Abstract
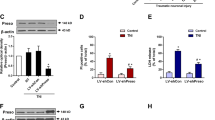
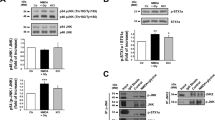
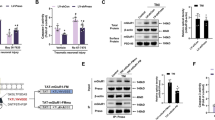
The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) is central to physiological and pathological functioning of neurons. Although promising results are beginning to be obtained in the treatment of dementias, clinical trials with NMDAR antagonists for stroke, trauma and neurodegenerative disorders, such as Hungtinton's disease, have failed before. In order to design effective therapies to prevent excitotoxic neuronal death, it is critical to characterize the consequences of excessive NMDAR activation on its expression and function. Previous data have reported partial downregulation of the NR1 and NR2B receptor subunits in response to excitotoxicity and cerebral ischemia. However, the effect of NMDAR overactivation on NR2A, a subunit fundamental to synaptic transmission and neuronal survival, is still elusive. In this study, we report the rapid and extensive proteolytic processing of NR2A, together with the scaffolding protein postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95), induced by excitotoxic stimulation of cortical neurons in vitro and by transient focal cerebral ischemia. Processing of the C terminus of NR2A is irreversibly induced by brief agonist exposure of NR2B-containing receptors, and requires calcium influx and the activity of calpain, also responsible for PSD-95 cleavage. The outcome is a truncated NR2A subunit that is stable and capable to interact with NR1 at the surface of neurons, but lacking the structural domains required for association with scaffolding, downstream signaling and cytoskeletal proteins. Therefore, a rapid and significant uncoupling of synaptic NMDARs from downstream survival pathways is expected to occur during ischemia. This novel mechanism induced by excitotoxicity helps to explain the failure of most therapies based on NMDAR antagonists.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mori H, Mishina M . Structure and function of the NMDA receptor channel. Neuropharmacology 1995; 34: 1219–1237.
Lipton SA, Rosenberg PA . Excitatory amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders. N Engl J Med 1994; 330: 613–622.
Choi DW . Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron 1988; 1: 623–634.
Moghaddam B . Bringing order to the glutamate chaos in schizophrenia. Neuron 2003; 40: 881–884.
Monyer H, Burnashev N, Laurie DJ, Sakmann B, Seeburg PH . Developmental and regional expression in the rat brain and functional properties of four NMDA receptors. Neuron 1994; 12: 529–540.
Westbrook GL . Glutamate receptor update. Curr Opin Neurobiol 1994; 4: 337–346.
Moriyoshi K, Masu M, Ishii T, Shigemoto R, Mizuno N, Nakanishi S . Molecular cloning and characterization of the rat NMDA receptor. Nature 1991; 354: 31–37.
Ishii T, Moriyoshi K, Sugihara H, Sakurada K, Kadotani H, Yokoi M et al. Molecular characterization of the family of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 2836–2843.
Thomas CG, Miller AJ, Westbrook GL . Synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptor NR2 subunits in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 2006; 95: 1727–1734.
Tovar KR, Westbrook GL . The incorporation of NMDA receptors with a distinct subunit composition at nascent hippocampal synapses in vitro. J Neurosci 1999; 19: 4180–4188.
Li JH, Wang YH, Wolfe BB, Krueger KE, Corsi L, Stocca G et al. Developmental changes in localization of NMDA receptor subunits in primary cultures of cortical neurons. Eur J Neurosci 1998; 10: 1704–1715.
Rumbaugh G, Vicini S . Distinct synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors in developing cerebellar granule neurons. J Neurosci 1999; 19: 10603–10610.
Husi H, Ward MA, Choudhary JS, Blackstock WP, Grant SG . Proteomic analysis of NMDA receptor-adhesion protein signaling complexes. Nat Neurosci 2000; 3: 661–669.
Hardingham GE, Fukunaga Y, Bading H . Extrasynaptic NMDARs oppose synaptic NMDARs by triggering CREB shut-off and cell death pathways. Nat Neurosci 2002; 5: 405–414.
Papadia S, Stevenson P, Hardingham NR, Bading H, Hardingham GE . Nuclear Ca2+ and the cAMP response element-binding protein family mediate a late phase of activity-dependent neuroprotection. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 4279–4287.
Chen HS, Lipton SA . The chemical biology of clinically tolerated NMDA receptor antagonists. J Neurochem 2006; 97: 1611–1626.
Ikonomidou C, Turski L . Why did NMDA receptor antagonists fail clinical trials for stroke and traumatic brain injury? Lancet Neurol 2002; 1: 383–386.
Gascón S, Deogracias R, Sobrado M, Roda JM, Renart J, Rodriguez-Peña A et al. Transcription of the NR1 subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor is down-regulated by excitotoxic stimulation and cerebral ischemia. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 35018–35027.
Simpkins KL, Guttmann RP, Dong Y, Chen Z, Sokol S, Neumar RW et al. Selective activation induced cleavage of the NR2B subunit by calpain. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 11322–11331.
Neumar RW, Xu YA, Gada H, Guttmann RP, Siman R . Cross-talk between calpain and caspase proteolytic systems during neuronal apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 14162–14167.
Dong YN, Wu HY, Hsu FC, Coulter DA, Lynch DR . Developmental and cell-selective variations in N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor degradation by calpain. J Neurochem 2006; 88: 206–217.
Dong YN, Waxman EA, Lynch DR . Interactions of postsynaptic density-95 and the NMDA receptor 2 subunit control calpain-mediated cleavage of the NMDA receptor. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 11035–11045.
Wu HY, Yuen EY, Lu YF, Matsushita M, Matsui H, Yan Z et al. Regulation of N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptors by calpain in cortical neurons. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 21588–21593.
Qiu S, Hua YL, Yang F, Chen YZ, Luo JH . Subunit assembly of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors analyzed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 24923–24930.
Hironaka K, Umemori H, Tezuka T, Mishina M, Yamamoto T . The protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPMEG interacts with glutamate receptor delta 2 and epsilon subunits. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 16167–16173.
Nakazawa T, Komai S, Tezuka T, Hisatsune C, Umemori H, Semba K et al. Characterization of Fyn-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation sites on GluR epsilon 2 (NR2B) subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 693–699.
Lois C, Hong EJ, Pease S, Brown EJ, Baltimore D . Germline transmission and tissue-specific expression of transgenes delivered by lentiviral vectors. Science 2002; 295: 868–872.
Rose K, Goldberg MP, Choi DW . Citotoxicity in murine neocortical cell culture. Methods Toxicol 1993; 1A: 46–60.
Chen ST, Hsu CY, Hogan EL, Maricq H, Balentine JD . A model of focal ischemic stroke in the rat: reproducible extensive cortical infarction. Stroke 1986; 17: 738–743.
Liu TH, Beckman JS, Freeman BA, Hogan EL, Hsu CY . Polyethylene glycol-conjugated superoxide dismutase and catalase reduce ischemic brain injury. Am J Physiol 1989; 256: H589–H593.
Kornau HC, Schenker LT, Kennedy MB, Seeburg PH . Domain interaction between NMDA receptor subunits and the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95. Science 1995; 269: 1737–1740.
Matesic DF, Lin RC . Microtubule-associated protein 2 as an early indicator of ischemia-induced neurodegeneration in the gerbil forebrain. J Neurochem 1994; 63: 1012–1020.
Koh JY, Choi DW . Vulnerability of cultured cortical neurons to damage by excitotoxins: differential susceptibility of neurons containing NADPH-diaphorase. J Neurosci 1988; 8: 2153–2163.
Williams K . Ifenprodil discriminates subtypes of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor: selectivity and mechanisms at recombinant heteromeric receptors. Mol Pharmacol 1993; 44: 851–859.
Siman R, Noszek JC . Excitatory amino acids activate calpain I and induce structural protein breakdown in vivo. Neuron 1988; 1: 279–287.
Hong SC, Goto Y, Lanzino G, Soleau S, Kassell NF, Lee KS . Neuroprotection with a calpain inhibitor in a model of focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 1994; 25: 663–669.
Hong SC, Lanzino G, Goto Y, Kang SK, Schottler F, Kassell NF et al. Calcium-activated proteolysis in rat neocortex induced by transient focal ischemia. Brain Res 1994; 661: 43–50.
Mizuta I, Katayama M, Watanabe M, Mishina M, Ishii K . Developmental expression of NMDA receptor subunits and the emergence of glutamate neurotoxicity in primary cultures of murine cerebral cortical neurons. Cell Mol Life Sci 1998; 54: 721–725.
Sans N, Petralia RS, Wang YX, Blahos II J, Hell JW, Wenthold RJ . A developmental change in NMDA receptor-associated proteins at hippocampal synapses. J Neurosci 2000; 20: 1260–1271.
Wechsler A, Teichberg VI . Brain spectrin binding to the NMDA receptor is regulated by phosphorylation, calcium and calmodulin. EMBO J 1998; 17: 3931–3939.
Fukaya M, Kato A, Lovett C, Tonegawa S, Watanabe M . Retention of NMDA receptor NR2 subunits in the lumen of endoplasmic reticulum in targeted NR1 knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 4855–4860.
Mori H, Manabe T, Watanabe M, Satoh Y, Suzuki N, Toki S et al. Role of the carboxy-terminal region of the GluR epsilon2 subunit in synaptic localization of the NMDA receptor channel. Neuron 1998; 21: 571–580.
Sprengel R, Suchanek B, Amico C, Brusa R, Burnashev N, Rozov A et al. Importance of the intracellular domain of NR2 subunits for NMDA receptor function in vivo. Cell 1998; 92: 279–289.
Ikonomidou C, Bosch F, Miksa M, Bittigau P, Vockler J, Dikranian K et al. Blockade of NMDA receptors and apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Science 1999; 283: 70–74.
Ikonomidou C, Stefovska V, Turski L . Neuronal death enhanced by N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 12885–12890.
Olney JW, Wozniak DF, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Farber NB, Bittigau P, Ikonomidou C . Drug-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Brain Pathol 2002; 12: 488–498.
Young D, Lawlor PA, Leone P, Dragunow M, During MJ . Environmental enrichment inhibits spontaneous apoptosis, prevents seizures and is neuroprotective. Nat Med 1999; 5: 448–453.
Vanderklish PW, Bahr BA . The pathogenic activation of calpain: a marker and mediator of cellular toxicity and disease states. Int J Exp Pathol 2000; 81: 323–339.
Bano D, Young KW, Guerin CJ, Lefeuvre R, Rothwell NJ, Naldini L et al. Cleavage of the plasma membrane Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in excitotoxicity. Cell 2005; 120: 275–285.
Biegon A, Fry PA, Paden CM, Alexandrovich A, Tsenter J, Shohami E . Dynamic changes in N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors after closed head injury in mice: implications for treatment of neurological and cognitive deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 5117–5122.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant SAF2003-02327 (MD-G) from ‘Dirección General de Investigación Científica y Técnica’ (Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología). MD-G is a researcher of the Ramón y Cajal Program. SG is a recipient of a predoctoral fellowship from Comunidad de Madrid. We thank Dr T Yamamoto for the generous gift of pME18S-HA-NR2A and pME18S-HA-NR2B, and Dr J Luo for plasmid YFP-NR2B. Plasmid Syn-GFP was generated in collaboration with Dr P Scheiffele and Dr FG Scholl (Columbia University, NY, USA). We are grateful to E Abantos for technical support. We also thank Dr J Renart and T Iglesias for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website (http://www.nature.com/mp)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gascón, S., Sobrado, M., Roda, J. et al. Excitotoxicity and focal cerebral ischemia induce truncation of the NR2A and NR2B subunits of the NMDA receptor and cleavage of the scaffolding protein PSD-95. Mol Psychiatry 13, 99–114 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4002017
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4002017
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cerebrolysin reduces excitotoxicity by modulation of cell-death proteins in delayed hours of ischemic reperfusion injury
Metabolic Brain Disease (2023)
-
Resveratrol Preconditioning Protects Against Ischemia-Induced Synaptic Dysfunction and Cofilin Hyperactivation in the Mouse Hippocampal Slice
Neurotherapeutics (2023)
-
The NR2B-targeted intervention alleviates the neuronal injuries at the sub-acute stage of cerebral ischemia: an exploration of stage-dependent strategy against ischemic insults
Experimental Brain Research (2023)
-
eNOS-dependent S-nitrosylation of the NF-κB subunit p65 has neuroprotective effects
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Excitotoxic targeting of Kidins220 to the Golgi apparatus precedes calpain cleavage of Rap1-activation complexes
Cell Death & Disease (2019)