Abstract
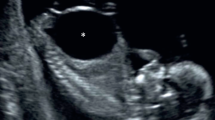
In fetal intestinal perforation, inflammation leads to production of ascites. Small bowel is usually involved by perforation with the distal ileum the most frequent site. We report the first case of prenatal perforation of the intraperitoneal part of the rectum, which presented as severe ascites at a 37 weeks’ gestation antenatal ultrasonography. As none of the reported causes of intestinal perforation were identified in our case, its etiology remained idiopathic.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis MQ, Cywes S, Rode H . Prenatal perforation of the extraperitoneal part of the rectum, associated with a developmental defect of the pelvic floor. Z Kinderchir 1984; 39: 271–273.
Zelop C, Benacerraff B . The cause and natural history of fetal ascites. Prenat Diagn 1994; 14: 941–946.
Foster MA, Nyberg DA, Mahony BS, Mack LA, Marks WM, Raabe RD . Meconium peritonitis: prenatal sonographic findings and their clinical significance. Radiology 1987; 165: 661–665.
Chalubinski K, Deutinger J, Bernaschek G . Meconium peritonitis: extrusion of meconium and different sonographical appearances in relation to the stage of the disease. Prenatal Diagn 1992; 12: 631–636.
Casaccia G, Trucchi A, Nahom A, Aite L, Lucidi V, Giorlandino C et al. The impact of cystic fibrosis on neonatal intestinal obstruction: the need for prenatal/neonatal screening. Pediat Surg Int 2003; 19: 75–78.
Schlensker KH, Gunther H, Bolte A . Prenatal diagnosis of fetal meconium peritonitis, therapy and clinical course. With a contribution to the differential diagnosis of fetal ascites. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 1984; 44: 435–440.
Schmider A, Henrich W, Reles A, Kjos S, Dudenhausen JW . Etiology and prognosis of fetal ascites. Fetal Diagn Ther 2003; 18: 230–236.
Favre R, Dreux S, Dommergues M, Dumez Y, Luton D, Oury JF et al. Nonimmune fetal ascites: a series of 79 cases. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004; 190: 407–412.
Stringer MD, Drake DP . Hirschsprung's disease presenting as neonatal gastrointestinal perforation. Br J Surg 1991; 78: 188–189.
Agrawala G, Predanic M, Perni SC, Chasen ST . Isolated fetal ascites caused by bowel perforation due to colonic atresia. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2005; 17: 291–294.
Fines B, Ben-Ami TE, Yousefzadeh DK . Traumatic prenatal sigmoid perforation due to amniocentesis. Pediat Radiol 2001; 31: 440–443.
Young DG . Thermometers and rectal perforations in the neonate. Arch Dis Child 1979; 54: 242.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casaccia, G., Giorlandino, C., Catalano, O. et al. Prenatal rectal perforation: an unsuspected cause of isolated ascites. J Perinatol 26, 717–719 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211602
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211602