Abstract
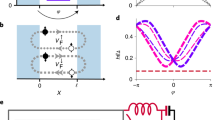
To study and control the behaviour of the spins of electrons that are moving through a metal or semiconductor is an outstanding challenge in the field of ‘spintronics’, where possibilities for new electronic applications based on the spin degree of freedom are currently being explored1,2,3,4,5. Recently, electrical control of spin coherence6 and coherent spin precession during transport7 was studied by optical techniques in semiconductors. Here we report controlled spin precession of electrically injected and detected electrons in a diffusive metallic conductor, using tunnel barriers in combination with metallic ferromagnetic electrodes as spin injector and detector. The output voltage of our device is sensitive to the spin degree of freedom only, and its sign can be switched from positive to negative, depending on the relative magnetization of the ferromagnetic electrodes. We show that the spin direction can be controlled by inducing a coherent spin precession caused by an applied perpendicular magnetic field. By inducing an average precession angle of 180°, we are able to reverse the sign of the output voltage.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prinz, G. A. Magnetoelectronics. Science 282, 1660–1663 (1998).
Wolf, S. A. et al. Spintronics: A spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science 294, 1488–1495 (2001).
Johnson, M. & Silsbee, R. H. Interfacial charge-spin coupling: Injection and detection of spin magnetization in metals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 55, 1790–1793 (1985).
Jedema, F. J., Filip, A. T. & van Wees, B. J. Electrical spin injection and accumulation at room temperature in an all-metal mesoscopic spin valve. Nature 410, 345–348 (2001).
Hernando, D. H., Nazarov, Yu. V., Brataas, V. & Bauer, G. E. W. Conductance modulation by spin precession in noncollinear ferromagnet normal-metal ferromagnet systems. Phys. Rev. B 62, 5700–5712 (2000).
Salis, G. et al. Electrical control of spin coherence in semiconductor nanostructures. Nature 414, 619–622 (2001).
Kikkawa, J. M. & Awschalom, D. D. Lateral drag of spin coherence in gallium arsenide. Nature 397, 139–141 (1999).
Schmidt, G. et al. Fundamental obstacle for electrical spin injection from a ferromagnetic metal into a diffusive semiconductor. Phys. Rev. B 62, R4790–R4793 (2000).
Rashba, E. I. Theory of electrical spin injection: Tunnel contacts as a solution of the conductivity mismatch problem. Phys. Rev. B 62, R16267–R16270 (2000).
Fert, A. & Jaffrès, H. Conditions for efficient spin injection from a ferromagnetic metal into a semiconductor. Phys. Rev. B 64, 184420–184428 (2001).
Jackel, L. D., Howard, R. E., Hu, E. L., Tennant, D. M. & Grabbe, P. 50-nm silicon structures fabricated with trilevel electron beam resist and reactive-ion etching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 39, 268–270 (1981).
Julliere, M. Tunneling between ferromagnetic films. Phys. Lett. A 54, 224–227 (1975).
Van Son, P., van Kempen, H. & Wyder, P. Boundary resistance of the ferromagnetic-nonferromagnetic metal interface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 2271–2273 (1987).
Jedema, F. J., Nijboer, M. S., Filip, A. T. & van Wees, B. J. Spin injection and spin accumulation in permalloy-copper mesoscopic spin valves.Preprint cond-mat/0111092 at 〈http://xxx.lanl.gov〉 (2002); Phys. Rev. B (submitted).
Johnson, M. Spin accumulation in gold films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 2142–2145 (1993).
Papaconstantopoulos, D. A. Handbook of the Band Structure of Elemental Solids (Plenum, New York, 1986).
Meservey, R. & Tedrow, P. M. Surface relaxation times of conduction-electron spins in superconductors and normal metals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 41, 805–808 (1978).
Monod, P. & Beneu, F. Conduction-electron spin flip by phonons in metals: Analysis of experimental data. Phys. Rev. B 19, 911–916 (1979).
Grimaldi, C. & Fulde, P. Spin-orbit scattering effects on the phonon emission and absorption in superconducting tunneling junctions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2550–2553 (1996).
Fabian, J. & Das Sarma, S. Phonon-induced spin relaxation of conduction electrons in aluminium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 1211–1214 (1999).
Johnson, M. & Silsbee, R. H. Coupling of electronic charge and spin at a ferromagnetic-paramagnetic metal interface. Phys. Rev. B 37, 5312–5325 (1988).
Johnson, M. & Silsbee, R. H. Spin-injection experiment. Phys. Rev. B 73, 5326–5335 (1988).
Rijks, Th. G. S. M., Coehoorn, R., de Jong, M. J. M. & de Jonge, W. J. M. Semiclassical calculations of the anisotropic magnetoresistance of NiFe-based thin films, wires, and multilayers. Phys. Rev. B 51, 283–291 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank the Stichting Fundamenteel Onderzoek der Materie (FOM) and NEDO (project ‘nano-scale control of magnetoelectronics for device applications’) for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jedema, F., Heersche, H., Filip, A. et al. Electrical detection of spin precession in a metallic mesoscopic spin valve. Nature 416, 713–716 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/416713a
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/416713a
This article is cited by
-
Spin Injection Behavior of CoFe/MgO/Si Tunnel Contacts: Effects of Radical Oxygen Annealing
Journal of Electronic Materials (2023)
-
Spin injection through energy-band symmetry matching with high spin polarization in atomically controlled ferromagnet/ferromagnet/semiconductor structures
NPG Asia Materials (2020)
-
2D materials for spintronic devices
npj 2D Materials and Applications (2020)
-
Long spin diffusion lengths in doped conjugated polymers due to enhanced exchange coupling
Nature Electronics (2019)
-
Spin inversion in graphene spin valves by gate-tunable magnetic proximity effect at one-dimensional contacts
Nature Communications (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.