Abstract
Because benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) may be influenced by plasma steroid hormones, we examined their relation in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. In 1993–1995, 18,000 cohort members provided blood. We selected as cases men who had had surgery for BPH (n=174) or who scored 20–35 points (n=126) on the American Urological Association index of severity of lower urinary tract symptoms. Cases were matched by age to men who scored≤3 points and without an enlarged prostate or elevated prostate-specific antigen. We estimated the odds ratio (OR) of BPH surgery and severe lower urinary tract symptoms for plasma testosterone (T), dihydrotestosterone (DHT), androstanediol glucuronide (AAG), estradiol (E2), and sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) in multivariable conditional logistic regression models.
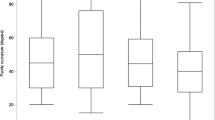
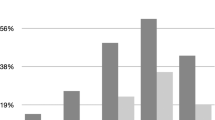
Compared to the lowest tertiles, men in the middle (OR=1.42) and top (OR=1.78) tertiles of AAG were at increased risk for having either BPH surgery or severe lower urinary tract symptoms (P-trend=0.02). Men in the middle (OR=0.58) and top (OR=0.60) tertiles of E2 were at lower risk. T level was unrelated to surgery and symptoms.
Our findings support opposing roles for DHT, reflected by its metabolite AAG, and E2 in the etiology of BPH.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Platz, E., Kawachi, I., Rimm, E. et al. Plasma steroid hormones, surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia, and severe lower urinary tract symptoms. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2, 285–289 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500380
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500380
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Relationship Between the Metabolic Syndrome and BPH-Related Voiding Dysfunction
Current Bladder Dysfunction Reports (2014)
-
History of weight and obesity through life and risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia
International Journal of Obesity (2005)
-
Association between markers of the metabolic syndrome and lower urinary tract symptoms in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III)
International Journal of Obesity (2005)