Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
To study the effect of spironolactone on dietary electrolyte supplementation, pulmonary function, and electrolyte balance in premature infants with chronic lung disease.
STUDY DESIGN
A double-blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled trial was designed to study two groups of low birth weight infants with chronic lung disease at Pennsylvania Hospital. The placebo group received chlorothiazide and a placebo, and the spironolactone group received chlorothiazide and spironolactone during the 2-week study period. A two-tailed t-test was used to determine equivalence between the two groups.
RESULTS
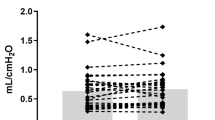
Pulmonary compliance, resistance and tidal volume, serum sodium and potassium, and FIO2, were not statistically different between the two groups. The need for sodium and/or potassium chloride did not differ between the two groups, nor did the quantity of each salt.
CONCLUSION The addition of spironolactone did not reduce the requirement for supplemental electrolytes, nor did it improve pulmonary mechanics or electrolyte balance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was funded by the Newborn Pediatrics Research Fund. D. J. H. was supported in part by a training grant from the National Institutes of Health (HL-07027).
Presented in part at the annual meeting of The Society for Pediatric Research, Washington, DC, May 1997.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffman, D., Gerdes, J. & Abbasi, S. Pulmonary Function and Electrolyte Balance Following Spironolactone Treatment in Preterm Infants With Chronic Lung Disease: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Trial. J Perinatol 20, 41–45 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7200307
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7200307
This article is cited by
-
The association between diuretic class exposures and enteral electrolyte use in infants developing grade 2 or 3 bronchopulmonary dysplasia in United States children’s hospitals
Journal of Perinatology (2021)
-
Routine use of diuretics in very-low birth-weight infants in the absence of supporting evidence
Journal of Perinatology (2011)
-
Diuretics and Chronic Lung Disease of Prematurity
Journal of Perinatology (2001)