Abstract
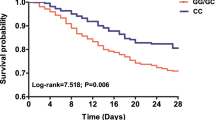
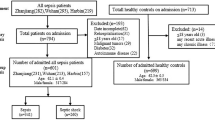
Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response syndrome to infection. Human β-defensin 1 (DEFB1) is a multifunctional mediator in infection and inflammation, which has been largely explored in ex vivo studies. The present case–control study was designed to investigate whether DEFB1 genomic variations are associated with the susceptibility to and the outcome of severe sepsis in 211 patients with severe sepsis and 157 ethnic-matched healthy controls. After correcting for multiple testing, the −44G/C was the only polymorphism found to show significant associations with both the susceptibility to and the fatal outcome of severe sepsis (P=0.0049, odd ratio (OR) 1.971 and P=0.002, OR 2.406, respectively). Haplotype −20A/−44C/−52G showed a protective role against severe sepsis (P=0.0066, OR 0.6751), whereas haplotype −20G/−44G/−52G served as a risk factor for the fatal outcome of severe sepsis (P=0.0052, OR 2.427). These findings provide further evidence that β-defensin 1 may play a role in the pathogenesis of severe sepsis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen J . The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature 2002; 420: 885–891.
Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE . The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 138–150.
Lin MT, Albertson TE . Genomic polymorphisms in sepsis. Crit Care Med 2004; 32: 569–579.
Cobb JP, O'Keefe GE . Injury research in the genomic era. Lancet 2004; 363: 2076–2083.
Yang D, Biragyn A, Hoover DM, Lubkowski J, Oppenheim JJ . Multiple roles of antimicrobial defensins, cathelicidins, and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin in host defense. Annu Rev Immunol 2004; 22: 181–215.
Ganz T . Defensins: antimicrodial peptides of innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3: 710–720.
Bensch KW, Raida M, Magert HJ, Schulz-Knappe P, Forssmann WG . hBD-1: a novel β-defensin from human plasma. FEBS Lett 1995; 368: 331–335.
Goldman MJ, Anderson GM, Stolzenberg ED, Kari UP, Zasloff M, Wilson JM . Human beta-defensin-1 is a salt-sensitive antibiotic in lung that is inactivated in cystic fibrosis. Cell 1997; 88: 553–560.
Valore EV, Park CH, Quayle AJ, Wiles KR, McCray Jr PB, Ganz T . Human beta-defensin-1: an antimicrobial peptide of urogenital tissues. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 1633–1642.
Fang XM, Shu Q, Chen QX, Book M, Sahl HG, Hoeft A et al. Differential expression of alpha- and beta-defensins in human peripheral blood. Eur J Clin Invest 2003; 33: 82–87.
Joly S, Organ CC, Johnson GK, McCray Jr PB, Guthmiller JM . Correlation between beta-defensin expression and induction profiles in gingival keratinocytes. Mol Immunol 2005; 42: 1073–1084.
Sherman H, Chapnik N, Froy O . Albumin and amino acids upregulate the expression of human beta-defensin 1. Mol Immunol 2005; 43: 1617–1623.
Schaller-Bals S, Schulze A, Bals R . Increased levels of antimicrobial peptides in tracheal aspirates of newborn infants during infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 165: 992–995.
Hiratsuka T, Nakazato M, Ihi T, Minematsu T, Chino N, Nakanishi T et al. Structural analysis of human beta-defensin-1 and its significance in urinary tract infection. Nephron 2000; 85: 34–40.
Dommisch H, Acil Y, Dunsche A, Winter J, Jepsen S . Differential gene expression of human beta-defensins (hBD-1, -2, -3) in inflammatory gingival diseases. Oral Microbiol Immunol 2005; 20: 186–190.
Yang D, Chertov O, Bykovskaia SN, Chen Q, Buffo MJ, Shogan J et al. β-defensins: linking innate and adaptive immunity through dendritic and T cell CCR6. Science 1999; 286: 525–528.
Sun L, Finnegan CM, Kish-Catalone T, Blumenthal R, Garzino-Demo P, La Terra Maggiore GM et al. Human β-defensins suppress human immunodeficiency virus infection: potential role in mucosal protection. J Virol 2005; 79: 14318–14329.
Wehkamp J, Harder J, Weichenthal M, Mueller O, Herrlinger KR, Fellermann K et al. Inducible and constitutive beta-defensins are differentially expressed in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2003; 9: 215–223.
Nusbaum C, Mikkelsen TS, Zody MC, Asakawa S, Taudien S, Garber M et al. DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 8. Nature 2006; 439: 331–335.
Hollox EJ, Armour JA, Barber JC . Extensive normal copy number variation of a beta-defensin antimicrobial-gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 591–600.
Aldred PM, Hollox EJ, Armour JA . Copy number polymorphism and expression level variation of the human alpha-defensin genes DEFA1 and DEFA3. Hum Mol Genet 2005; 14: 2045–2052.
Chen Q, Book M, Fang X, Hoeft A, Stuber F . Screening of copy number polymorphisms in human beta-defensin genes using modified real-time quantitative PCR. J Immunol Methods 2006; 308: 231–240.
Linzmeier RM, Ganz T . Copy number polymorphisms are not a common feature of innate immune genes. Genomics 2006; 88: 122–126.
Braida L, Boniotto M, Pontillo A, Tovo PA, Amoroso A, Crovella S . A single-nucleotide polymorphism in the human beta-defensin 1 gene is associated with HIV-1 infection in Italian children. AIDS 2004; 18: 1598–1600.
Leung TF, Li CY, Liu EK, Tang NL, Chan IH, Yung E et al. Asthma and atopy are associated with DEFB1 polymorphisms in Chinese children. Genes Immun 2006; 7: 59–64.
Levy H, Raby BA, Lake S, Tantisira KG, Kwiatkowski D, Lazarus R et al. Association of defensin beta-1 gene polymorphisms with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005; 115: 252–258.
Matsushita I, Hasegawa K, Nakata K, Yasuda K, Tokunaga K, Keicho N . Genetic variants of human beta-defensin-1 and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 291: 17–22.
Jurevic RJ, Bai M, Chadwick RB, White TC, Dale BA . Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in human beta-defensin 1: high-throughput SNP assays and association with Candida carriage in type I diabetics and nondiabetic controls. J Clin Microbiol 2003; 41: 90–96.
Motzkus D, Schulz-Maronde S, Heitland A, Schulz A, Forssmann WG, Jubner M et al. The novel β-defensin DEFB123 prevents lipopolysaccharide-mediated effects in vitro and in vivo. FASEB J 2006; 20: E997–E1004.
Sun CQ, Arnold R, Fernandez-Golarz C, Parrish AB, Almekinder T, He J et al. Human β-defensin-1, a potential chromosome 8p tumor suppressor: control of transcription and induction of apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 8542–8549.
Shu Q, Shi Z, Zhao ZY, Chen Z, Yao HP, Chen QX et al. Protection against pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia and sepsis-induced lung injury by overexpression of β-defensin 2 in rats. Shock 2006; 26: 365–371.
Fellermann K, Stange DE, Schaeffeler E, Schmalzl H, Wehkamp J, Bevins CL et al. A chromosome 8 gene-cluster polymorphism with low human beta-defensin 2 gene copy number predisposes to Crohn disease of the colon. Am J Hum Genet 2006; 79: 439–448.
Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D et al. 2001SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International sepsis definitions conference. Crit Care Med 2003; 31: 1250–1256.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30471662).
The authors disclose no financial interests that are relevant to the research or constitute a conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, QX., Lv, C., Huang, LX. et al. Genomic variations within DEFB1 are associated with the susceptibility to and the fatal outcome of severe sepsis in Chinese Han population. Genes Immun 8, 439–443 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364401
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364401
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Beta-defensin 1, aryl hydrocarbon receptor and plasma kynurenine in major depressive disorder: metabolomics-informed genomics
Translational Psychiatry (2018)
-
Beta-defensin gene (DEFB1) polymorphisms are associated with the susceptibility to chronic respiratory diseases
Genes & Genomics (2016)
-
Genome-wide immunity studies in the rabbit: transcriptome variations in peripheral blood mononuclear cells after in vitro stimulation by LPS or PMA-Ionomycin
BMC Genomics (2015)
-
Amplifying renal immunity: the role of antimicrobial peptides in pyelonephritis
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2015)
-
Narrowing down the distal border of the copy number variable beta-defensin gene cluster on human 8p23
BMC Research Notes (2014)