Abstract
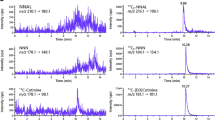
We report a new approach for assessing human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA) by measuring BPA in urine after enzymatic deglucuronidation. This method involves addition of 13C 12-labeled BPA, enzymatic deconjugation, solid-phase extraction, and derivatization with pentafluorobenzyl bromide. The product of the derivatization is separated by gas chromatography followed by mass spectrometric detection using negative chemical ionization and selected ion monitoring. Using this analysis method, urine samples fortified with both a constant level of labeled BPA and a range of unlabeled BPA levels (0.27–10.6 ng/ml) demonstrated constant percentage recovery. In addition, a range of urine sample volumes (0.25–10.0 ml) with constant amounts of added internal standard produced a linear response (r2=0.99). The method limit of detection was 0.12 ng/ml. This method was validated by duplicate analyses using gas chromatography coupled to a high-resolution mass spectrometer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BPA:
-
bisphenol A
- EI+:
-
positive electron ionization
- GC/HRMS:
-
gas chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometric detection
- GC/MS:
-
gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometric detection
- Hg:
-
mercury
- m/z:
-
mass to charge ratio
- NCI:
-
negative chemical ionization
- SPE:
-
solid-phase extraction
- TMS:
-
trimethylsilyl
References
Ashby J, Bisphenol A and dental sealants: the inappropriateness of continued reference to a single female patient, Environ Health Perspect (1997) 105: 362
Blount BC Milgram KE Silva M Malek N Reidy JA Needham LL and Brock JW, Quantitative detection of eight phthalate metabolites in human urine using HPLC-APCIMS/MS, Anal Chem (2000) 72: 4127–4134
Brotons JA Olea-Serrano MF Villalobos M Pedraza V and Olea N, Xenoestrogens released from laquer coating in food cans, Environ Health Perspect (1995) 103: 6008–6012
Daneshvar M, and Brooks JB, Improved procedure for preparation of pentafluorobenzyl derivatives of carboxylic acids for analysis by gas chromatography with electron capture detection, J Chromatgr (1988) 433: 248–256
Del Olmo M Zafra A Navas NA and Vilchez JL, Trace determination of phenol, bisphenol A, and bisphenol A digycidyl ether in mixtures by excitation fluorescence following micro liquid–liquid extraction using partial least squares regression, Analyst (1999) 124: 385–390
Gandara JS Abuin SP Losado PP and Lozano JS, Determination of bisphenol A and F in noncured epoxy resins by RP–HPLC–fluorescence techniques, J Chromatogr Sci (1993) 31: 450–454
Hofmann U, Holzer S, and Meese CO, Pentafluorophenyldiazoalkanes as novel derivatization reagents for the determination of sensitive carboxylic acids by gas chromatography–negative ion mass spectrometry, J Chromatogr (1990) 508: 349–356
Hoyle WC and Budway R, Bisphenol A in food cans, Environ Health Perspect (1997) 105: 570–571
Imai Y, Comments on estrogenicity of resin-based composites and sealants used in dentistry, Environ Health Perspect (1999) 107: A290
Jacobsson S, Larsson A, and Arbin A, Extractive pentafluorobenzylation of formic, acetic and levulinic, benzoic and phthalic acids studied by liquid chromatography and dual-oven capillary gas chromatography, J Chromatogr (1988) 447: 329–340
Knaak J, and Sullivan L, Metabolism of bisphenol A in the rat, Toxicol Appl Pharmacol (1966) 8: 175–184
Laws SC Carey SA Ferrell JM Bodman GJ and Cooper RL, Estrogenic activity of octylphenol, nonylphenol, bisphenol A, and methoxychlor in rats, Toxicol Sci (2000) 254: 154–167
Long X Steinmetz R Nira B-J Caperall-Grant A Young PCM Nephew KP and Bigsby RM, Strain differences in vaginal responses to the xenoestrogen bisphenol A, Environ Health Perspect (2000) 108: 243–247
Matsumoto G, Ishwatari R, and Hanya T, Gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric identification of phenols and aromatic acids in river waters, Water Res (1977) 11: 693–698
Olea N Pulgar R Perez P Olea-Serrano F Rivas A Novillo-Fetrell A Pedraza V Soto AM and Shonnenshein C, Estrogenicity of resin-based composites and sealants used in dentistry, Environ Health Perspect (1996) 104: 298–305
Pirkle J Sampson EJ Needham LL Patterson DG and Ashley DL, Using biological monitoring to assess human exposure to toxicants, Environ Health Perspect (1995) 103: 45–48
Pottenger LH Domoradzki JY Markham DA Hansen SC Cagen SZ and Wacchter JM Jr., The relative bioavailability and metabolism of bisphenol A in rats is dependent upon the route of administration, Toxicol Sci (2000) 54: 3–18
Sajika J, Takahashi K, and Yonekubo J, Sensitive method for the determination of bisphenol-A in serum using two systems of high performance chromatography, J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl (1999) 736: 255–261
Staples CA Dorn PB Klecka GM O'block ST and Harris LR, A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A, Chemosphere (1998) 36: 2149–2173
Yoshimura Y Brock JW Makino, T and Nakazawa H 2000 Determination of bisphenol A in human serum by GC/MS, Anal Chem Acta In press
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Japan. Brand names are given for reference and do not constitute endorsement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BROCK, J., YOSHIMURA, Y., BARR, J. et al. Measurement of bisphenol A levels in human urine. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 11, 323–328 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jea.7500174
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jea.7500174
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Derivatization gas chromatography negative chemical ionization mass spectrometry for the analysis of trace organic pollutants and their metabolites in human biological samples
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2020)
-
Environmental chemicals mediated the effect of old housing on adult health problems: US NHANES, 2009–2010
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2015)
-
Higher urinary heavy metal, phthalate and arsenic concentrations accounted for 3–19% of the population attributable risk for high blood pressure: US NHANES, 2009–2012
Hypertension Research (2014)
-
Determination of selected endocrine disrupting compounds in human fetal and newborn tissues by GC-MS
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2014)
-
Quantitative determination of free and total bisphenol A in human urine using labeled BPA glucuronide and isotope dilution mass spectrometry
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2014)