Abstract
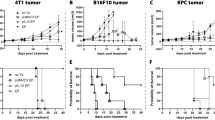
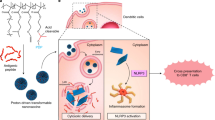
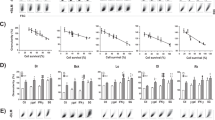
Malignant melanoma involving the oral cavity has a highly metastatic potential. Curative surgery is required to resect extensive oral tissues and often results in dysfunction as well as a severe cosmetic deformity in patients with the disease. An alternative technology for the local and sustained delivery of cytokines for cancer immunotherapy has been shown to induce tumor regression, suppression of metastasis, and development of systemic antitumor immunity. However, local immunization of the oral cavity has not previously been studied. In this study, we examined the efficacy of particle-mediated oral gene transfer on luciferase and green fluorescent protein production. The results showed that these proteins were more significantly expressed in oral mucosa than the skin, stomach, liver, and muscle. Using an established oral melanoma model in hamsters, particle-mediated oral gene gun therapy with interleukin (IL) 12 cDNA was then conducted. The results indicated that direct bombardment of mouse IL-12 cDNA suppressed tumor formation and improved the survival rate. The skin tumor model created by inoculation of melanoma cells was also significantly inhibited by the oral bombardment of IL-12 cDNA coupled with an irradiated melanoma vaccine administrated to the oral mucosa, compared to treatment with a percutaneous vaccine. IL-12 gene gun therapy, combined with an oral mucosal vaccine, induced interferon-γ mRNA expression in the host spleen for a long time. These results suggest that immunization of oral mucosa may induce systemic antitumor immunity more efficiently than immunization of the skin and that oral mucosa may be one of the most suitable tissues for cancer gene therapy by means of particle-mediated gene transfer. Cancer Gene Therapy (2001) 8, 705–712
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hicks MJ, Flaitz CM . Oral mucosal melanoma: epidemiology and pathobiology Oral Oncol 2000 36: 152–169
Rogers RS, Gibson LE . Mucosal, genital, and unusual clinical variants of melanoma Mayo Clin Proc 1997 72: 362–366
Dilloo D, Bacon K, Holden W, et al . Combined chemokine and cytokine gene transfer enhances antitumor immunity Nat Med 1996 2: 1090–1095
Roth JA, Cristiano RJ . Gene therapy for cancer: what have we done and where are we going? J Natl Cancer Inst 1997 89: 21–39
Gilboa E . Immunotherapy of cancer with genetically modified tumor vaccines Semin Oncol 1996 23: 101–107
Brunda MJ, Luistro L, Warrier RR, et al . Antitumor and antimetastatic activity of interleukin 12 against murine tumors J Exp Med 1993 178: 1223–1230
Tahara H, Zeh HJ, Storkus WJ, et al . Fibroblasts genetically engineered to secrete interleukin 12 can suppress tumor growth and induce antitumor immunity to a murine melanoma in vivo Cancer Res 1994 54: 182–189
Nastala CL, Edington HD, McKinney TG, et al . Recombinant IL-12 administration induces tumor regression in association with IFN-gamma production J Immunol 1994 153: 1697–1706
Tannenbaum CS, Wicker N, Armstrong D, et al . Cytokine and chemokine expression in tumors of mice receiving systemic therapy with IL-12 J Immunol 1996 156: 693–699
Rakhmilevich AL, Turner J, Ford MJ, et al . Gene gun–mediated skin transfection with interleukin 12 gene results in regression of established primary and metastatic murine tumors Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996 93: 6291–6296
Manetti R, Parronchi P, Giudizi MG, et al . Natural killer cell stimulatory factor (interleukin 12 [IL-12]) induces T helper type 1 (Th1)–specific immune responses and inhibits the development of IL-4–producing Th cells J Exp Med 1993 177: 1199–1204
Hsieh CS, Macatonia SE, Tripp CS, Wolf SF, O'Garra A, Murphy KM . Development of TH1 CD4+ T cells through IL-12 produced by Listeria -induced macrophages Science 1993 260: 547–549
Martinotti A, Stoppacciaro A, Vagliani M, et al . CD4 T cells inhibit in vivo the CD8-mediated immune response against murine colon carcinoma cells transduced with interleukin-12 genes Eur J Immunol 1995 25: 137–146
Tsung K, Meko JB, Peplinski GR, Tsung YL, Norton JA . IL-12 induces T helper 1–directed antitumor response J Immunol 1997 158: 3359–3365
Cui J, Shin T, Kawano T, et al . Requirement for Valpha14 NKT cells in IL-12–mediated rejection of tumors Science 1997 278: 1623–1626
Brunda MJ, Luistro L, Hendrzak JA, Fountoulakis M, Garotta G, Gately MK . Role of interferon-gamma in mediating the antitumor efficacy of interleukin-12 J Immunother Emphasis Tumor Immunol 1995 17: 71–77
Gately MK, Warrier RR, Honasoge S, et al . Administration of recombinant IL-12 to normal mice enhances cytolytic lymphocyte activity and induces production of IFN-gamma in vivo Int Immunol 1994 6: 157–167
Orange JS, Salazar-Mather TP, Opal SM, et al . Mechanism of interleukin 12–mediated toxicities during experimental viral infections: role of tumor necrosis factor and glucocorticoids J Exp Med 1995 181: 901–914
Marshall E . Cancer trial of interleukin 12 halted Science 1995 268: 1555
Johnston SA . Biolistic transformation: microbes to mice Nature 1990 346: 776–777
Cheng L, Ziegelhoffer PR, Yang N-S . In vivo promoter activity and transgene expression in mammalian somatic tissues evaluated using particle bombardment Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993 90: 4455–4459
Yang NS, Sun WH . Gene gun and other nonviral approaches for cancer gene therapy Nat Med 1995 1: 481–483
Sun WH, Burkholder JK, Sun J, et al . In vivo cytokine gene transfer by gene gun reduces tumor growth in mice Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 2889–2893
Mahvi DM, Burkholder JK, Turner J, et al . Particle-mediated gene transfer of granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor cDNA to tumor cells: implications for a clinically relevant tumor vaccine Hum Gene Ther 1996 7: 1535–1543
Hosoya Y, Kobyashi E, Yoshida S, et al . Introduction of cytokine genes into rat solid neoplasms with a hand-held gene gun: I. Effect of IL-12 plus TNF-α gene transfection on subcutaneous tumor Ann Cancer Res Ther 1998 7: 39–42
Yamasaki M, Hashiguchi N, Tsukamoto T, Osumi T . Variant form of green and blue fluorescent proteins adapted for use in mammalian cells Bioimages 1998 6: 1–7
Yoshida Y, Kobayashi E, Endo H, et al . Introduction of DNA into rat liver with a hand-held gene gun: distribution of the expressed enzyme, [32P] DNA, and Ca2+ flux Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997 234: 695–700
Keller ET, Burkholder JK, Shi F, et al . In vivo particle-mediated cytokine gene transfer into canine oral mucosa and epidermis Cancer Gene Ther 1996 3: 186–191
Kobayashi M, Fitz L, Ryan M, et al . Identification and purification of natural killer cell stimulatory factor (NKSF), a cytokine with multiple biologic effects on human lymphocytes J Exp Med 1989 170: 827–845
D'Andrea A, Rengaraju M, Valiante NM, et al . Production of natural killer cell stimulatory factor (interleukin 12) by peripheral blood mononuclear cells J Exp Med 1992 176: 1387–1398
Barrett AW, Cruchley AT, Williams DM . Oral mucosal Langerhans' cells Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 1996 7: 36–58
Hasseus B, Jontell M, Bergenholtz G, Eklund C, Dahlgren UI . Langerhans cells from oral epithelium are more effective in stimulating allogeneic t-cells in vitro than Langerhans cells from skin epithelium J Dent Res 1999 78: 751–758
Pepin LF, Roger T, Morisset J, Seman M . Preferential V delta 1 expression among TcR gamma/delta–bearing T cells in human oral epithelium Scand J Immunol 1993 37: 289–294
Fujihashi K, Taguchi T, Aicher WK, et al . Immunoregulatory functions for murine intraepithelial lymphocytes: gamma/delta T cell receptor–positive (TCR+) T cells abrogate oral tolerance, while alpha/beta TCR+ T cells provide B cell help J Exp Med 1992 175: 695–707
Banchereau J, Steinman RM . Dendritic cells and the control of immunity Nature 1998 392: 245–252
Schultz J, Pavlovic J, Strack B, Nawrath M, Moelling K . Long-lasting anti-metastatic efficiency of interleukin 12-encoding plasmid DNA Hum Gene Ther 1999 10: 407–417
Cassatella MA, Meda L, Gasperini S, D'Andrea A, Ma X, Trinchieri G . Interleukin-12 production by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes Eur J Immunol 1995 25: 1–5
Kawakami Y, Rosenberg SA . Human tumor antigens recognized by T-cells Immunol Res 1997 16: 313–339
Kawakami Y, Eliyahu S, Delgado CH, et al . Cloning of the gene coding for a shared human melanoma antigen recognized by autologous T cells infiltrating into tumor Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994 91: 3515–3519
Kawakami Y, Eliyahu S, Delgado CH, et al . Identification of a human melanoma antigen recognized by tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes associated with in vivo tumor rejection Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994 91: 6458–6462
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Osumi (Himeji Institute of Technology, Hyogo, Japan) for donating a GFP plasmid, phGFP-105-C1, and S. Wolf (Genetic Institute, Cambridge, MA) for donating a murine IL-12 expression plasmid, pCAGGS-IL-12. We greatly appreciate the skillful technical assistance of Kyoko Okamaoto and Noriko Hayashi. This work was partially supported by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. (No. 13470261)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Murakami, T., Hakamata, Y. et al. Gene gun–mediated oral mucosal transfer of interleukin 12 cDNA coupled with an irradiated melanoma vaccine in a hamster model: Successful treatment of oral melanoma and distant skin lesion. Cancer Gene Ther 8, 705–712 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700363
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700363
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The effects of mesenchymal stem cells injected via different routes on modified IL-12-mediated antitumor activity
Gene Therapy (2011)
-
Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of interleukin-23 shows prophylactic but not therapeutic antitumor effects
Cancer Gene Therapy (2008)
-
Cell and Tissue Targeting of Nucleic Acids for Cancer Gene Therapy
Pharmaceutical Research (2007)
-
Long-lasting gene expression by particle-mediated intramuscular transfection modified with bupivacaine: combinatorial gene therapy with IL-12 and IL-18 cDNA against rat sarcoma at a distant site
Cancer Gene Therapy (2003)