Abstract
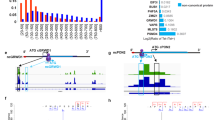
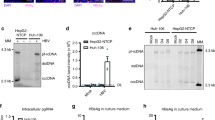
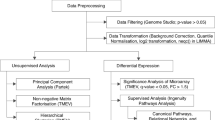
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a major health concern world wide, and few effective treatments have been developed. It has recently been reported that inhibiting host-cell proteins can prevent viral infection. The human genome may contain more genes required for HBV infection and replication than the viral genome. A systematic approach to find these potential antiviral targets is by host gene expression analysis using DNA microarrays. The aim of this study was to identify and validate novel cellular anti-HBV targets. The Human Whole Genome Bioarray was used to analyze differentially expressed genes in HepG2.2.15 cells and HepG2 cells. Altered gene expression in HepG2.2.15 cells was studied following treatment with the anti-HBV drug, lamivudine. Genes that were differentially expressed during HBV infection and reversed with anti-HBV drugs were validated by semiquantitative reverse transcription-PCR. Bioinformatics analysis revealed ABHD2, EREG, ACVR2B, CDC34, KHDRBS3 and RORA as potential cellular anti-HBV targets. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides were used to test the antiviral activity of these potential targets. Results strongly suggested that inhibition of ABHD2 or EREG significantly blocked HBV propagation in HepG2.2.15 cells. This study demonstrates that ABHD2 and EREG are essential for HBV propagation and provides strong evidence that these proteins could be used as potential targets for anti-HBV drugs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seeger C, Mason WS . Hepatitis B virus biology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2000; 64: 51–68.
Parkin DM, Pisani P, Munoz N et al. The global health burden of infection associated cancers [J]. Cancer Surv 1999; 33: 5–33.
Hoofnagle JH, DiBisceglie AM . The treatment of chronic viral hepatitis. N Engl J Med 1997; 336: 347–356.
Nassal M . Hepatitis B virus replication: novel roles for virus–host interactions. Intervirology 1998; 42: 100–116.
Ganem D . The X files – one step closer to closure. Science 2001; 294: 2299–2300.
Tang H, Banks KE, Anderson AL, McLachlan A . Hepatitis B virus transcription and replication. Drug News Perspect 2001; 14: 325–334.
Wing BA, Brown EP, Shenk T et al. DNA microarrays: a powerful new tool for analysis of the virus–host interaction. DDT 2001; 6 (15, suppl.): s67–s71.
Smith MW, Yue ZN, Korth MJ, Do HA, Boix L, Fausto N et al. Hepatitis C virus and liver disease: global transcriptional profiling and identification of potential markers. Hepatology 2003; 38: 1458–1467.
Wieland SF, Vega RG, Muller R, Evans CF, Hilbush B, Guidotti LG et al. Searching for interferon-induced genes that inhibit hepatitis B virus replication in transgenic mouse hepatocytes. J Virol 2003; 77: 1227–1236.
Feitelson MA . Hepatitis B virus in hepatocarcinogenesis. J Cell Physiol 1999; 181: 188–202.
Park SG, Jung G . Human hepatitis B virus polymerase interacts with the molecular chaperonin Hsp60. J Virol 2001; 75: 6962–6968.
Cho G, Park S-G, Jung G . Localization of HSP90 binding sites in the human hepatitis B virus polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000; 269: 191–196.
Ori A, Zauberman A, Doitch G, Paran N, Oren M, Shaul Y . p53 binds and represses the HBV enhancer: an adjacent enhancer element can reverse the transcription effect of p53. EMBO J 1998; 17: 544–553.
Panteva M, Korkaya H, Jameel S . Hepatitis viruses and the MAPK pathway: is this a survival strategy? Virus Res 2003; 92: 131–140.
Reeves PM, Bommarius B, Lebeis S, McNulty S, Christensen J, Swimm A et al. Disabling poxvirus pathogenesis by inhibition of Abl-family tyrosine kinases. Nat Med 2005; 11: 731–739.
Moses AV, Jarvis MA, Raggo C, Bell YC, Ruhl R, Luukkonen BG et al. Kaposi's sarcomaassociated herpesvirus-induced upregulation of the c-kit proto-oncogene, as identified by gene expression profiling, is essential for the transformation of endothelial cells. J Virol 2002; 76: 8383–8399.
Zhu H, Cong JP, Yu D, Bresnahan WA, Shenk TE . Inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 blocks human cytomegalovirus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 3932–3937.
Jenner RG, Maillard K, Kellam P . Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-infected primary effusion lymphoma has a plasma cell gene expression profile. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 10399–10404.
del Real G, Jimenez-Baranda S, Mira E, Lacalle RA, Lucas P, Gomez-Mouton C et al. Statins inhibit HIV-1 infection by down-regulating rho activity. J Exp Med 2004; 200: 541–547.
Bordier BB, Marion PL, Glenn JS . A prenylation inhibitor prevents production of infectious hepatitis delta virus particles. J Virol 2002; 76: 10465–10472.
Bordier BB, Ohkanda J, Liu P, Lee SY, Salazar FH, Marion PL et al. In vivo antiviral efficacy of prenylation inhibitors against hepatitis delta virus. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 407–414.
Hirsch AJ, Medigeshi GR, Nelson JA . The Src family kinase c-Yes is required for maturation of West Nile virus particles. J Virol 2005; 79: 11943–11951.
Otsuka M, Aizaki H, Kato N, Suzuki T, Miyamura T, Omata M et al. Differential cellular gene expression induced by hepatitis B and C viruses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 300: 443–447.
Gervain J, Papp I, Csondes M . Determination of the lamivudine-resistant mutants of hepatitis B virus. Orv Hetil 2003; 144: 1251–1256.
Tarn C, Bilodeau ML, Hullinger RL, Andrisani OM . Differential immediate early gene expression in conditional hepatitis B virus pX-transforming versus nontransforming hepatocyte cell lines. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 2327–2336.
Lee YI, Lee S, Poo HR . The human hepatitis B virus transactivator X gene product regulates Sp1 mediated transcription of an insulin-like growth factor II promoter 4. Oncogene 1998; 16: 2367–2380.
Kang-Park S, Lee JH, Shin JH, Lee YI . Activation of the IGF-II gene by HBV-X protein requires PKC and p44/p42 MAP kinase signalings. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 283: 303–307.
Yoo YD, Ueda H, Park K, Flanders KC, Lee YI, Jay G et al. Regulation of transforming growth factor-_1 expression by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) X transactivator. J Clin Invest 1996; 97: 388–395.
Pan J, Clayton M, Feitelson MA . Hepatitis B virus X antigen promotes transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) activity by up-regulation of TGF-beta1 and down-regulation of alpha2-macroglobulin. J Gen Virol 2004; 85 (Part 2): 275–282.
Zhang Z-D, Cheng J, Zhang S-L et al. Cloning and characterization of a human hepatocyte protein, carboxypeptidase N, which binds and activates core promoter of hepatitis B virus. World Chin J Digestol 2003; 11: 1131–1134.
Turner MA, Yang X, Yin D, Kuczera K, Borchardt RT, Howell PL . Structure and function of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. 2000; 33: 101–125.
Banerjee AK . 5′-terminal cap structure in eucaryotic messenger ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev 1980; 44: 175–205.
Holmquist M . Alpha/beta-hydrolase fold enzymes: structures, functions and mechanisms. Curr Protein Pept Sci 2000; 1: 209–235.
Xi QS, Pan W, Zhang Q, Qian XG, Li ZP, Gan RB et al. On the mechanism of growth inhibition of epiregulin in A431 epidermal carcinoma cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 2000; 32: 601–604.
Pugh JC, Summers JW . Infection and uptake of duck hepatitis B virus by duck hepatocytes maintained in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. Virology 1989; 172: 564–572.
Turin F, Borel C, Benchaib M, Kay A, Jamard C, Guguen-Guillouzo C et al. n-Butyrate, a cell cycle blocker, inhibits early amplification of duck hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA after in vitro infection of duck hepatocytes. J Virol 1996; 70: 2691–2696.
Ozer A, Khaoustov VI, Mearns M, Lewis DE, Genta RM, Darlington GJ et al. Effect of hepatocyte proliferation and cellular DNA synthesis on hepatitis B virus replication. Gastroenterology 1996; 110: 1519–1528.
Rumin S, GuguenGuillouzo C . Long-term productive episomal hepatitis B virus replication in primary cultures of adult human hepatocytes infected in vitro. J Viral Hepat 1996; 3: 227–238.
Kraemer K, Fuessel S, Schmidt U, Kotzsch M, Schwenzer B, Wirth MP et al. Antisense-mediated hTERT inhibition specifically reduces the growth of human bladder cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9 (10 Part 1): 3794–3800.
Sells MA, Zelent AZ, Shvartsman M, Acs G . Replication hepatitis B virus in HepG2 cells that produce infectious virions. J Virol 1988; 62: 2836–2844.
Sells MA, Chen ML, Acs G . Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987; 84: 1005–1009.
Doong SL, Tsai CH, Schinazi RF, Liotta DC, Cheng YC . Inhibition of the replication of hepatitis B virus in vitro by 2′,3′-dideoxy-3′-thiacytidine and related analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88: 8495–8499.
Uhlmann E, Peyman A, Ryte A, Schmidt A, Buddecke E . Use of minimal modified antisense oligonucleotides for specific inhibition of gene expression. Methods Enzymol 1999; 313: 268–284.
Cohen JS . Oligonucleotide therapy. In: Crooke ST, Lebleu B (eds). Antisense Research and Applications. CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, 1993: 205–221.
He YY, Wang SQ, Chen SH et al. Construction and clinical application of a new fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction technique for HBV detection. Chin J Hepatol 2001; 9: 376–377.
Wang SQ, Wang XH, Chen SH, Guan W . A new fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction technique. Anal Biochem 2002; 309: 206–211.
Acknowledgements
This work is a Key Program supported by grant from the national nature science foundation of China (No. 30530650), a grant from National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 30625041) and the special funds for major state basic research program of China (973 program) (NO. 2005CB522902). We acknowledge Yiwei Fan for synthesizing the ASODNs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, X., Yang, J., Sun, D. et al. Whole genome expression profiling of hepatitis B virus-transfected cell line reveals the potential targets of anti-HBV drugs. Pharmacogenomics J 8, 61–70 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500459
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500459
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Emerging Therapies for Chronic Hepatitis B and the Potential for a Functional Cure
Drugs (2023)
-
Hepatitis B virus induces G1 phase arrest by regulating cell cycle genes in HepG2.2.15 cells
Virology Journal (2011)
-
Epiregulin as a key molecule to suppress hepatitis B virus propagation in vitro
Archives of Virology (2009)
-
Systems biology and the host response to viral infection
Nature Biotechnology (2007)