Abstract
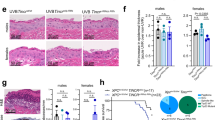
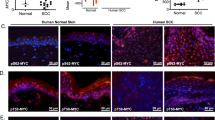
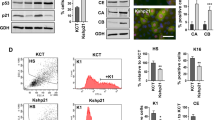
Prior reports suggest that p53 protein status may influence the response to gene transduction with wild-type (wt) p53. Adenoviral vectors containing the p53 gene were administered to normal keratinocytes, to squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) lines with varied p53 protein status (absent, mutant, wt, or degraded by papillomavirus), as well as to tumors formed in severe combined immunodeficient mice. The percentage of cells undergoing apoptosis, G1 growth arrest, WAF1/p21 induction, and in vivo tumor progression were studied after wt p53 gene transduction. Apoptosis developed first in normal keratinocytes, next in SCCs lacking p53 protein, and last in SCCs with mutant or degraded p53 protein. All of the cell lines studied demonstrated an increase in WAF1/p21 protein, but only those lacking p53 protein showed G1 arrest. Tumors lacking p53 protein were more susceptible to p53 overexpression than those containing mutant or degraded p53 protein. The endogenous p53 protein status of SCCs appears to influence the outcome of p53 gene transduction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
St. John, L., Sauter, E., Herlyn, M. et al. Endogenous p53 gene status predicts the response of human squamous cell carcinomas to wild-type p53. Cancer Gene Ther 7, 749–756 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700166
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700166
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
p63, a key regulator of Ago2, links to the microRNA-144 cluster
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
CRISPR-based kinome-screening revealed MINK1 as a druggable player to rewire 5FU-resistance in OSCC through AKT/MDM2/p53 axis
Oncogene (2022)
-
Immunologic and metabolic characteristics of HPV-negative and HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinomas are strikingly different
Virchows Archiv (2014)
-
Gene therapy for malignant mesothelioma: Current prospects and challenges
Cancer Gene Therapy (2013)
-
Upregulated p53 expression activates apoptotic pathways in wild-type p53-bearing mesothelioma and enhances cytotoxicity of cisplatin and pemetrexed
Cancer Gene Therapy (2012)