Abstract
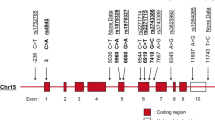
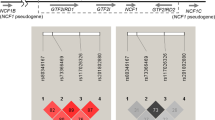
CD19 regulates the signaling for B lymphocyte development, activation and proliferation. In mice, CD19 deficiency and overexpression were shown to result in hypogammaglobulinemia and autoantibody production, respectively. In the present study, we screened for the polymorphisms of CD19 , and examined the detected polymorphisms for the association with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Crohn’s disease and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Two SNPs, c.705G>T (P235P and IVS14-30C>T, were decreased (P = 0.0096 and P = 0.028, respectively), in SLE. A GT repeat polymorphism, c.*132(GT)12–18, was detected within the 3’-untranslated region, and individuals with ⩾15 times repeat was significantly increased in the independent two groups of Japanese SLE patients (P = 0.011 and P = 0.035, respectively); the overall difference between total SLE and controls was striking (P = 0.0061). No association was observed for RA and Crohn’s disease. In addition, no variations other than the common polymorphisms were detected in four patients with common variable immunodeficiency, the phenotype of which resembles CD19 deficient mice. In Caucasian SLE families, this GT repeat polymorphism was rare. CD19 mRNA level in the isolated peripheral blood B lymphocytes was lower in individuals possessing (GT)15–18 alleles compared with those without these alleles, both in controls and in SLE patients; however, the difference did not reach statistical significance. These results suggested that either the slight reduction in the CD19 mRNA level associated with the elongation of GT repeat, or an allele of another locus in linkage disquilibrium with CD19 (GT)15–18, may be associated with susceptibility to SLE in Japanese.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nadler LM, Anderson KC, Marti G et al. B4, a human B lymphocyte-associated antigen expressed on normal, mitogen-activated, and malignant B lymphocytes J Immunol 1983 131: 244–250
Tedder TF, Isaacs CM . Isolation of cDNAs encoding the CD19 antigen of human and mouse B lymphocytes. A new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily J Immunol 1989 143: 712–717
Zhou LJ, Ord DC, Hughes AL, Tedder TF . Structure and domain organization of the CD19 antigen of human, mouse, and guinea pig B lymphocytes. Conservation of the extensive cytoplasmic domain J Immunol 1991 147: 1424–1432
Matsumoto AK, Kopicky-Burd J, Carter RH, Tuveson DA, Tedder TF, Fearon DT . Intersection of the complement and immune systems: a signal transduction complex of the B lymphocyte-containing complement receptor type 2 and CD19 J Exp Med 1991 173: 55–64
Bradbury LE, Kansas GS, Levy S, Evans RL, Tedder TF . The CD19/CD21 signal transducing complex of human B lymphocytes includes the target of antiproliferative antibody-1 and Leu-13 molecules J Immunol 1992 149: 2841–2850
Iida K, Nadler L, Nussenzweig V . Identification of the membrane receptor for the complement fragment C3d by means of a monoclonal antibody J Exp Med 1983 158: 1021–1033
Weis JJ, Tedder TF, Fearon DT . Identification of a 145,000 Mr membrane protein as the C3d receptor (CR2) of human B lymphocytes Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1984 81: 881–885
Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M, Poe JC, Steeber DA, Tedder TF . CD19 can regulate B lymphocyte signal transduction independent of complement activation J Immunol 2001 167: 3190–3200
de Fougerolles AR, Batista F, Johnsson E, Fearon DT . IgM and stromal cell-associated heparan sulfate/heparin as complement-independant ligands for CD19 Eur J Immunol 2001 31: 2189–2199
Uckun FM, Burkhardt AL, Jarvis L et al. Signal transduction through the CD19 receptor during discrete developmental stages of human B-cell ontogeny J Biol Chem 1993 268: 21172–21184
Kitanaka A, Ito C, Coustan-Smith E, Campana D . CD38 ligation in human B cell progenitors triggers tyrosine phosphorylation of CD19 and association of CD19 with lyn and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase J Immunol 1997 159: 184–192
Xiao J, Messinger Y, Jin J, Myers DE, Bolen JB, Uckun FM . Signal transduction through the β1 integrin family surface adhesion molecules VLA-4 and VLA-5 of human B-cell precursors activates CD19 receptor-associated protein-tyrosine kinases J Biol Chem 1996 271: 7659–7664
Hippen KL, Buhl AM, D’Ambrosio D, Nakamura K, Persin C, Cambier JC . FcγRIIB1 inhibition of BCR-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis and Ca2+mobilization is integrated by CD19 dephosphorylation Immunity 1997 7: 49–58
Kiener PA, Lioubin MN, Rohrschneider LR, Ledbetter JA, Nadler SG, Diegel ML . Co-ligation of the antigen and Fc receptors gives rise to the selective modulation of intracellular signaling in B cells. Regulation of the association of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and inositol 5’-phosphatase with the antigen receptor complex J Biol Chem 1997 272: 3838–3844
Engel P, Zhou LJ, Ord DC, Sato S, Koller B, Tedder TF . Abnormal B lymphocyte development, activation, and differentiation in mice that lack or overexpress the CD19 signal transduction molecule Immunity 1995 3: 39–50
Rickert RC, Rajewsky K, Roes J . Impairment of T-cell-dependent B-cell responses and B-1 cell development in CD19-deficient mice Nature 1995 376: 352–355
Sato S, Steeber DA, Tedder TF . The CD19 signal transduction molecule is a response regulator of B-lymphocyte differentiation Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 11558–11562
Sato S, Ono N, Steeber DA, Pisetsky DS, Tedder TF . CD19 regulates B lymphocyte signaling thresholds critical for the development of B-1 lineage cells and autoimmunity J Immunol 1996 157: 4371–4378
Sato S, Miller AS, Howard MC, Tedder TF . Regulation of B lymphocyte development and activation by the CD19/ CD21/CD81/Leu 13 complex requires the cytoplasmic domain of CD19 J Immunol 1997 159: 3278–3287
Sato S, Steeber DA, Jansen PJ, Tedder TF . CD19 expression levels regulate B lymphocyte development: human CD19 restores normal function in mice lacking endogenous CD19 J Immunol 1997 158: 4662–4669
Fehr T, Rickert RC, Odermatt B et al. Antiviral protection and germinal center formation, but impaired B cell memory in the absence of CD19 J Exp Med 1998 188: 145–155
Zhou LJ, Smith HM, Waldschmidt TJ, Schwarting R, Daley J, Tedder TF . Tissue-specific expression of the human CD19 gene in transgenic mice inhibits antigen-independent B-lymphocyte development Mol Cell Biol 1994 14: 3884–3894
Inaoki M, Sato S, Weintraub BC, Goodnow CC, Tedder TF . CD19-regulated signaling thresholds control peripheral tolerance and autoantibody production in B lymphocytes J Exp Med 1997 186: 1923–1931
Fujimoto M, Poe JC, Inaoki M, Tedder TF . CD19 regulates B lymphocyte responses to transmembrane signals Semin Immunol 1998 10: 267–277
Tuveson DA, Carter RH, Soltoff SP, Fearon DT . CD19 of B cells as a surrogate kinase insert region to bind phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase Science 1993 260: 986–989
Hugot JP, Laurent-Puig P, Gower-Rousseau C et al. Mapping of a susceptibility locus for Crohn’s disease on chromosome 16 Nature 1996 379: 821–823
Cornélis F, Fauré S, Martinez M et al. New susceptibility locus for rheumatoid arthritis suggested by a genome-wide linkage study Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998 95: 10746–10750
Hugot JP, Chamaillard M, Zouali H et al. Asociation of NOD2 leucine-rich repeat variants with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease Nature 2001 411: 599–603
Ogura Y, Bonen DK, Inohara N et al. A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease Nature 2001 411: 603–606
Klinman DM . B-cell abnormalities characteristic of systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Wallace DJ, Hahn BH (eds) Dubois’ Lupus Erythematosus (5th edn) Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore 1997 195–206
Sato S, Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M, Tedder TF, Takehara K . Quantitative genetic variation in CD19 expression correlates with autoimmunity J Immunol 2000 165: 6635–6643
Dunnen JT, Antonarakis SE . Mutation nomenclature extensions and suggestions to describe complex mutations: a discussion Hum Mutat 2000 15: 7–12
Nomenclature for the description of sequence variations (http://www.dmd.nl/mutnomen.html)
McCracken S, Fong N, Yankulov K et al. The C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II couples mRNA processing to transcription Nature 1997 385: 357–361
Conne B, Stutz A, Vassalli JD . The 3´ untranslated region of messenger RNA: A molecular ‘hotspot’ for pathology? Nat Med 2000 6: 637–641
D’Alfonso S, Rampi M, Bocchio D, Colombo G, Scorza-Smeraldi R, Momigliano-Richardi P . Systemic lupus erythematosus candidate genes in the Italian population: evidence for a significant association with interleukin-10 Arthritis Rheum 2000 43: 120–128
Gaffney PM, Kearns GM, Shark KB et al. A genome-wide search for susceptibility genes in human systemic lupus erythematosus sib-pair families Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998 95: 14875–14879
Moser KL, Neas BR, Salmon JE et al. Genome scan of human systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence for linkage on chromosome 1q in African-American pedigrees Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998 95: 14869–14874
Moser KL, Gray-McGuire C, Kelly J et al. Confirmation of genetic linkage between human systemic lupus erythematosus and chromosome 1q41 Arthritis Rheum 1999 42: 1902–1907
Gaffney PM, Ortmann WA, Selby SA et al. Genome screening in human systemic lupus erythematosus: results from a second Minnesota cohort and combined analyses of 187 sib-pair families Am J Hum Genet 2000 66: 547–556
Gray-McGuire C, Moser KL, Gaffney PM et al. Genome scan of human systemic lupus erythematosus by regression modeling: evidence of linkage and epistasis at 4p16-15.2 Am J Hum Genet 2000 67: 1460–1469
Lindqvist AK, Steinsson K, Johanneson B et al. A susceptibility locus for human systemic lupus erythematosus (hSLE1) on chromosome 2q J Autoimmun 2000 14: 169–178
Shai R, Quismorio FP, Li L et al. Genome-wide screen for systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility genes in multiplex families Hum Mol Genet 1999 8: 639–644
Tedder TF, Inaoki M, Sato S . The CD19-CD21 complex regulates signal transduction thresholds governing humoral immunity and autoimmunity Immunity 1997 6: 107–118
Tokunaga K, Imanishi T, Takahashi K, Juji T . On the origin and disoersal of East Asian populations as viewed from HLA haplotypes. In: Akazawa T, Szathmary EJ (eds) Prehistoric Mongoloid Dispersals Oxford University Press: Oxford 1996 187–197
Qian Y, Santiago C, Borrero M, Tedder TF, Clarke SH . Lupus-specific antiribonucleoprotein B cell tolerance in nonautoimmune mice is maintained by differentiation to B-1 and governed by B cell receptor signaling thresholds J Immunol 2001 166: 2412–2419
Hashimoto H, Nishimura Y, Dong RP et al. HLA antigens in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus Scand J Rheumatol 1994 23: 191–196
Tsuchiya N, Kawasaki A, Tsao BP, Komata T, Grossman JM, Tokunaga K . Analysis of the association of HLA-DRB1 and TNFA promoter polymorphisms with SLE using transmission disequilibrium test Genes Immun 2001 2: 317–322
Komata T, Tsuchiya N, Matsushita M, Hagiwara K, Tokunaga K . Association of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (TNFR2) polymorphism with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus Tissue Antigens 1999 53: 527–533
Kyogoku C, Dijstelbloem HM, Tsuchiya N et al. Association of Fcγ receptor gene polymorphisms in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Contribution of FCGR2Bto the genetic susceptibility to SLE Arthritis Rheum 2002 46: 1242–1254
Hatta Y, Tsuchiya N, Matsushita M, Shiota M, Hagiwara K, Tokunaga K . Identification of the gene variations in human CD22 Immunogenetics 1999 49: 280–286
Kozmik Z, Wang S, Dorfler P, Adams B, Busslinger M . The promoter of the CD19 gene is a target for the B-cell-specific transcription factor BSAP Mol Cell Biol 1992 12: 2662–2672
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis Arthritis Rheum 1988 31: 315–324
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus Arthritis Rheum 1982 25: 1271–1277
Tsuchiya N, Shiota M, Moriyama S et al. MICA allele typing of HLA-B27 positive Japanese patients with seronegative spondylarthropathies and healthy individuals: differential linkage disequilibrium with HLA-B27 subtypes Arthritis Rheum 1998 41: 68–73
Bannai M, Tokunaga K, Lin L et al. Discrimination of human HLA-DRB1 alleles by PCR-SSCP (single-strand conformation polymorphism) method Eur J Immunogenet 1994 21: 1–9
Spielman RS, McGinnis RE, Ewens WJ . Transmission test for linkage disequilibrium: the insulin gene region and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) Am J Hum Genet 1993 52: 506–516
Terwilliger JD, Ott J . Handbook of Human Linkage Analysis Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore 1994 pp 188–193
Imanishi T, Akaza T, Kimura A, Tokunaga K, Gojobori T . Estimation of allele and haplotype frequencies for HLA and complement loci In: Tsuji K, Aizawa M, Sasazuk T (eds) HLA 1991 Vol. 1 Oxford University Press: Oxford 1992 pp 76–79
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to Dr Shinichi Sato and Dr Makoto Inaoki (Department of Dermatology, Kanazawa University), Dr Manabu Fujimoto (International Medical Center of Japan), Mr Satoshi Makino and Mr Koichi Okamoto (Department of Genetic Information, Tokai University) for helpful discussions, to Dr Jun Ohashi (Department of Human Genetics, The University of Tokyo) for statistical analysis, to Dr Nelson Tsuno (Department of Transfusion Medicine, The University of Tokyo), Michiko Shiota, Tae Komata, Minae Kawashima, Aya Kawasaki and Chieko Kyogoku (Department of Human Genetics, The University of Tokyo) for helpful assistance and discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas (C), Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, and a grant from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. New polymorphisms described in this study have been deposited in GenBank/ EMBL/ DDBJ accession No. AB052799, AB052814, AB052815, AB052816, AB052817 and AB052818.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuroki, K., Tsuchiya, N., Tsao, B. et al. Polymorphisms of human CD19 gene: possible association with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in Japanese. Genes Immun 3 (Suppl 1), S21–S30 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6363906
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6363906
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Intracellular B Lymphocyte Signalling and the Regulation of Humoral Immunity and Autoimmunity
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2017)
-
Individual and epistatic effects of genetic polymorphisms of B-cell co-stimulatory molecules on susceptibility to pemphigus foliaceus
Genes & Immunity (2009)
-
Similar CD19 Dysregulation in Two Autoantibody-Associated Autoimmune Diseases Suggests a Shared Mechanism of B-Cell Tolerance Loss
Journal of Clinical Immunology (2007)
-
Looking back and looking forward
Genes & Immunity (2003)
-
The genetic etiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: a short dispatch from the combat zone
Genes & Immunity (2002)