Abstract
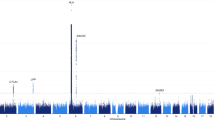
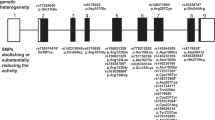
Autoimmune Addison's disease (AAD) is often associated with other components in autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes (APS). Whereas APS I is caused by mutations in the AIRE gene, the susceptibility genes for AAD and APS II are unclear. In the present study, we investigated whether polymorphisms or copy number variations in the AIRE gene were associated with AAD and APS II. First, nine SNPs in the AIRE gene were analyzed in 311 patients with AAD and APS II and 521 healthy controls, identifying no associated risk. Second, in a subgroup of 25 of these patients, AIRE sequencing revealed three novel polymorphisms. Finally, the AIRE copy number was determined by duplex quantitative PCR in 14 patients with APS I, 161 patients with AAD and APS II and in 39 healthy subjects. In two Scandinavian APS I patients previously reported to be homozygous for common AIRE mutations, we identified large deletions of the AIRE gene covering at least exon 2 to exon 8. We conclude that polymorphisms in the AIRE gene are not associated with AAD and APS II. We further suggest that DNA analysis of the parents of patients found to be homozygous for mutations in AIRE, always should be performed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Vaidya B, Imrie H, Geatch DR, Perros P, Ball SG, Baylis PH et al. Association analysis of the cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) and autoimmune regulator-1 (AIRE-1) genes in sporadic autoimmune Addison's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 688–691.
Kemp EH, Ajjan RA, Husebye ES, Peterson P, Uibo R, Imrie H et al. A cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) gene polymorphism is associated with autoimmune Addison's disease in English patients. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1998; 49: 609–613.
Blomhoff A, Lie BA, Kemp EH, Weetman AP, Akselsen HE, Myhre AG et al. Polymorphisms in the CTLA4 gene region confer susceptibility to Addison's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 3474–3476.
Velaga MR, Wilson V, Jennings CE, Owen CJ, Herington S, Donaldson PT et al. The codon 620 tryptophan allele of the lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase (LYP) gene is a major determinant of Graves' disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 5862–5865.
Myhre AG, Undlien DE, Lovas K, Uhlving S, Nedrebo BG, Fougner KJ et al. Autoimmune adrenocortical failure in Norway autoantibodies and human leukocyte antigen class II associations related to clinical features. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 618–623.
Park YS, Sanjeevi CB, Robles D, Yu L, Rewers M, Gottlieb PA et al. Additional association of intra-MHC genes, MICA and D6S273, with Addison's disease. Tissue Antigens 2002; 60: 155–163.
Bilbao JR, Martin-Pagola A, Perez De Nanclares G, Calvo B, Vitoria JC, Vazquez F et al. HLA-DRB1 and MICA in autoimmunity: common associated alleles in autoimmune disorders. Ann NY Acad Sci 2003; 1005: 314–318.
Yu L, Brewer KW, Gates S, Wu A, Wang T, Babu SR et al. DRB1*04 and DQ alleles: expression of 21-hydroxylase autoantibodies and risk of progression to Addison's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84: 328–335.
Gambelunghe G, Falorni A, Ghaderi M, Laureti S, Tortoioli C, Santeusanio F et al. Microsatellite polymorphism of the MHC class I chain-related (MIC-A and MIC-B) genes marks the risk for autoimmune Addison's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84: 3701–3707.
Betterle C, Zanchetta R . Update on autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes (APS). Acta Biomed Ateneo Parmense 2003; 74: 9–33.
Perheentupa J . Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91: 2843–2850.
Ahonen P, Myllarniemi S, Sipila I, Perheentupa J . Clinical variation of autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED) in a series of 68 patients. N Engl J Med 1990; 322: 1829–1836.
Anderson MS, Venanzi ES, Klein L, Chen Z, Berzins SP, Turley SJ et al. Projection of an immunological self shadow within the thymus by the aire protein. Science 2002; 298: 1395–1401.
Liston A, Gray DH, Lesage S, Fletcher AL, Wilson J, Webster KE et al. Gene dosage—limiting role of Aire in thymic expression, clonal deletion, and organ-specific autoimmunity. J Exp Med 2004; 200: 1015–1026.
Liston A, Lesage S, Gray DH, Boyd RL, Goodnow CC . Genetic lesions in T-cell tolerance and thresholds for autoimmunity. Immunol Rev 2005; 204: 87–101.
Turunen JA, Wessman M, Forsblom C, Kilpikari R, Parkkonen M, Pontynen N et al. Association analysis of the AIRE and insulin genes in Finnish type 1 diabetic patients. Immunogenetics 2006; 58: 331–338.
Jin Y, Bennett DC, Amadi-Myers A, Holland P, Riccardi SL, Gowan K et al. Vitiligo-associated multiple autoimmune disease is not associated with genetic variation in AIRE. Pigment Cell Res 2007; 20: 402–404.
Lovas K, Husebye ES . Addison's disease. Lancet 2005; 365: 2058–2061.
Boe AS, Knappskog PM, Myhre AG, Sorheim JI, Husebye ES . Mutational analysis of the autoimmune regulator (AIRE) gene in sporadic autoimmune Addison's disease can reveal patients with unidentified autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I. Eur J Endocrinol 2002; 146: 519–522.
Wolff AS, Erichsen MM, Meager A, Magitta NF, Myhre AG, Bollerslev J et al. Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 in Norway: phenotypic variation, autoantibodies, and novel mutations in the autoimmune regulator gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92: 595–603.
Ekwall O, Hedstrand H, Grimelius L, Haavik J, Perheentupa J, Gustafsson J et al. Identification of tryptophan hydroxylase as an intestinal autoantigen. Lancet 1998; 352: 279–283.
Meager A, Visvalingam K, Peterson P, Moll K, Murumagi A, Krohn K et al. Anti-interferon autoantibodies in autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome type 1. PLoS Med 2006; 3: e289.
Andreasson H, Gyllensten U, Allen M . Real-time DNA quantification of nuclear and mitochondrial DNA in forensic analysis. Biotechniques 2002; 33: 402–404, 407–411.
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ . Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 263–265.
Dudbridge F . UNPHASED user guide. Technical support 2006/5. MRC Biostatistics Unit: Cambridge, UK, 2006.
Gabriel SB, Schaffner SF, Nguyen H, Moore JM, Roy J, Blumenstiel B, et al. The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science 2002; 296: 2225–2229.
Soderbergh A, Rorsman F, Halonen M, Ekwall O, Bjorses P, Kampe O et al. Autoantibodies against aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase identifies a subgroup of patients with Addison's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 460–463.
Cihakova D, Trebusak K, Heino M, Fadeyev V, Tiulpakov A, Battelino T et al. Novel AIRE mutations and P450 cytochrome autoantibodies in Central and Eastern European patients with APECED. Hum Mutat 2001; 18: 225–232.
Heino M, Scott HS, Chen Q, Peterson P, Maebpaa U, Papasavvas MP et al. Mutation analyses of North American APS-1 patients. Hum Mutat 1999; 13: 69–74.
Ferrera F, Rizzi M, Sprecacenere B, Balestra P, Sessarego M, Di Carlo A et al. AIRE gene polymorphisms in systemic sclerosis associated with autoimmune thyroiditis. Clin Immunol 2007; 122: 13–17.
Tazi-Ahnini R, Cork MJ, Gawkrodger DJ, Birch MP, Wengraf D, McDonagh AJ et al. Role of the autoimmune regulator (AIRE) gene in alopecia areata: strong association of a potentially functional AIRE polymorphism with alopecia universalis. Tissue Antigens 2002; 60: 489–495.
Uchida D, Hatakeyama S, Matsushima A, Han H, Ishido S, Hotta H et al. AIRE functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase. J Exp Med 2004; 199: 167–172.
Bottomley MJ, Stier G, Pennacchini D, Legube G, Simon B, Akhtar A et al. NMR structure of the first PHD finger of autoimmune regulator protein (AIRE1). Insights into autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED) disease. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 11505–11512.
Ilmarinen T, Eskelin P, Halonen M, Ruppell T, Kilpikari R, Torres GD et al. Functional analysis of SAND mutations in AIRE supports dominant inheritance of the G228W mutation. Hum Mutat 2005; 26: 322–331.
Cetani F, Barbesino G, Borsari S, Pardi E, Cianferotti L, Pinchera A et al. A novel mutation of the autoimmune regulator gene in an Italian kindred with autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy, acting in a dominant fashion and strongly cosegregating with hypothyroid autoimmune thyroiditis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 4747–4752.
Stolarski B, Pronicka E, Korniszewski L, Pollak A, Kostrzewa G, Rowinska E et al. Molecular background of polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy syndrome in a Polish population: novel AIRE mutations and an estimate of disease prevalence. Clin Genet 2006; 70: 348–354.
Nithiyananthan R, Heward JM, Allahabadia A, Barnett AH, Franklyn JA, Gough SC . A heterozygous deletion of the autoimmune regulator (AIRE1) gene, autoimmune thyroid disease, and type 1 diabetes: no evidence for association. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000; 85: 1320–1322.
Meyer G, Donner H, Herwig J, Bohles H, Usadel KH, Badenhoop K . Screening for an AIRE-1 mutation in patients with Addison's disease, type 1 diabetes, Graves' disease and Hashimoto's thyroiditis as well as in APECED syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2001; 54: 335–338.
Goswami R, Gupta N, Ray D, Rani R, Tomar N, Sarin R et al. Polymorphisms at +49A/G and CT60 sites in the 3′ UTR of the CTLA-4 gene and APECED-related AIRE gene mutations analysis in sporadic idiopathic hypoparathyroidism. Int J Immunogenet 2005; 32: 393–400.
Rizzi M, Ferrera F, Filaci G, Indiveri F . Disruption of immunological tolerance: role of AIRE gene in autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 2006; 5: 145–147.
Acknowledgements
The following physicians have kindly provided clinical data: A-G Myhre, K Fougner, K Lima, S Skare, S Uhlving, U Schafroth and D Veimo. Dag E Undlien is thanked for giving us control DNA. The technical help from Sigrid Erdal and Elin Theodorsen is greatly acknowledged. The study has been supported by grants from Helse-Bergen, the Norwegian Research Council and the EU 6th framework programme (EurAPS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Disclosure of conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest for this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bøe Wolff, A., Oftedal, B., Johansson, S. et al. AIRE variations in Addison's disease and autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes (APS): partial gene deletions contribute to APS I. Genes Immun 9, 130–136 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364457
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364457
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Autoimmune Polyendocrinopathy Candidiasis Ectodermal Dystrophy
Journal of Clinical Immunology (2015)