Abstract
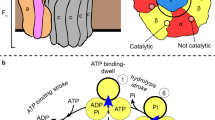
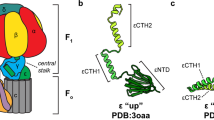
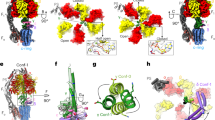
F1FO ATP synthases use a transmembrane proton gradient to drive the synthesis of cellular ATP. The structure of the cytosolic F1 portion of the enzyme and the basic mechanism of ATP hydrolysis by F1 are now well established, but how proton translocation through the transmembrane FO portion drives these catalytic changes is less clear. Here we describe the structural changes in the proton-translocating FO subunit c that are induced by deprotonating the specific aspartic acid involved in proton transport. Conformational changes between the protonated and deprotonated forms of subunit c provide the structural basis for an explicit mechanism to explain coupling of proton translocation by FO to the rotation of subunits within the core of F1. Rotation of these subunits within F1 causes the catalytic conformational changes in the active sites of F1 that result in ATP synthesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams,J. P., Leslie,A. G. W., Lutter,R. & Walker,J. E. Structure at 2.8 Å resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature 370, 621–628 (1994).
Bianchet,M. A., Hullihen,J., Pedersen,P. L. & Amzel,L. M. The 2.8-Å structure of rat liver F1-ATPase: Configuration of a critical intermediate in ATP synthesis/hydrolysis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 11065–11070 (1998).
Weber,J. & Senior,A. E. Catalytic mechanism of F1-ATPase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1319, 19–58 (1997).
Boyer,P. The ATP synthase—a splendid molecular machine. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 66, 717–749 (1997).
Duncan,T. M., Bulygin,V. V., Zhou,Y., Hutcheon,M. L. & Cross,R. L. Rotation of subunits during catalysis by Escherichia coli F1 ATPase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 10964–10968 (1995).
Sabbert,D., Engelbrecht,S. & Junge,W. Intersubunit rotation in active F-ATPase. Nature 381, 623–625 (1996).
Noji,H., Yasuda,R., Yoshida,M. & Kinosita,K. J. Direct observation of the rotation of F1-ATPase. Nature 386, 299–302 (1997).
Fillingame,R. H. in The Bacteria. Vol. XII. (ed. Krulwich, T. A.) 345–391 (Academic, New York, 1990).
Jones,P. C. & Fillingame,R. H. Genetic fusions of subunit c in the FO sector of H+-transporting ATP synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 29701–29705 (1998).
Birkenhäger,R., Hopper,M., Deckers-Hebestreit,G., Mayar,F. & Altendorf,K. The FO complex of the Escherichia coli ATP synthase: Investigation by electron spectroscopic imaging and immunoelectron microscopy. Eur. J. Biochem. 230, 58–67 (1995).
Takeyasu,K. et al. Molecular imaging of Escherichia coli F1FO-ATPase in reconstituted membranes using atomic force microscopy. FEBS Lett. 392, 110–113 (1996).
Singh,S., Turina,P., Bustamante,C. J., Keller,D. J. & Capaldi,R. Topographical structure of membrane-bound Escherichia coli F1FO ATP synthase in aqueous buffer. FEBS Lett. 397, 30–34 (1996).
Jones,P. C., Jiang,W. & Fillingame,R. H. Arrangement of the multicopy H+-translocating subunit c in the membrane sector of the Escherichia coli F1FO ATP synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 17178–17185 (1998).
Jiang,W. & Fillingame,R. H. Interacting helical faces of subunits a and c in the F1FO ATP synthase of Escherichia coli defined by disulfide cross-linking. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6607–6612 (1998).
Aris,J. P. & Simoni,R. D. Cross-linking and labeling of the Escherichia coli F1FO-ATP synthase reveal a compact hydrophilic portion of FO close to an F1 catalytic subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 14599–14609 (1983).
Hermolin,J., Gallant,J. & Fillingame,R. H. Topology, organization, and function of the psi subunit in the FO sector of the H+-ATPase of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 14550–14555 (1983).
Rodgers,A. J. W. et al. The subunit δ-subunit b domain of the Escherichia coli F1FO ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 31058–31064 (1997).
Watts,S. D., Zhang,Y., Fillingame,R. H. & Capaldi,R. A. The γ subunit in the Escherichia coli ATP synthase complex (ECF1FO) extends through the stalk and contacts the c subunits of the FO part. FEBS Lett. 368, 235–238 (1995).
Hermolin,J., Dmitriev,O. Y., Zhang,Y. & Fillingame,R. H. Defining the domain of binding of F1 subunit ε with the polar loop of FO subunit c in the Escherichia coli ATP synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 17011–17016 (1999).
Fillingame,R. H., Girvin,M. E., Jiang,W., Valiyaveetil,F. & Hermolin,J. Subunit interactions coupling H+ transport and ATP synthesis in F1FO ATP synthase. Acta Physiol. Scand. 643, 163–168 (1998).
Girvin,M. E., Rastogi,V. K., Abildgaard,F., Markley, J. L. & Fillingame,R. H. Solution structure of the transmembrane H+-transporting subunit c of the F1FO ATP synthase. Biochemistry 37, 8817–8824 (1998).
Matthey,U., Kaim,G., Braun,D., Wüthrich,K. & Dimroth,P. NMR studies of subunit c of the ATP synthase from Propiogenium modestum in dodecylsulfate micelles. Eur. J. Biochem. 261, 459–467 (1999).
Norwood,T. J., Crawford,D. A., Steventon,M. E., Driscoll,P. C. & Campbell,I. D. Heteronuclear 1H-15N nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the c subunit of the Escherichia coli F1FO ATP synthase: assignment and secondary structure. Biochemistry 31, 6285–6290 (1992).
Junge,W., Lill,H. & Engelbrecht,S. ATP synthase: an electrochemical transducer with rotatory mechanics. Trends Biochem. Sci. 22, 420–423 (1997).
Zuiderweg,E. R. P. & Fesik,S. W. Heteronuclear three-dimensional NMR spectroscopy of the inflammatory protein C5a. Biochemistry 28, 2387–2391 (1989).
Assadi-Porter,F. M. & Fillingame,R. H. Proton-translocating carboxyl of subunit c of F1FOH+-ATP synthase: the unique environment suggested by the pKa determined by 1H NMR. Biochemistry 34, 16186–16193 (1995).
Rastogi,V. K. & Girvin,M. E. 1H, 13C, and 15N assignments and secondary structure of the high pH form of subunit c of the F1FO ATP synthase. J. Biomol. NMR 13, 91–92 (1999).
Stein,E. G., Rice,L. M. & Brünger,A. T. Torsion-angle molecular dynamics as a new efficient tool for NMR structure calculation. J. Magn. Reson. 124, 154–164 (1997).
Brünger,A. T. et al. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998).
Baxter,N. J. & Williamson,M. P. Temperature dependence of 1H chemical shifts in proteins. J. Biomol. NMR 9, 359–369 (1997).
Kuszewski,J., Qin,J., Gronenborn,A. M. & Clore,G. M. The impact of direct refinement against 13Cα and 13Cβ chemical shifts on protein structure determination by NMR. J. Magn. Reson. Ser. B 106, 92–96 (1995).
Kuszewski,J., Gronenborn,A. M. & Clore,G. M. The impact of direct refinement against proton chemical shifts on protein structure determination by NMR. J. Magn. Reson. Ser. B 107, 293–297 (1995).
Dmitriev,O. Y., Jones,P. C. & Fillingame,R. H. Modeling the oligomeric arrangement of subunit c in the F1FO ATP synthase from the structure of the monomeric subunit and cross-linking in the native-enzyme. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7785–7790 (1999).
Groth,G & Walker,J. E. Model of the c-subunit oligomer in the membrane domain of F-ATPases. FEBS Lett. 410, 117–123 (1997).
Girvin,M. E. & Fillingame,R. H. Determination of local protein structure by spin label difference 2D NMR: the region neighboring Asp61 of subunit c of the F1FO ATP synthase. Biochemistry 34, 1635–1645 (1995).
Valiyaveetil,F. I. & Fillingame,R. H. On the role of Arg-210 and Glu-219 of subunit a in proton translocation by the Escherichia coli F1FO-ATP synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 32635–32641 (1997).
Yamada,H., Moriyama,Y., Maeda,M. & Futai,M. Transmembrane topology of Escherichia coli H+-ATPase (ATP synthase) subunit a. FEBS Lett. 290, 34–38 (1996).
Jager,H., Birkenhager,R., Stalz,W. D., Altendorf,K. & Deckers-Hebestreit,G. Topology of subunit a of the Escherichia coli ATP synthase. Eur. J. Biochem. 251, 122–132 (1998).
Valiyaveetil,F. I., Fillingame,R. H. Transmembrane topography of subunit a in the Escherichia coli F1FO ATP synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 16241–16247 (1998).
Wada,T., Long,J. C., Zhang,D. & Vik,S. B. A novel labeling approach supports the five-transmembrane model of subunit a of the Escherichia coli ATP synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 17353–17357 (1999).
Sigrist-Nelson,K. & Azzi,A. The proteolipid subunit of chloroplast adenosine triphosphatase complexes: mobility, accessibility, and interactions by a spin label technique. J. Biol. Chem. 254, 4470–4474 (1979).
Vik,S. B. & Antonio,B. J. A mechanism of proton translocaton by F1FO ATP synthases suggested by double mutants of the a subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 30364–30369 (1994).
Elston,T., Wang,H. & Oster,G. Energy transduction in ATP synthase. Nature 391, 510–513 (1998).
Howitt,S. M., Rodgers,A. J. W., Hatch,L. P., Gibson,F. & Cox,G. B. The coupling of the relative movement of the a and c subunits of the FO to the conformational changes in the F1-ATPase. J. Bioenerg. Biomemb. 28, 415–420 (1996).
Kato-Yamada,Y., Noji,H., Yasuda,R., Kinosita,K & Yoshida,M. Direct observation of the rotation of the ε subunit in F1-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 19375–19377 (1998).
Miller,M. J., Oldenburg,M. & Fillingame,R. H. The essential carboxyl group in subunit c of the F1FO ATP synthase can be moved and H+ translocating function retained. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 87, 4900–4904 (1990).
Dimroth,P., Wang,H., Grabe,M. & Oster,G. Energy transduction in the sodium F-ATPase of Propiogenium modestum. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 4735–4737 (1999).
Ermler,U., Fritzsch,G., Buchanan,S. K. & Michel,H. Structure of the photosynthetic reaction centre from Rhodobacter sphaeroides at 2.65 Å resolution: cofactors and protein–cofactor interactions. Structure 2, 925–936 (1994).
Koradi,R., Billeter,M. & Wüthrich,K. MOLMOL: a program for the display and analysis of macromolecular structures. J. Mol. Graphics 14, 51–55 (1996).
Kraulis,P. J. MOLSCRIPT: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Cahill for assistance with the NMR experiments, and M. Brenowitz and V. Schramm for critical reading and discussion of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rastogi, V., Girvin, M. Structural changes linked to proton translocation by subunit c of the ATP synthase. Nature 402, 263–268 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/46224
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/46224
This article is cited by
-
Energy landscapes and dynamics of ion translocation through membrane transporters: a meeting ground for physics, chemistry, and biology
Journal of Biological Physics (2021)
-
Genetic inhibition of an ATP synthase subunit extends lifespan in C. elegans
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Direct assignment of 13C solid-state NMR signals of TFoF1 ATP synthase subunit c-ring in lipid membranes and its implication for the ring structure
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2018)
-
The FOF1 ATP synthase: from atomistic three-dimensional structure to the rotary-chemical function
Photosynthesis Research (2017)
-
A mechano-chemiosmotic model for the coupling of electron and proton transfer to ATP synthesis in energy-transforming membranes: a personal perspective
Photosynthesis Research (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.