Abstract
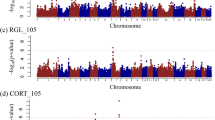
Advanced intercross line (AIL) is a powerful tool for high-resolution mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTLs). Several AILs have been generated to refine QTLs since the method was proposed about a decade ago. However, no AIL has been used for identifying novel QTLs. Here we used an AIL to test this possibility. We genotyped 308 (DBA/1 × FVB/N) F11/12 AIL mice with 109 informative markers covering four chromosomes, with an average intermarker distance of 5.5 Mb. Several normally distributed quantitative traits involved in the immune response during the course of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA), such as anti-collagen II antibodies, T-cell subset proportions and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production were taken as phenotypes. Four QTLs, namely Ciaa1, Lctlp1, Lctlp2 and Rosq1, controlling anti-collagen II IgG2a levels, lymph nodes CD8+ T cell proportion and ROS production were identified with support intervals of 15, 14, 8 and 8 Mb, respectively. Alleles of Lctlp1 and Lctlp2 suppressing CD8+ T cell proportion as well as the Rosq1 allele enhancing ROS production were correlated with higher CIA severity scores. Taken together, we successfully used an AIL to identify novel QTLs controlling immune responses during CIA with relatively small support intervals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Darvasi A, Soller M . Advanced intercross lines, an experimental population for fine genetic mapping. Genetics 1995; 141: 1199–1207.
Iraqi F, Clapcott SJ, Kumari P, Haley CS, Kemp SJ, Teale AJ . Fine mapping of trypanosomiasis resistance loci in murine advanced intercross lines. Mamm Genome 2000; 11: 645–648.
Wang X, Le Roy I, Nicodeme E, Li R, Wagner R, Petros C et al. Using advanced intercross lines for high-resolution mapping of HDL cholesterol quantitative trait loci. Genome Res 2003; 13: 1654–1664.
Wang M, Lemon WJ, Liu G, Wang Y, Iraqi FA, Malkinson AM et al. Fine mapping and identification of candidate pulmonary adenoma susceptibility 1 genes using advanced intercross lines. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 3317–3324.
Ehrich TH, Hrbek T, Kenney-Hunt JP, Pletscher LS, Wang B, Semenkovich CF et al. Fine-mapping gene-by-diet interactions on chromosome 13 in a LG/J × SM/J murine model of obesity. Diabetes 2005; 54: 1863–1872.
Zhang S, Lou Y, Amstein TM, Anyango M, Mohibullah N, Osoti A et al. Fine mapping of a major locus on chromosome 10 for exploratory and fear-like behavior in mice. Mamm Genome 2005; 16: 306–318.
Jagodic M, Becanovic K, Sheng JR, Wu X, Backdahl L, Lorentzen JC et al. An advanced intercross line resolves Eae18 into two narrow quantitative trait loci syntenic to multiple sclerosis candidate loci. J Immunol 2004; 173: 1366–1373.
Sheng JR, Jagodic M, Dahlman I, Becanovic K, Nohra R, Marta M et al. Eae19, a new locus on rat chromosome 15 regulating experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Genetics 2005; 170: 283–289.
Jennen DG, Vereijken AL, Bovenhuis H, Crooijmans RM, van der Poel JJ, Groenen MA . Confirmation of quantitative trait loci affecting fatness in chickens. Genet Sel Evol 2005; 37: 215–228.
Bennett KE, Flick D, Fleming KH, Jochim R, Beaty BJ, Black WC . Quantitative trait loci that control dengue-2 virus dissemination in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Genetics 2005; 170: 185–194.
Bauer K, Yu X, Wernhoff P, Koczan D, Thiesen HJ, Ibrahim SM . Identification of new quantitative trait loci in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2004; 50: 3721–3728.
Yu X, Bauer K, Wernhoff P, Koczan D, Moller S, Thiesen HJ et al. Fine mapping of collagen-induced arthritis quantitative trait Loci in an advanced intercross line. J Immunol 2006; 177: 7042–7049.
Valdar W, Solberg LC, Gauguier D, Burnett S, Klenerman P, Cookson WO et al. Genome-wide genetic association of complex traits in heterogeneous stock mice. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 879–887.
Jackson AU, Galecki AT, Burke DT, Miller RA . Genetic polymorphisms in mouse genes regulating age-sensitive and age-stable T cell subsets. Genes Immun 2003; 4: 30–39.
Karlsson J, Zhao X, Lonskaya I, Neptin M, Holmdahl R, Andersson A . Novel quantitative trait loci controlling development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and proportion of lymphocyte subpopulations. J Immunol 2003; 170: 1019–1026.
Kono DH, Burlingame RW, Owens DG, Kuramochi A, Balderas RS, Balomenos D et al. Lupus susceptibility loci in New Zealand mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 10168–10172.
Morel L, Rudofsky UH, Longmate JA, Schiffenbauer J, Wakeland EK . Polygenic control of susceptibility to murine systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity 1994; 1: 219–229.
Vyse TJ, Kotzin BL . Genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Immunol 1996; 8: 843–851.
Becker KG, Simon RM, Bailey-Wilson JE, Freidlin B, Biddison WE, McFarland HF et al. Clustering of non-major histocompatibility complex susceptibility candidate loci in human autoimmune diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 9979–9984.
Moser KL, Neas BR, Salmon JE, Yu H, Gray-McGuire C, Asundi N et al. Genome scan of human systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence for linkage on chromosome 1q in African-American pedigrees. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 14869–14874.
Paul WE . Interleukin-4: a prototypic immunoregulatory lymphokine. Blood 1991; 77: 1859–1870.
Droge W . Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev 2002; 82: 47–95.
Perl A, Banki K . Genetic and metabolic control of the mitochondrial transmembrane potential and reactive oxygen intermediate production in HIV disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 2000; 2: 551–573.
Hinson TK, Damodaran TV, Chen J, Zhang X, Qumsiyeh MB, Seldin MF et al. Identification of putative transmembrane receptor sequences homologous to the calcium-sensing G-protein-coupled receptor. Genomics 1997; 45: 279–289.
Boldyrev A, Bulygina E, Makhro A . Glutamate receptors modulate oxidative stress in neuronal cells. A mini-review. Neurotox Res 2004; 6: 581–587.
Taneja V, Taneja N, Paisansinsup T, Behrens M, Griffiths M, Luthra H et al. CD4 and CD8 T cells in susceptibility/protection to collagen-induced arthritis in HLA-DQ8-transgenic mice: implications for rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 2002; 168: 5867–5875.
Siddiqi M, Garcia ZC, Stein DS, Denny TN, Spolarics Z . Relationship between oxidative burst activity and CD11b expression in neutrophils and monocytes from healthy individuals: effects of race and gender. Cytometry 2001; 46: 243–246.
Manly KF, Cudmore Jr RH, Meer JM . Map Manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mamm Genome 2001; 12: 930–932.
Lander ES, Botstein D . Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 1989; 121: 185–199.
Mangin B, Goffinet B, Rebai, A . Constructing confidence intervals for QTL location. Genetics 1994; 138: 1301–1308.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from EU FP5 (EUROME, EURO-RA). We thank Ilona Klamfuss for animal care and Dr Lena Wester-Rosenlöf for critical reading of the paper and helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Bauer, K., Wernhoff, P. et al. Using an advanced intercross line to identify quantitative trait loci controlling immune response during collagen-induced arthritis. Genes Immun 8, 296–301 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364385
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364385
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Fine-mapping QTLs in advanced intercross lines and other outbred populations
Mammalian Genome (2014)
-
Fine mapping and replication of QTL in outbred chicken advanced intercross lines
Genetics Selection Evolution (2011)
-
Contribution of genetic studies in rodent models of autoimmune arthritis to understanding and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Genes & Immunity (2007)