Abstract
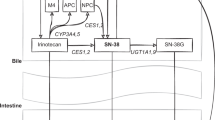
Genetic polymorphisms in hepatically expressed UGT1A1 and UGT1A9 contribute to the interindividual variability i-n irinotecan disposition and toxicity. We screened UGT1A1 (UGT1A1*60, g.−3140G>A, UGT1A1*28 and UGT1A1*6) and UGT1A9 (g.−118(T)9>10 and I399C>T) genes for polymorphic variants in the promoter and coding regions, and the genotypic effect of UGT1A9 I399C>T polymorphism on irinotecan disposition in Asian cancer patients was investigated. Blood samples were collected from 45 patients after administration of irinotecan as a 90 min intravenous infusion of 375 mg/m2 once in every 3 weeks. Genotypic–phenotypic correlates showed that cancer patients heterozygous or homozygous for the I399C>T allele had approximately 2-fold lower systemic exposure to SN-38 (P<0.05) and a trend towards a higher relative extent of glucuronidation (REG) of SN-38 (P>0.05). UGT1A1–1A9 diplotype analysis showed that patients harbouring the H1/H2 (TG6GT10T/GG6GT9C) diplotype had 2.4-fold lower systemic exposure to SN-38 glucuronide (SN-38G) compared with patients harbouring the H1/H5 (TG6GT10T/GG6GT10C) diplotype (P=0.025). In conclusion, this in vivo study supports the in vitro findings of Girard et al. and suggests that the UGT1A9 I399C>T variant may be an important glucuronidating allele affecting the pharmacokinetics of SN-38 and SN-38G in Asian cancer patients receiving irinotecan chemotherapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dutton GJ . Glucuronidation of drugs and other compounds. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 1980.
Tukey RH, Strassburg CP . Human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: metabolism, expression and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2000; 40: 581–616.
Owens IS, Ritter JK . Gene structure at the human UGT1 locus creates diversity in isozyme structure, structure specificity and regulation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res 1995; 51: 306–308.
Gong QH, Cho JW, Huang T, Potter C, Gholami N, Basu NK et al. Thirteen UDP glucuronosyltransferases genes are encoded at the human UGT1 gene complex locus. Pharmacogenetics 2001; 11: 357–368.
Radominska-Pandya A, Czernik PJ, Little JM, Battaglia E, Mackenzie PI . Structural and functional studies of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Drug Metab Rev 1999; 31: 817–899.
Harding D, Fournel-Gigleux S, Jackson MR, Burchell B . Cloning and substrate specificity of a human phenol UDP-glucuronosyltransferase expressed in COS-7 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988; 85: 8381–8385.
Ritter JK, Crawford JM, Owens IS . Cloning of two human liver bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase cDNAs with expression in COS-1 cells. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: 1043–1047.
Wooster R, Sutherland L, Ebner T, Clarke D, Da Cruz e Silva O, Burchell B . Cloning and stable expression of a new member of the human liver phenol/bilirubin:UDP-glucuronosyltransferase cDNA family. Biochem J 1991; 278: 465–469.
Mojarabbi B, Butler R, Mackenzie PI . cDNA cloning and characterization of the human UDP-glucuronosyltranbsferase, UGT1A3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 225: 785–790.
Strassburg CP, Oldhafer K, Manns MP, Tukey RH . Differential expression of the UGT1A locus in human liver, biliary and gastric tissue. Identification if UGT1A7 and UGT1A10 transcripts in extrahepatic tissue. Mol Pharmacol 1997; 52: 212–220.
Strassburg CP, Manns MP, Tukey RH . Expression of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A locus in human colon. Identification and characterization of novel extrahepatic UGT1A8. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 8719–8726.
Saltz LB, Cox JV, Blanke C, Rosen LS, Fehrenbacher L, Moore MJ et al. Irinotecan plus fluorouracil and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. Irinotecan Study Group. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 905–914.
Kawato Y, Aonuma M, Hirota Y, Kuga H, Sato K . Intracellular roles of SN-38, a metabolite of the camptothecin derivative CPT-11, in the antitumour effect of CPT-11. Cancer Res 1991; 51: 4187–4191.
Rivory LP, Robert J . Identification and kinetics of a beta-glucuronide metabolite of SN-38 in human plasma after administration of the camptothecin derivative irinotecan. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1995; 36: 176–179.
Haaz MC, Rivory L, Jantet S, Ratanasavanh D, Robert J . Glucuronidation of SN-38, the active metabolite of irinotecan, by human hepatic microsomes. Pharmacol Toxicol 1997; 80: 91–96.
Rivory LP, Riou JF, Haaz MC, Sable S, Vuilhorgne M, Commercon A et al. Identification and properties of a major plasma metabolite of irinotecan (CPT-11) isolated from the plasma of patients. Cancer Res 1996; 56: 3689–3694.
Dodds HM, Haaz MC, Riou JF, Robert J, Rivory LP . Identification of a new metabolite of CPT-11 (irinotecan): pharmacological properties and activation of SN-38. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1998; 286: 578–583.
Rivory LP . Metabolism of CPT-11. Impact on activity. Ann NY Acad Sci 2000; 922: 205–215.
Ando Y, Saka H, Ando M, Sawa T, Muro K, Ueoka H et al. Polymorphisms of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene and irinotecan toxicity: a pharmacogenetic analysis. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 6921–6926.
Iyer L, Das S, Janisch L, Wen M, Ramirez J, Karrison T et al. UGT1A1*28 polymorphism as a determinant or irinotecan disposition and toxicity. Pharmacogenomics J 2002; 2: 43–47.
Gagne JF, Montminy V, Belanger P, Journault K, Gaucher G, Guillemette C . Common human UGT1A polymorphisms and the altered metabolism of irinotecan active metabolite 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin (SN-38). Mol Pharmacol 2002; 62: 608–617.
Carlini LE, Meropol NJ, Bever J, Andria ML, Hill T, Gold P et al. UGT1A7 and UGT1A9 polymorphisms predict response and toxicity in colorectal cancer patients treated with capecitabine/irinotecan. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 1226–1236.
Toffoli G, Cecchin E, Corona G, Russo A, Buonadonna A, D'Andrea M et al. The role of UGT1A1*28 polymorphism in the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of irinotecan in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 3061–3068.
Sai K, Saeki M, Saito Y, Ozawa S, Katori N, Jinno H et al. UGT1A1 haplotypes associated with reduced glucuronidation and increased serum bilirubin in irinotecan-administered Japanese patients with cancer. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2004; 75: 501–515.
Kitagawa C, Ando M, Ando Y, Sekido Y, Wakai K, Imaizumi K et al. Genetic polymorphism in the Phenobarbital-responsive enhancer module of the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 gene and irinotecan toxicity. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2005; 15: 35–41.
Villeneuve L, Girard H, Fortier LC, Gagne JF, Guillemette C . Novel functional polymorphisms in the UGT1A7 and UGT1A9 glucuronidating enzymes in Caucasian and African-American subjects and their impact on the metabolism of 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin and flavopiridol anticancer drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003; 307: 117–128.
Girard H, Court MH, Bernard O, Fortier LC, Villeneuve L, Hao Q et al. Identification of common polymorphisms in the promoter of the UGT1A9 gene: evidence that UGT1A9 protein and activity levels are strongly genetically controlled in the liver. Pharmacogenetics 2004; 14: 501–515.
Yamanaka H, Nakajima M, Katoh M, Hara Y, Tachibana O, Yamashita J et al. A novel polymorphism in the promoter region of human UGT1A9 gene (UGT1A9*22) and its effects on the transcriptional activity. Pharmacogenetics 2004; 14: 329–332.
Girard H, Villeneuve L, Court MH, Fortier LC, Caron P, Hao Q et al. The novel UGT1A9 intronic I399 polymorphism appears as a predictor of 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin glucuronidation levels in the liver. Drug Metab Dispos 2006; 34: 1220–1228.
Yamanaka H, Nakajima M, Katoh M, Hara Y, Tachibana O, Yamashita J et al. A novel polymorphism in the promoter region of human UGT1A9 gene (UGT1A9*22) and its effects on the transcriptional activity. Pharmacogenetics 2004; 14: 329–332.
Han J-Y, Lim H-S, Shin ES, Yoo Y-K, Park YH, Lee Y-E et al. Comprehensive analysis of UGT1A polymorphisms predictive for pharmacokinetics and treatment outcome in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer treated with irinotecan and cisplatin. J Clin Oncol 2006; 15: 2237–2244.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Singapore Cancer Syndicate (SCS-PS0023) and NMRC (NMRC/0814/2003) for funding this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Duality of interest
None declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sandanaraj, E., Jada, S., Shu, X. et al. Influence of UGT1A9 intronic I399C>T polymorphism on SN-38 glucuronidation in Asian cancer patients. Pharmacogenomics J 8, 174–185 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500473
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500473
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Analysis of influencing factors on monohydroxylated derivative of oxcarbazepine plasma concentration in children with epilepsy
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2022)
-
Comparison of the Pharmacokinetics of RIPK1 Inhibitor GSK2982772 in Healthy Western and Japanese Subjects
European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (2021)
-
Effects of UGT1A9 genetic polymorphisms on monohydroxylated derivative of oxcarbazepine concentrations and oxcarbazepine monotherapeutic efficacy in Chinese patients with epilepsy
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2017)
-
The effect of UGTs polymorphism on the auto-induction phase II metabolism-mediated pharmacokinetics of dihydroartemisinin in healthy Chinese subjects after oral administration of a fixed combination of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine
Malaria Journal (2014)
-
Polymorphisms of UGT1A9 and UGT2B7 influence the pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid after a single oral dose in healthy Chinese volunteers
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2013)