Abstract
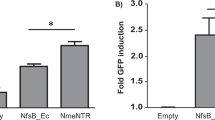
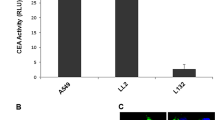
We constructed a series of adenoviral (Ad) vectors that express the Candida albicans cytosine deaminase (CD) suicide gene under the transcriptional control of either the human α-lactalbumin (ALA) or ovine β-lactoglobulin (BLG) promoter (Ad.ALA.CD and Ad.BLG.CD, respectively). The Ad.ALA.CD and the Ad.BLG.CD vectors converted the prodrug 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC) to the toxic nucleotide analog 5-fluorouracil in a breast cancer cell-specific manner, with a conversion rate of 40% and 52% in T47D cells and 50% and 41% in MCF7 cells, respectively. No significant conversion (≤3%) was observed in an immortalized nontumorigenic breast epithelial cell line (MCF10A) and a human osteosarcoma cell line (U2OS). Adenovirus vector-based prodrug conversion of the 5-FC in T47D and MCF7 in the presence of 1 mg/mL of 5-FC led to cytotoxicity that resulted in a nearly complete cell death (≥90%) after 5 days, whereas MCF10A and U2OS cells remained resistant (≤10%). Nude mice harboring T47D-derived breast tumors that were injected intratumorally (i.t.) with therapeutic adenovirus vectors at a dose of 2 × 108 plaque-forming units and treated systemically with 5-FC at a concentration of 500 mg/kg/day showed a marked reduction in tumor mass within 30 days when compared with animals that received vector alone. Animal survival was significantly prolonged after 72 days in mice treated with therapeutic vectors in conjunction with prodrug when compared with control animals. These preclinical data are sufficiently promising to warrant further studies of this transcriptional targeting approach to breast cancer treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, L., Krotz, S., Weitzman, S. et al. Breast cancer-specific expression of the Candida albicans cytosine deaminase gene using a transcriptional targeting approach. Cancer Gene Ther 7, 845–852 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700191
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700191
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Isocytosine deaminase Vcz as a novel tool for the prodrug cancer therapy
BMC Cancer (2019)
-
Human amniotic fluid-derived stem cells expressing cytosine deaminase and thymidine kinase inhibits the growth of breast cancer cells in cellular and xenograft mouse models
Cancer Gene Therapy (2012)
-
Potential antitumor therapeutic strategies of human amniotic membrane and amniotic fluid-derived stem cells
Cancer Gene Therapy (2012)
-
Potent, tumor-specific gene expression in an orthotopic hepatoma rat model using a Survivin-targeted, amplifiable adenoviral vector
Gene Therapy (2011)
-
A prophylactic vaccine for breast cancer? Why not?
Breast Cancer Research (2010)