Abstract
Objectives:
To investigate postnatal lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) kinetics in term neonates and to test its diagnostic accuracy for early-onset bacterial infection (EOBI).
Study design:
A total of 99 neonates with clinical and serological signs of EOBI comprised the study group; 198 neonates with risk factors, but without EOBI, served as controls. LBP, C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) were determined.
Results:
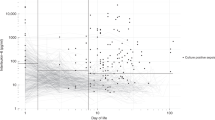
LBP in the noninfected group increased until 24 h after birth (P<0.05 vs 6 h). LBP and CRP correlated strongly in neonates with suspected EOBI (r=0.63). Although LBP reached a higher sensitivity than CRP 6 and 12 h after clinical suspicion (45 (24–68) and 79% (54–94) vs 9 (0–24) and 39% (17–64); P<0.05)), EOBI was most reliably detected by IL-8.
Conclusion:
LBP kinetics were age-dependent. LBP was not sufficiently sensitive in the prediction of EOBI.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ng PC . Diagnostic markers of infection in neonates. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2004; 89: F229–F235.
Mathers NJ, Pohlandt F . Diagnostic audit of C-reactive protein in neonatal infection. Eur J Pediatr 1987; 146: 147–151.
Hack CE, Hart M, van Schijndel RJ, Eerenberg AJ, Nuijens JH, Thijs LG et al. Interleukin-8 in sepsis: relation to shock and inflammatory mediators. Infect Immun 1992; 60: 2835–2842.
Orlikowsky TW, Neunhoeffer F, Goelz R, Eichner M, Henkel C, Zwirner M et al. Evaluation of IL-8-Concentrations in Plasma and Lysed EDTA-Blood in Healthy Neonates and Those with suspected Early Onset Bacterial Infection. Pediatr Res 2004; 56: 804–809.
Schumann RR, Kirschning CJ, Unbehaun A, Aberle HP, Knope HP, Lamping N et al. Lipopolysaccharide binding protein: its role and therapeutical potential in inflammation and sepsis. Biochem Soc Trans 1994; 22: 80–82.
Wright SD, Ramos RA, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ, Mathison JC . CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science 1990; 249: 1431–1433.
Dammann O, Leviton A . Maternal intrauterine infection, cytokines, and brain damage in the preterm newborn. Pediatr Res 1997; 42: 1–8.
Ng PC, Li K, Wong RP, Chui K, Wong E, Li G et al. Proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine responses in preterm infants with systemic infections. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2003; 88: F209–F213.
Froon AH, Dentener MA, Greve JW, Ramsay G, Buurman WA . Lipopolysaccharide toxicity-regulating proteins in bacteremia. J Infect Dis 1995; 171: 1250–1257.
Rietschel ET, Brade H, Holst O, Brade L, Muller-Loennies S, Mamat U et al. Bacterial endotoxin: chemical constitution, biological recognition, host response, and immunological detoxification. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 1996; 216: 39–81.
Grunfeld C, Marshall M, Shigenaga JK, Moser AH, Tobias P, Feingold KR . Lipoproteins inhibit macrophage activation by lipoteichoic acid. J Lipid Res 1999; 40: 245–252.
Berner R, Furll B, Stelter F, Drose J, Muller HP, Schutt C . Elevated levels of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and soluble CD14 in plasma in neonatal early-onset sepsis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2002; 9: 440–445.
Pavcnik-Arnol M, Hojker S, Derganc M . Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in critically ill neonates and children with suspected infection: comparison with procalcitonin, interleukin-6, and C-reactive protein. Intensive Care Med 2004; 30: 1454–1460.
Berendt D, Dembinski J, Heep A, Bartmann P . Lipopolysaccharide binding protein in preterm infants. Arch Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2004; 89: F551–554.
Franz AR, Kron M, Pohlandt F, Steinbach G . Comparison of procalcitonin with interleukin 8, C-reactive protein and differential white blood cell count for the early diagnosis of bacterial infections in newborn infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1999; 18: 666–671.
Franz AR, Bauer K, Schalk A, Garland SM, Bowman ED, Rex K et al. Measurement of interleukin 8 in combination with C-reactive protein reduced unnecessary antibiotic therapy in newborn infants: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2004; 114: 1–8.
Chiesa C, Panero A, Osborn JF, Simonetti AF, Pacifico L . Diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: a clinical and laboratory challenge. Clin Chem 2004; 50: 279–287.
Schroedl W, Jaekel L, Krueger M . C-reactive protein and antibacterial activity in blood plasma of colostrum-fed calves and the effect of lactulose. J Dairy Sci 2003; 86: 3313–3320.
Turner MA, Power S, Emmerson AJ . Gestational age and the C reactive protein response. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2004; 89: F272–F273.
Vreugdenhil AC, Dentener MA, Snoek AM, Greve JW, Buurman WA . Lipopolysaccharide binding protein and serum amyloid A secretion by human intestinal epithelial cells during the acute phase response. J Immunol 1999; 163: 2792–2798.
Dentener MA, Vreugdenhil AC, Hoet PH, Vernooy JH, Nieman FH, Heumann D et al. Production of the acute-phase protein lipopolysaccharide-binding protein by respiratory type II epithelial cells: implications for local defense to bacterial endotoxins. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2000; 23: 146–153.
Hsu KK, Pelton SI, Shapiro DS . Detection of group B streptococcal bacteremia in simulated intrapartum antimicrobial prophylaxis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2003; 45: 23–27.
Buttery JP . Blood cultures in newborns and children: optimising an everyday test. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2002; 87: F25–F28.
Ottolini MC, Lundgren K, Mirkinson LJ, Cason S, Ottolini MG . Utility of complete blood count and blood culture screening to diagnose neonatal sepsis in the asymptomatic at risk newborn. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2003; 22: 430–434.
Luck S, Torny M, d’Agapeyeff K, Pitt A, Heath P, Breathnach A et al. Estimated early-onset group B streptococcal neonatal disease. Lancet 2003; 361: 1953–1954.
Hengst JM . The role of C-reactive protein in the evaluation and management of infants with suspected sepsis. Adv Neonatal Care 2003; 3: 3–13.
Pourcyrous M, Bada HS, Korones SB, Baselski V, Wong SP . Significance of serial C-reactive protein responses in neonatal infection and other disorders. Pediatrics 1993; 92: 431–435.
Messer J, Eyer D, Donato L, Gallati H, Matis J, Simeonai U . Evaluation of interleukin-6 and soluble receptors of tumor necrosis factor for early diagnosis of neonatal infection. J Pediatr 1996; 129: 574–580.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orlikowsky, T., Trüg, C., Neunhoeffer, F. et al. Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in noninfected neonates and those with suspected early-onset bacterial infection. J Perinatol 26, 115–119 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211422
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211422
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Glycosylation deficiency of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and corticosteroid-binding globulin associated with activity and response to treatment for rheumatoid arthritis
Journal of Translational Medicine (2020)
-
Neutrophil and monocyte CD64 indexes, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in sepsis of critically ill neonates and children
Intensive Care Medicine (2009)
-
Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, lipopolysaccharide, and soluble CD14 in sepsis of critically ill neonates and children
Intensive Care Medicine (2007)