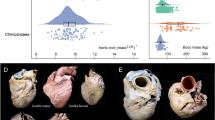
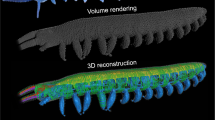
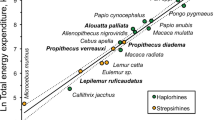
This snake can synthesize fresh heart muscle to cope with extra metabolic demand.
Abstract
Oxygen consumption by carnivorous reptiles increases enormously after they have eaten a large meal in order to meet metabolic demands, and this places an extra load on the cardiovascular system. Here we show that there is an extraordinarily rapid 40% increase in ventricular muscle mass in Burmese pythons (Python molurus) a mere 48 hours after feeding, which results from increased gene expression of muscle-contractile proteins. As this fully reversible hypertrophy occurs naturally, it could provide a useful model for investigating the mechanisms that lead to cardiac growth in other animals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper, G. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 49, 501–518 (1987).
Richey, P. A. & Brown, S. P. J. Sports Sci. 16, 129–141 (1998).
Secor, S. M. & Diamond, J. Nature 395, 659–662 (1998).
Secor, S. M. & Diamond, J. Am. J. Physiol. 272, R902–R912 (1997).
Starck, J. M. & Beese, K. J. Exp. Biol. 204, 325–335 (2001).
Vliegen, H. W., Bruschke, A. V. G. & Van Der Laarse, A. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A: Physiol. 95, 109–114 (1990).
Secor, S. M., Hicks, J. W. & Bennett, A. F. J. Exp. Biol. 203, 2447–2454 (2000).
Morgan, H. E. et al. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 49, 533–543 (1987).
Quinn, K. E. et al. Biophys. J. 74, A355 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andersen, J., Rourke, B., Caiozzo, V. et al. Postprandial cardiac hypertrophy in pythons. Nature 434, 37–38 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/434037a
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/434037a
This article is cited by
-
Utility of the burmese Python as a model for studying plasticity of extreme physiological systems
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (2023)
-
SR-B1-/-ApoE-R61h/h Mice Mimic Human Coronary Heart Disease
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy (2023)
-
Novel treatment strategies for chronic kidney disease: insights from the animal kingdom
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2018)
-
Growth and stress response mechanisms underlying post-feeding regenerative organ growth in the Burmese python
BMC Genomics (2017)
-
AMPK Prevents Palmitic Acid‐Induced Apoptosis and Lipid Accumulation in Cardiomyocytes
Lipids (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.