Abstract
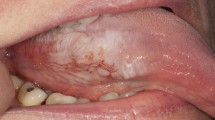
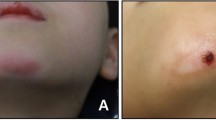
The following case report shows the unfortunate side effects of minocycline therapy used in the management of facial acne. All three features of discoloration affecting the skin, bone and dentition were found. A 46-year-old patient presented with adult onset discoloration of the dentition following prolonged minocycline therapy. In addition, oral and cutaneous pigmentation were noted. Unfortunately, the undesirable cosmetic appearance of facial acne was exchanged for permanent discoloration of the dentition. When considering prolonged minocycline therapy, patients would benefit from dialogue between the medical and dental practitioners, so that the risk of this potential side effect can be assessed in a more informed way
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, K., Cheshire, D. & Vance, A. Oral and systemic effects of prolonged minocycline therapy. Br Dent J 185, 560–562 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.4809867
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.4809867
This article is cited by
-
Examine the skin and thoroughly review medical/medication history when considering a diagnosis of drug-induced pigmentation
Drugs & Therapy Perspectives (2019)
-
An Update on Drug-Induced Pigmentation
American Journal of Clinical Dermatology (2019)
-
Feeling blue? Minocycline-induced staining of the teeth, oral mucosa, sclerae and ears – a case report
British Dental Journal (2013)
-
Tooth discolouration and staining: a review of the literature
British Dental Journal (2001)