepatocarcinogenesis through c-Met autocrine activation and enhanced angiogenesis in transgenic mice treated with diethylnitrosamine. Oncogene. 2002;21:1791–1799.
Tajima H, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T . Hepatocyte growth factor has potent anti-proliferative activity in various tumor cell lines. FEBS Lett. 1991;291:229–232.
Shiota G, Rhoads DB, Wang TC, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:373–377.
Miyazaki M, Gohda E, Tsuboi S, et al. Human hepatocyte growth factor stimulates the growth of HUH-6 clone 5 human hepatoblastoma cells. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1992;16:145–154.
Neaud V, Faouzi S, Guirouilh J, et al. Human hepatic myofibroblasts increase invasiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells: evidence for a role of hepatocyte growth factor. Hepatology. 1997;26:1458–1466.
Liu ML, Mars WM, Michalopoulos GK . Hepatocyte growth factor inhibits cell proliferation in vivo of rat hepatocellular carcinomas induced by diethylnitrosamine. Carcinogenesis. 1995;16:841–843.
Shiota G, Kawasaki H, Nakamura T, et al. Inhibitory effect of hepatocyte growth factor on metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma in transgenic mice. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 1996;91:33–39.
Santoni-Rugiu E, Preisegger KH, Kiss A, et al. Inhibition of neoplastic development in the liver by hepatocyte growth factor in a transgenic mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:9577–9582.
Fontijn R, Hop C, Brinkman HJ, et al. Maintenance of vascular endothelial cell-specific properties after immortalization with an amphotrophic replication-deficient retrovirus containing human papilloma virus 16 E6/E7 DNA. Exp Cell Res. 1995;216:199–207.
Heideman DAM, Snijders PJF, Bloemena E, et al. Absence of tpr-met and expression of c-met in human gastric mucosa and carcinoma. J Pathol. 2001;194:428–435.
Borset M, Lien E, Espevik T, et al. Concomitant expression of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and the receptor c-MET in human myeloma cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:24655–24661.
Koochekpour S, Jeffers M, Rulong S, et al. Met and hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor expression in human gliomas. Cancer Res. 1997;57:5391–5398.
Maulik G, Shrikhande A, Kijima T, et al. Role of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor, c-Met, in oncogenesis and potential for therapeutic inhibition. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002;13:41–59.
Nakabayashi M, Morishita R, Nakagami H, et al. HGF/NK4 inhibited VEGF-induced angiogenesis in in vitro cultured endothelial cells and in vivo rabbit model. Diabetologia. 2003;46:115–123.
Kuba K, Matsumoto K, Ohnishi K, et al. Kringle 1–4 of hepatocyte growth factor inhibits proliferation and migration of human microvascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;279:846–852.
Alemany R, Balague C, Curiel DT . Replicative adenoviruses for cancer therapy. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18:723–727.
Heise C, Kirn DH . Replication-selective adenoviruses as oncolytic agents. J Clin Invest.. 2000;105:847–851.
Motoi F, Sunamura M, Ding L, et al. Effective gene therapy for pancreatic cancer by cytokines mediated by restricted replication-competent adenovirus. Hum Gene Ther. 2000;11:223–235.
Maemondo M, Saijo Y, Narumi K, et al. Gene therapy with secretory leukoprotease inhibitor promoter-controlled replication-competent adenovirus for non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64:4611–4620.
Folkman J . Antiangiogenic gene therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:9065–9066.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr K. Matsumoto and Dr T. Nakamura (Osaka University Medical School, Suita, Osaka, Japan) for providing the NK4 cDNA, and Jeroen Mastenbroek and Diederik van den Berg for technical assistance. We thank Elisabeth Bloemena for helping with immunohistochemical examinations and Paul van Diest for help with determination of microvessel density. This work was supported by a research grant from the Pasman Foundation. Renée Overmeer and Daniëlle Heideman are supported by grants from the Dutch Digestive Diseases Foundation (WS02-31 and WS95-12, respectively). Victor van Beusechem is supported by a research fellowship of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heideman, D., Overmeer, R., van Beusechem, V. et al. Inhibition of angiogenesis and HGF-cMET-elicited malignant processes in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells using adenoviral vector-mediated NK4 gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 12, 954–962 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700856
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700856
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MiRNA199a-3p suppresses tumor growth, migration, invasion and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting VEGFA, VEGFR1, VEGFR2, HGF and MMP2
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
Advanced Hepatocellular Cancer: the Current State of Future Research
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2016)
-
Hepatic stellate cells: central modulators of hepatic carcinogenesis
BMC Gastroenterology (2015)
-
Abl interconnects oncogenic Met and p53 core pathways in cancer cells
Cell Death & Differentiation (2011)
-
Anti-metastatic effects of viral and non-viral mediated Nk4 delivery to tumours
Genetic Vaccines and Therapy (2009)